1235. Algorithm - Map Reduce - DraftMap and Reduce
Implement Map Reduce.
1. What is MapReduce?
MapReduce is a processing technique and a program model for distributed computing based on java. The major advantage of MapReduce is that it is easy to scale data processing over multiple computing nodes. The MapReduce algorithm contains two important tasks, namely Map and Reduce.
- Map takes a set of data and converts it into another set of data, where individual elements are broken down into tuples (key/value pairs).
- Secondly, reduce task, which takes the output from a map as an input and combines those data tuples into a smaller set of tuples. As the sequence of the name MapReduce implies, the reduce task is always performed after the map job.
Below diagram shows the process of using MapReduce to count the number of words from multiple sources.
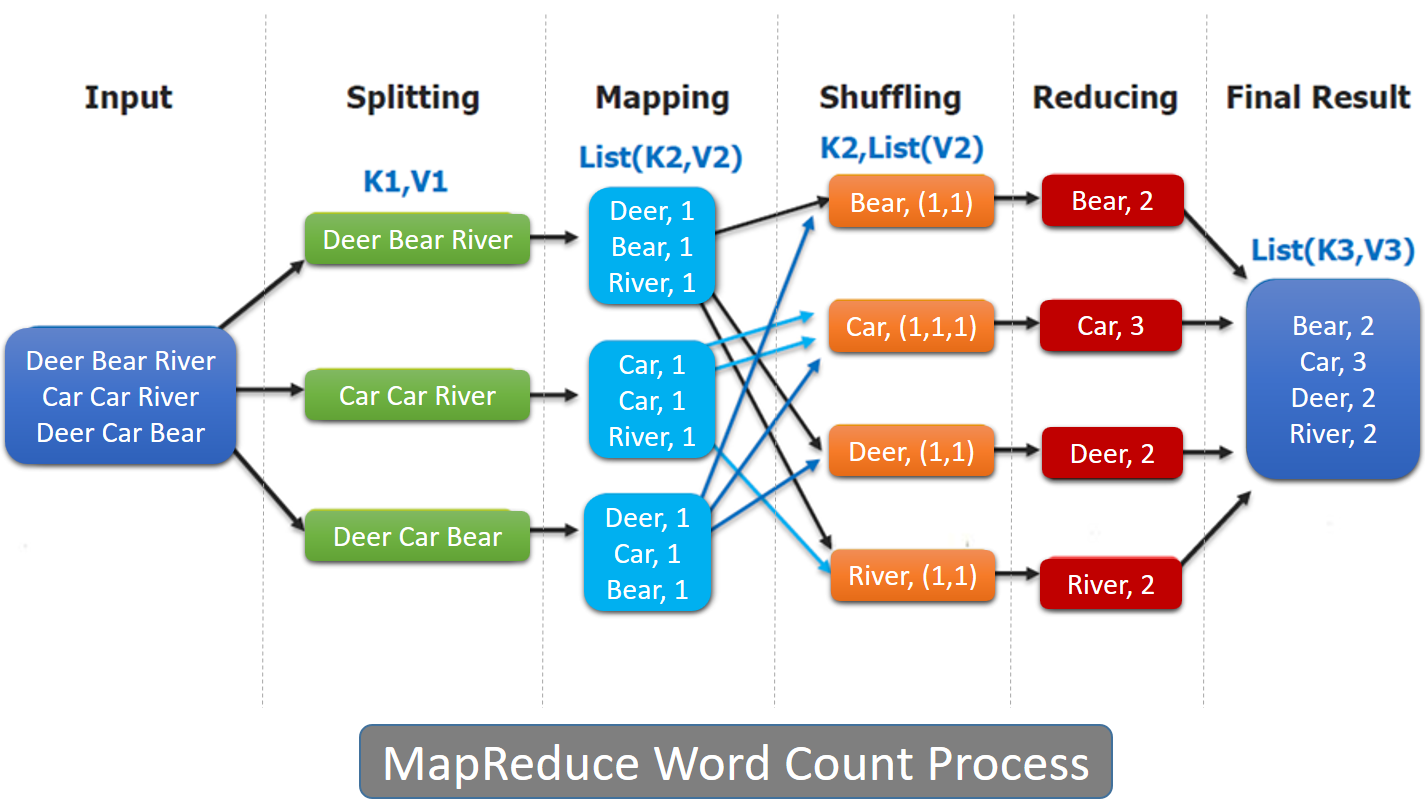
2. Implementation of MapReduce
public class TopKFrequentWords {
//HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
public static class Map {
public void map(String aa, Document value,
OutputCollector<String, Integer> output) {
// Write your code here
// Output the results into output buffer.
// Ps. output.collect(String key, int value);
String content = value.content.trim();
String[] words = content.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if (!words[i].isEmpty()) {
output.collect(words[i], 1);
}
}
}
}
public static class Reduce {
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> countMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
int top = 0;
public void setup(int k) {
// initialize your data structure here
top = k;
}
public void reduce(String key, Iterator<Integer> values) {
// Write your code here
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next();
}
countMap.put(key, sum);
}
public void cleanup(OutputCollector<String, Integer> output) {
HashMap<String, Integer> sortedMap = sortByComparator(countMap);
int i = 0;
for (String key : sortedMap.keySet()) {
if (i >= top) {
break;
}
output.collect(key, sortedMap.get(key));
i++;
}
/*int cnt = 0;
top = Math.min(top, countMap.size());
Integer[] counts = countMap.values().toArray(new Integer[0]);
Arrays.sort(counts);
for (int i = counts.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (String key : countMap.keySet()) {
if (countMap.get(key) == counts[i]) {
output.collect(key, counts[i]);
cnt++;
if (cnt >= top) {
return;
}
}
}
}*/
}
private HashMap<String, Integer> sortByComparator(HashMap<String, Integer> unsortMap)
{
List<Entry<String, Integer>> list = new LinkedList<Entry<String, Integer>>(unsortMap.entrySet());
// Sorting the list based on values
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<String, Integer>>()
{
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> o1,
Entry<String, Integer> o2)
{
int val1 = o1.getValue();
int val2 = o2.getValue();
String key1 = o1.getKey();
String key2 = o2.getKey();
if (val1 == val2) {
return key1.compareTo(key2);
} else {
return val2 - val1;
}
}
});
// Maintaining insertion order with the help of LinkedList
HashMap<String, Integer> sortedMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : list)
{
sortedMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return sortedMap;
}
}
}