1125. Data Structure - B+ TreeB+ Tree
Introduce B+ Tree and its properties.
1. B+ Tree
1.1 What is B+ Tree?
B+ Tree is an extension of B Tree which allows efficient insertion, deletion and search operations.
In B Tree, Keys and records both can be stored in the internal as well as leaf nodes. Whereas, in B+ tree, records (data) can only be stored on the leaf nodes while internal nodes can only store the key values.
The leaf nodes of a B+ tree are linked together in the form of a singly linked lists to make the search queries more efficient.
B+ Tree are used to store the large amount of data which can not be stored in the main memory. Due to the fact that, size of main memory is always limited, the internal nodes (keys to access records) of the B+ tree are stored in the main memory whereas, leaf nodes are stored in the secondary memory.
The internal nodes of B+ tree are often called index nodes. A B+ tree of order 3 is shown in the following figure.
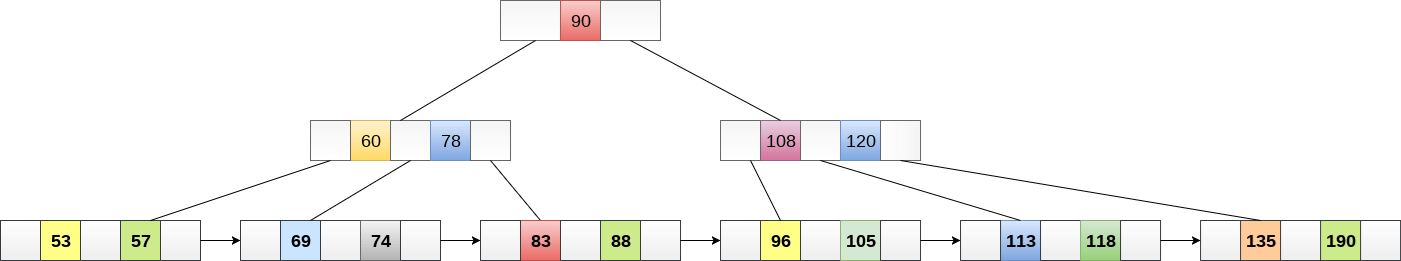
1.2 Advantages of B+ Tree
- Records can be fetched in equal number of disk accesses.
- Height of the tree remains balanced and less as compare to B tree.
- We can access the data stored in a B+ tree sequentially as well as directly.
- Keys are used for indexing.
- Faster search queries as the data is stored only on the leaf nodes.
1.3 B Tree VS B+ Tree
| No. | B Tree | B+ Tree |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Search keys can not be repeatedly stored. | Redundant search keys can be present. |
| 2 | Data can be stored in leaf nodes as well as internal nodes | Data can only be stored on the leaf nodes. |
| 3 | Searching for some data is a slower process since data can be found on internal nodes as well as on the leaf nodes. | Searching is comparatively faster as data can only be found on the leaf nodes. |
| 4 | Deletion of internal nodes are so complicated and time consuming. | Deletion will never be a complexed process since element will always be deleted from the leaf nodes. |
| 5 | Leaf nodes can not be linked together. | Leaf nodes are linked together to make the search operations more efficient. |
2. B Tree Operations
2.1 Searching
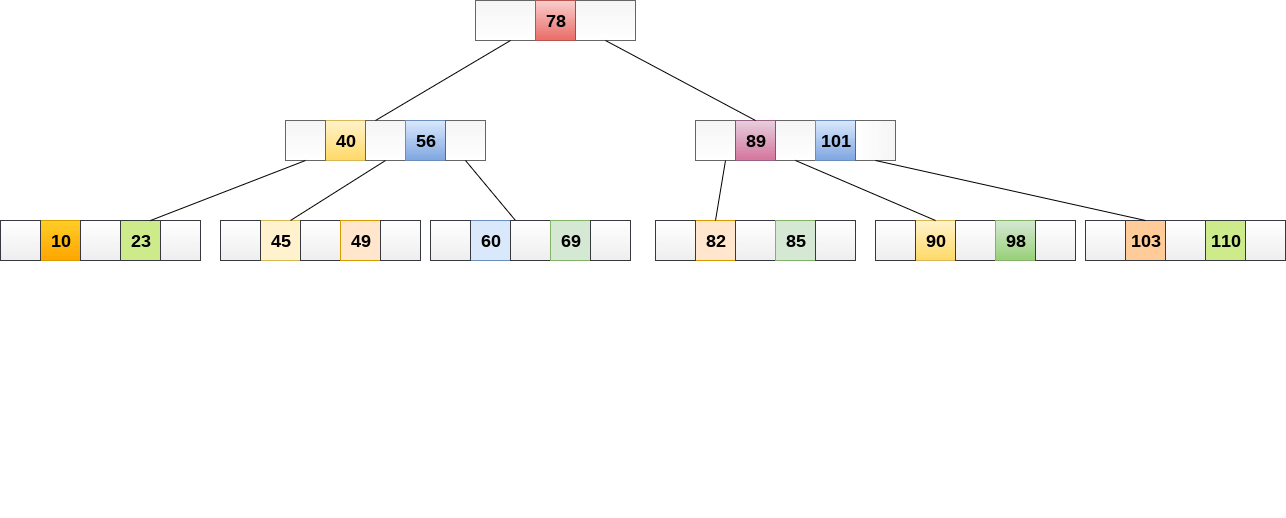
Searching in B Trees is similar to that in Binary search tree. For example, if we search for an item 49 in the following B Tree. The process will something like following :
- Compare item 49 with root node 78. since 49 < 78 hence, move to its left sub-tree.
- Since, 40<49<56, traverse right sub-tree of 40.
- 49>45, move to right. Compare 49.
- match found, return.
Searching in a B tree depends upon the height of the tree. The search algorithm takes O(log n) time to search any element in a B tree.
2.2 Insertion in B+ Tree
Three steps:
- Insert the new node as a leaf node
- If the leaf doesn’t have required space, split the node and copy the middle node to the next index node.
- If the index node doesn’t have required space, split the node and copy the middle element to the next index page.
Example :
Insert the value 195 into the B+ tree of order 5 shown in the following figure.
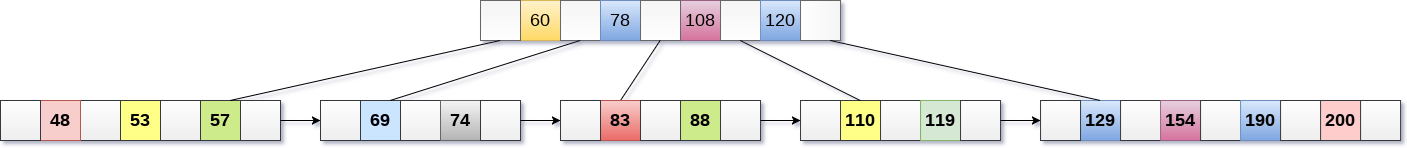 195 will be inserted in the right sub-tree of 120 after 190. Insert it at the desired position.
195 will be inserted in the right sub-tree of 120 after 190. Insert it at the desired position.
 The node contains greater than the maximum number of elements i.e. 4, therefore split it and place the median node up to the parent.
The node contains greater than the maximum number of elements i.e. 4, therefore split it and place the median node up to the parent.
 Now, the index node contains 6 children and 5 keys which violates the B+ tree properties, therefore we need to split it, shown as follows.
Now, the index node contains 6 children and 5 keys which violates the B+ tree properties, therefore we need to split it, shown as follows.
2.3 Deletion in B+ Tree
Three steps:
- Delete the key and data from the leaves.
- if the leaf node contains less than minimum number of elements, merge down the node with its sibling and delete the key in between them.
- if the index node contains less than minimum number of elements, merge the node with the sibling and move down the key in between them.
Example:
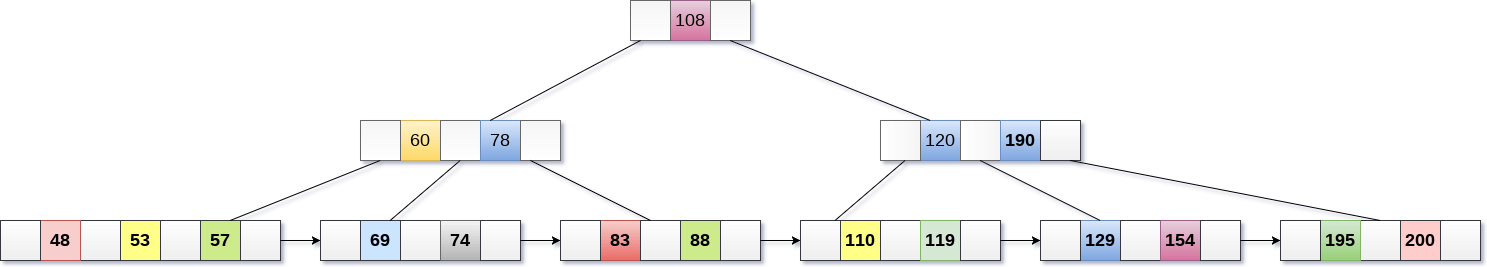
Delete the key 200 from the B+ Tree shown in the following figure.
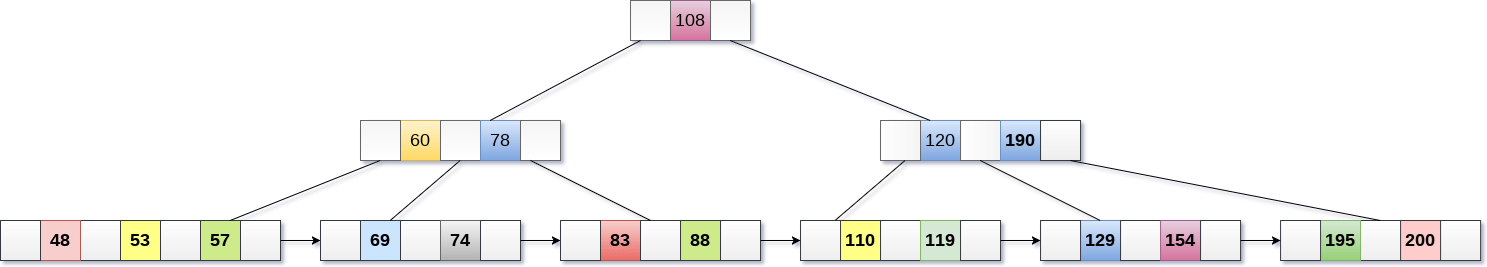 200 is present in the right sub-tree of 190, after 195. delete it.
200 is present in the right sub-tree of 190, after 195. delete it.
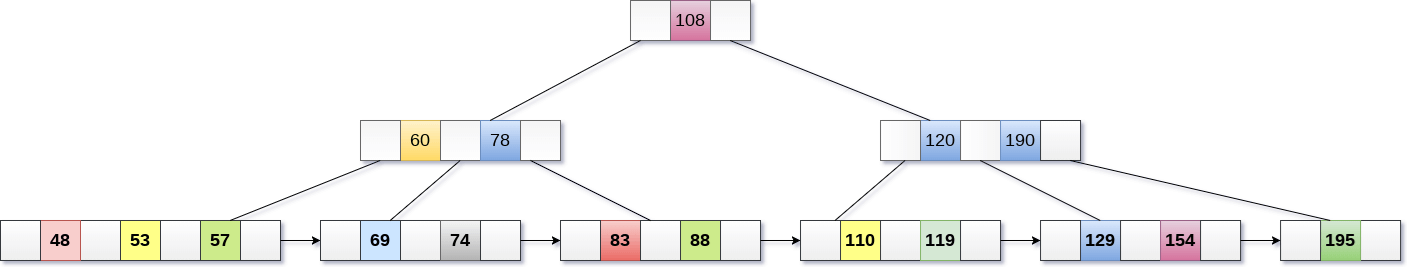 Merge the two nodes by using 195, 190, 154 and 129.
Merge the two nodes by using 195, 190, 154 and 129.
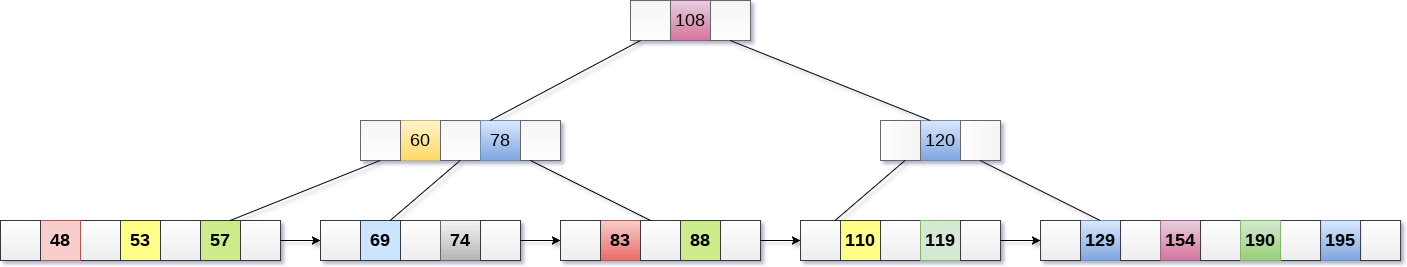 Now, element 120 is the single element present in the node which is violating the B+ Tree properties. Therefore, we need to merge it by using 60, 78, 108 and 120.
Now, element 120 is the single element present in the node which is violating the B+ Tree properties. Therefore, we need to merge it by using 60, 78, 108 and 120.
Now, the height of B+ tree will be decreased by 1.
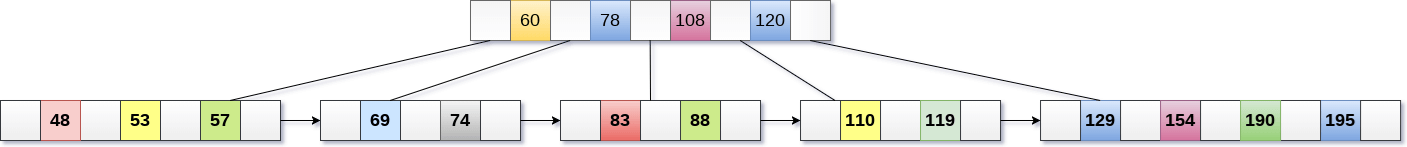
3. Implementation
// https://github.com/linli2016/BPlusTree
public class BPTree<TKey extends Comparable<TKey>, TValue> {
private BTreeNode<TKey> root;
public BPTree() {
this.root = new BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue>();
}
/**
* Insert a new key and its associated value into the B+ tree.
*/
public void insert(TKey key, TValue value) {
BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue> leaf = this.findLeafNodeShouldContainKey(key);
leaf.insertKey(key, value);
if (leaf.isOverflow()) {
BTreeNode<TKey> n = leaf.dealOverflow();
if (n != null)
this.root = n;
}
}
/**
* Search a key value on the tree and return its associated value.
*/
public TValue search(TKey key) {
BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue> leaf = this.findLeafNodeShouldContainKey(key);
int index = leaf.search(key);
return (index == -1) ? null : leaf.getValue(index);
}
/**
* Delete a key and its associated value from the tree.
*/
public void delete(TKey key) {
BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue> leaf = this.findLeafNodeShouldContainKey(key);
if (leaf.delete(key) && leaf.isUnderflow()) {
BTreeNode<TKey> n = leaf.dealUnderflow();
if (n != null)
this.root = n;
}
}
/**
* Search the leaf node which should contain the specified key
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue> findLeafNodeShouldContainKey(TKey key) {
BTreeNode<TKey> node = this.root;
while (node.getNodeType() == TreeNodeType.InnerNode) {
node = ((BTreeInnerNode<TKey>)node).getChild( node.search(key) );
}
return (BTreeLeafNode<TKey, TValue>)node;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code BTree} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BPTree<String, String> st = new BPTree<String, String>();
st.insert("www.cs.princeton.edu", "128.112.136.12");
st.insert("www.cs.princeton.edu", "128.112.136.11");
st.insert("www.princeton.edu", "128.112.128.15");
st.insert("www.yale.edu", "130.132.143.21");
st.insert("www.simpsons.com", "209.052.165.60");
st.insert("www.apple.com", "17.112.152.32");
st.insert("www.amazon.com", "207.171.182.16");
st.insert("www.ebay.com", "66.135.192.87");
st.insert("www.cnn.com", "64.236.16.20");
st.insert("www.google.com", "216.239.41.99");
st.insert("www.nytimes.com", "199.239.136.200");
st.insert("www.microsoft.com", "207.126.99.140");
st.insert("www.dell.com", "143.166.224.230");
st.insert("www.slashdot.org", "66.35.250.151");
st.insert("www.espn.com", "199.181.135.201");
st.insert("www.weather.com", "63.111.66.11");
st.insert("www.yahoo.com", "216.109.118.65");
System.out.println("cs.princeton.edu: " + st.search("www.cs.princeton.edu"));
System.out.println("hardvardsucks.com: " + st.search("www.harvardsucks.com"));
System.out.println("simpsons.com: " + st.search("www.simpsons.com"));
System.out.println("apple.com: " + st.search("www.apple.com"));
System.out.println("ebay.com: " + st.search("www.ebay.com"));
System.out.println("dell.com: " + st.search("www.dell.com"));
System.out.println();
//System.out.println("size: " + st.size());
//System.out.println("height: " + st.height());
System.out.println(st);
System.out.println();
}
}