1221. Algorithm - Dynamic ProgrammingDP
Introduce dynamic programming.
1. Dynamic Programming
1.1 When to use DP?
- Maximum/Minimum
- Yes/No
- Count(*)
- Can’t sort or swap
1.2 DP Types
- Matrix DP (10%)
- Sequence DP (40%)
- Two Sequences DP (40%)
- Backpack (10%)
1.3 Implementation of DP
- Memorization Search(Drawback: extra space)
- Loop
2. Matrix DP
2.1 Unique Paths
2.1.1 Problem Description
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below). How many possible unique paths are there?
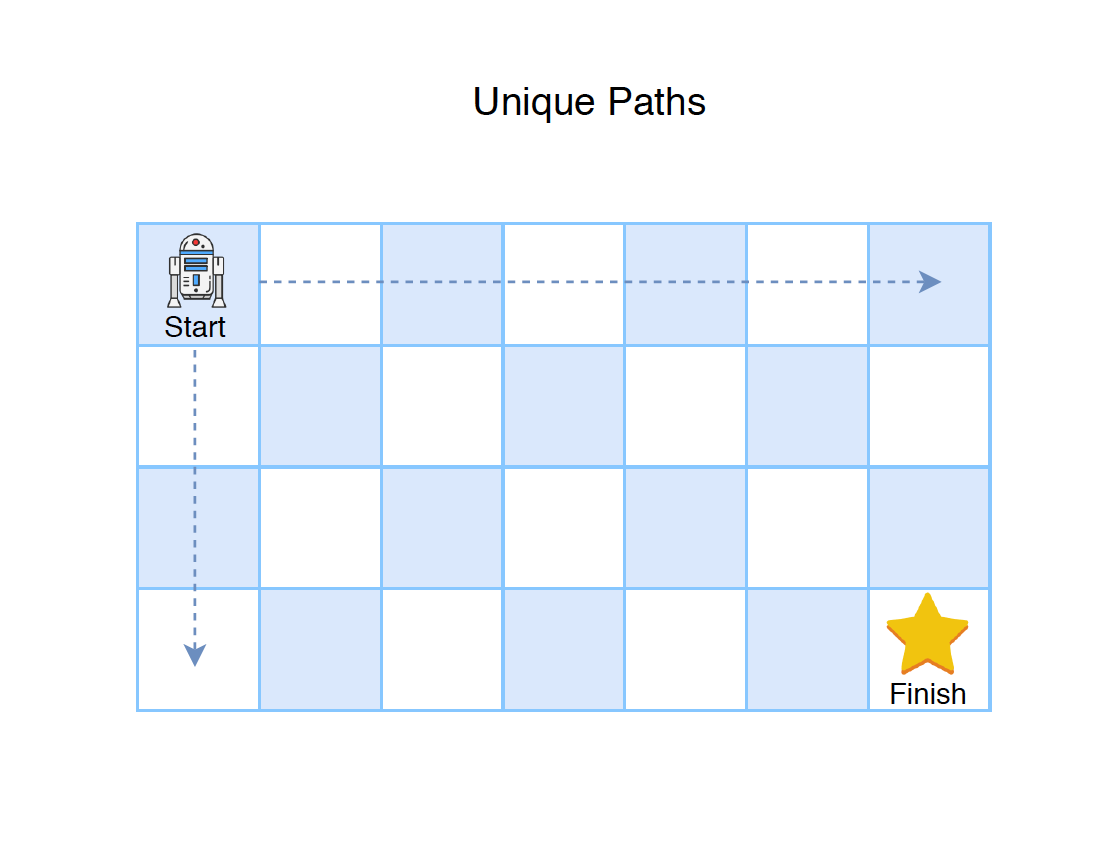
2.1.2 Solution with Matrix(Two-dimensional array)
// time: O(m*n), space: O(m*n)
public int uniquePathMatrix(int m, int n) {
if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
// Initialization
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
// Calculate dp[i][j]
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
// time: O(m*n), space: O(m*n), without separated initialization
public int uniquePathMatrix2(int m, int n) {
if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
dp[i][j] = 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
}
- Time complexity: $O(m*n)$
- Space complexity: $O(m*n)$
2.1.3 Solution with One-dimensional Array
Use one-dimensional array instead of the matrix. Same time complexity, but space is reduced to $O(n)$.
// time: O(m*n), space: O(n)
public int uniquePathArray(int m, int n) {
if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j == 0) {
dp[j] = 1;
} else {
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
// time: O(m*n), space: O(n), without checking the first column
public int uniquePath(int m, int n) {
if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (j > 0) {
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
- Time complexity: $O(m*n)$
- Space complexity: $O(n)$
2.2 Define Matrix with Larger Size
When to define a dp matrix with m+1 and n+1? see question LeetCode 221 - Maximal Square.
2.3 Classic Problems
3. Sequence DP
3.1 Fibonacci Numbers
3.1.1 Problem Description
Fibonacci Numbers are 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, … Now, given an integer N(N >= 0), return the Nth Fibonacci number.
3.1.2 Recursive Solution
// recursive implementation
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
- Time complexity: $O(2^n)$
- Space complexity: $O(1)$
3.1.3 DP Solution
// DP
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
- Time complexity: $O(n)$
- Space complexity: $O(n)$
3.1.4 Solution with Constant Space
// constant space
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int first = 0;
int second = 1;
int third = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return third;
}
- Time complexity: $O(n)$
- Space complexity: $O(1)$
3.2 Longest Increasing Subsequence
3.2.1 Problem Description
Given a sequence of integers, find the longest increasing subsequence (LIS). Your code should return the length of the LIS.
Example 1:
Input: [5,4,1,2,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: LIS is [1,2,3].
Example 2:
Input: [4,2,4,5,3,7]
Output: 4
Explanation: LIS is [2,4,5,7]
3.2.2 DP Solution(n^2)
// O(n^2)
public int longestIncreasingSubsequence(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
// dp[i], the longest length of LIS which ends at index i.
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { // check 0~i
if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n)$
Values of the dp array for input A=[4,2,4,5,3,7]. The answer is 4 and the longest increasing subsequence is [2,4,5,7].
| A[i]\dp[i] | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
3.2.3 Binary Search Solution(nlog(n))
Maintain a monotonic increasing array.
// O(nlog(n))
// https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rfZ4WnNKBk
public int longestIncreasingSubsequence3(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] arr = new int[nums.length]; // increasing array
// 10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18 -> 2,3,7,18
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 0, len, nums[i]);
if (index < 0) {
index = -(index + 1);
}
arr[index] = nums[i];
if (index == len) {
len++;
}
}
return len;
}
- Time Complexity: $O(nlog(n))$
- Space Complexity: $O(n)$
Values of the dp array for input A=[10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]. The answer is 4 and the longest increasing subsequence are [2,5,7,101], [2,5,7,18], [2,3,7,101] or [2,3,7,18].
| A[i]\arr[i] | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 101 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 101 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Here, the final array contains the correct LIS . But it is not guaranteed this is always the case. Take another input as example, A=[10,9,2,5,7,3,101,18]. The only difference with the previous input is that 7 and 3 are swapped. The answer is still 4. But the longest increasing subsequence are [2,5,7,101] and [2,5,7,18] only. [2,3,7,101] and [2,3,7,18] are not valid LIS any more, but we have the same final array [2,3,7,18,0,0,0,0] as the previous exmaple.
| A[i]\arr[i] | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 101 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 101 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
3.3 Classic Problems
- LeetCode 70 - Climbing Stairs
- LeetCode 55 - Jump Game
- LeetCode 45 - Jump Game II
- LeetCode 132 - Palindrome Partitioning II
- LeetCode 139 - Word Break
- LeetCode 140 - Word Break II
- LeetCode 674 - Longest Continuous Increasing Subsequence
- LeetCode 300 - Longest Increasing Subsequence
- LeetCode 198 - House Robber
- LeetCode 213 - House Robber II
4. Two Sequences DP
4.1 Longest Common Subsequence
4.1.1 Problem Description
Given two strings, find the longest common subsequence (LCS). Your code should return the length of LCS.
Example 1:
Input: "ABCD" and "EDCA"
Output: 1
Explanation: LCS is 'A' or 'D' or 'C'.
Example 2:
Input: "ABCD" and "EACB"
Output: 2
Explanation: LCS is "AC"
4.1.2 DP Solution(n^2)
// O(n^2)
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String A, String B) {
if (A == null || A.length() == 0 || B == null || B.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = A.length();
int n = B.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (A.charAt(i - 1) == B.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n^2)$
4.2 Uncrossed Lines
4.2.1 Problem Description
We write the integers of A and B (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines. Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
- A[i] == B[j];
- The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
- Each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example 1:
Input: A = [1,4,2], B = [1,2,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: We can draw line from A[0]=1 to B[0]=1 and line from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4. We cannot draw line
from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4 and line from A[2]=2 to B[1]=2 at the same time because they intersect each other.
Example 2:
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: One solution is A[0]=2 -> B[2]=2, A[1]=5 to B[4]=5 and A[3]=2 to B[5]=2
Example 3:
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: One solution is A[0]=1 -> B[0]=1 and A[3]=1 to B[4]=1
4.2.2 DP Solution(n^2)
This question is exactly same with Longest Common Sequence.
// same as longest common subsequence, O(n^2)
public int maxUncrossedLines(int[] A, int[] B) {
int m = A.length;
int n = B.length;
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (A[i-1] == B[j-1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n^2)$
4.3 Minimum Edit Distance
4.3.1 Problem Description
Given two strings A and B, find the minimum number of steps required to convert A to B. (each operation is counted as 1 step.) You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: A="horse", B="ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: A="intention", B="execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
4.3.2 DP Solution(n^2)
// O(n^2)
public int minDistance(String A, String B) {
int m = A.length();
int n = B.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (A.charAt(i - 1) == B.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
// 1) dp[i][j - 1], insert character at end of A
// 2) dp[i - 1][j], delete A's last character
// 3) dp[i - 1][j - 1], replace A's last character
dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n^2)$
4.4 Distinct Subsequences
4.4.1 Problem Description
Given two strings S and T. Count the number of distinct subsequences of S which equals T.
A subsequence of a string is a new string which is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, “ACE” is a subsequence of “ABCDE” while “AEC” is not)
Example 1:
Input: S = "rabbbit", T = "rabbit"
Output: 3
Explanation: You could remove any 'b' in S, so there are 3 ways to get T.
Example 2:
Input: S = "abcd", T = ""
Output: 1
Explanation: There is only 1 way to get T - remove all chars in S.
4.4.2 DP Solution(n^2)
// O(n^2)
public int numDistinct(String S, String T) {
int m = S.length();
int n = T.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (S.charAt(i - 1) == T.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]; // case 1: last character in T is same with that in S
}
dp[i][j] += dp[i-1][j]; // case 2: last character in T is not same with that in S
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n^2)$
4.5 Interleaving String
4.5.1 Problem Description
Given three strings: s1, s2, s3, determine whether s3 is formed by the interleaving of s1 and s2.
Example 1:
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbcbcac"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s1 = "", s2 = "", s3 = "1"
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbbaccc"
Output: false
4.5.2 DP Solution(n^2)
// O(n^2)
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
int m = s1.length();
int n = s2.length();
if (m + n != s3.length()) {
return false;
}
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[m+1][n+1];
dp[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i-1) == s3.charAt(i-1)) {
dp[i][0] = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s2.charAt(j-1) == s3.charAt(j-1)) {
dp[0][j] = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i+j-1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i-1][j];
}
if (s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i+j-1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
- Time Complexity: $O(n^2)$
- Space Complexity: $O(n^2)$
4.6 Classic Problems
- LeetCode 1143 - Longest Common Subsequence
- LeetCode 1035 - Uncrossed Lines
- LintCode 79 - Longest Common Substring
- LeetCode 72 - Edit Distance
- LeetCode 115 - Distinct Subsequences
- LeetCode 97 - Interleaving String
5. Game, Min-Max
6. Source Files
- Source files for Dynamic Programming on GitHub
- Dynamic Programming Diagrams(draw.io) in Google Drive