1145. Data Structure - Topological SortingTopological Sorting
Topological Sorting and related questions.
1. Topological Sorting
In computer science, a topological sort or topological ordering of a directed graph is a linear ordering of its vertices such that for every directed edge uv from vertex u to vertex v, u comes before v in the ordering.
- indegree
- outdegree
1.1 Problem Description
Given an directed graph, a topological order of the graph nodes is defined as follow:
- For each directed edge
A -> Bin graph, A must before B in the order list. - The first node in the order can be any node in the graph with no nodes direct to it.
Find any topological order for the given graph.
Example:
For graph as follow:
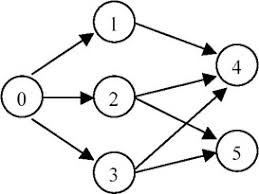
The topological order can be:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[0, 2, 3, 1, 5, 4]
...
1.2 Solution
Calculate InDegree, use BFS approach.
public class DirectedGraphNode {
int label;
List<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
public DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
label = x;
neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public class TopologicalSorting {
/*
* @param graph: A list of Directed graph node
* @return: Any topological order for the given graph.
*/
public List<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(List<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
if (graph == null || graph.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
// calculate indegree
Map<DirectedGraphNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (DirectedGraphNode node : graph) {
for (DirectedGraphNode neighbor : node.neighbors) {
map.put(neighbor, map.getOrDefault(neighbor, 0) + 1);
}
}
List<DirectedGraphNode> ans = new ArrayList<>();
// queue
Queue<DirectedGraphNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (DirectedGraphNode node : graph) {
if (!map.containsKey(node)) {
queue.offer(node);
ans.add(node);
}
}
// bfs
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
DirectedGraphNode node = queue.poll();
for (DirectedGraphNode neighbor : node.neighbors) {
map.put(neighbor, map.get(neighbor) - 1);
if (map.get(neighbor) == 0) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
ans.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2. Course Schedule
2.1 Problem Description
There are a total of numCourses courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to numCourses-1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair: [0,1].
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
Example 1:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]]
Output: true
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
Example 2:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should
also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
2.2 Solution
Topological Sorting, check if the number of visited course during BFS are same with the total number of courses.
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
if (numCourses <= 0) {
return false;
}
if (prerequisites == null || prerequisites.length == 0) {
return true;
}
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
int[] indegree = new int[numCourses];
for (int[] pre : prerequisites) {
indegree[pre[0]]++;
if (!graph.containsKey(pre[1])) {
graph.put(pre[1], new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(pre[1]).add(pre[0]);
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
int count = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int course = queue.poll();
count++;
if (graph.containsKey(course)) {
for (Integer nextCourse : graph.get(course)) {
indegree[nextCourse]--;
if (indegree[nextCourse] == 0) {
queue.offer(nextCourse);
}
}
}
}
return count == numCourses;
}
3. Alien Dictionary
3.1 Problem Description
There is a new alien language which uses the latin alphabet. However, the order among letters are unknown to you. You receive a list of non-empty words from the dictionary, where words are sorted lexicographically by the rules of this new language. Derive the order of letters in this language.
- You may assume all letters are in lowercase.
- The dictionary is invalid, if a is prefix of b and b is appear before a.
- If the order is invalid, return an empty string.
- There may be multiple valid order of letters, return the smallest in normal lexicographical order
Examples:
Example 1:
Input:["wrt","wrf","er","ett","rftt"]
Output:"wertf"
Explanation:
from "wrt"and"wrf" ,we can get 't'<'f'
from "wrt"and"er" ,we can get 'w'<'e'
from "er"and"ett" ,we can get 'r'<'t'
from "ett"and"rftt" ,we can get 'e'<'r'
So return "wertf"
Example 2:
Input:["z","x"]
Output:"zx"
Explanation:
from "z" and "x",we can get 'z' < 'x'
So return "zx"
3.2 Solution
Compare each word with its neighbor to calculate the indegree of each appeared character, then use topological sorting to find the letters in sequence.
/**
* @param words: a list of words
* @return: a string which is correct order
*/
public String alienOrder(String[] words) {
if (words == null || words.length == 0) {
return "";
}
// initialize degree
Map<Character, Integer> indegree = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
indegree.put(c, 0);
}
}
Map<Character, List<Character>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i < words.length; i++) {
String word1 = words[i - 1];
String word2 = words[i];
for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(word1.length(), word2.length()); j++) {
char c1 = word1.charAt(j);
char c2 = word2.charAt(j);
if (c1 != c2) {
if (!graph.containsKey(c1)) {
graph.put(c1, new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(c1).add(c2);
indegree.put(c2, indegree.get(c2) + 1);
break;
}
}
}
// use PriorityQueue instead of LinkedList for case "zy","zx" -> "yxz"
Queue<Character> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (char c : indegree.keySet()) {
if (indegree.get(c) == 0) {
queue.offer(c);
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
char c = queue.poll();
sb.append(c);
if (graph.containsKey(c)) {
for (char nextchar : graph.get(c)) {
indegree.put(nextchar, indegree.get(nextchar) - 1);
if (indegree.get(nextchar) == 0) {
queue.offer(nextchar);
}
}
}
}
return sb.length() == indegree.size() ? sb.toString() : "";
}