3534. Accessing Website Hosted in Docker of VirtualBox from Another MachineDocker, OpenGrok, and VirtualBox
Introduce how to access website hosted in docker of virtual machine from another machine.
1. VirtualBox + Docker
I’m assigned a task to find out how many customers have configured some specific validation rules in their production environment. What I have are the customization files fetched from server, they are in XML format. My idea is to use OpenGrok for search. Before using OpenGrok, we need to import these files to it. To make it reusable, I decide to setup OpenGrok in docker.
Steps:
- 1) Install VirtualBox on RedHat machine. RedHat is the host machine.
- 2) Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox. Ubuntu is the guest machine.
- 3) Create share folder between host and guest machine.
- 4) Install Docker in Ubuntu VM.
- 5) Create OpenGrok container.
- 6) Access OpenGrok from host machine.
- 7) Access OpenGrok from another machine.
2. Installation
2.1 Installing VirtualBox
Download proper VirtualBox for RedHat from https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads. Then, install VirtualBox
sudo yum install VirtualBox-5.2-5.2.10_122088_el7-1.x86_64.rpm
Add yourself to the vboxusers group using the “Users and Groups” application or the command line:
sudo usermod -a -G vboxusers [your_user_name]
2.2 Installing Ubuntu VM
Go to https://ubuntu.com/#download to download Ubuntu Desktop. Refer to Installing VirtualBox and Creating Ubuntu VM to install Ubuntu in virtual machine.
2.3 Creating Sharing Folder
First, create shared folder in host machine. Second, install VirtualBox Guest Additions for the Ubuntu VM. Devices -> Insert Guest Additions CD images..
 Then, refer to Sharing Files between Host and Guest in VirtualBox to connect the shared folder in host machine to guest machine.
Finally, the shared folder in RedHat locates in
Then, refer to Sharing Files between Host and Guest in VirtualBox to connect the shared folder in host machine to guest machine.
Finally, the shared folder in RedHat locates in
/home/johnny/SharedUbuntu
The shared folder in Ubuntu VM locates in
/media/sf_SharedUbuntu
2.4 Installing Docker in Ubuntu VM
Refer to Installing and Using Docker on Ubuntu to install Docker.
2.5 Creating OpenGrok Container
Create two directories in the shared folder. Put the xml files into the src folder.
$ mkdir -p /opengrok/src /opengrok/data
src- Contains your source files.data- Used by OpenGrok. OpenGrok will generate indexes for the source files and store them here.
Download OpenGrok Docker Image
docker pull scue/docker-opengrok
Run a Docker container and mount these two directories: src and data; this will automatically run indexing as a part of startup.
$ docker run --name=opengrok-cus1 -v /opengrok/src:/src -v /opengrok/data:/data -p 31030:8080 scue/docker-opengrok
The OpenGrok application is now running on http://localhost:31030/source/
2.6 Accessing OpenGrok from Host Machine
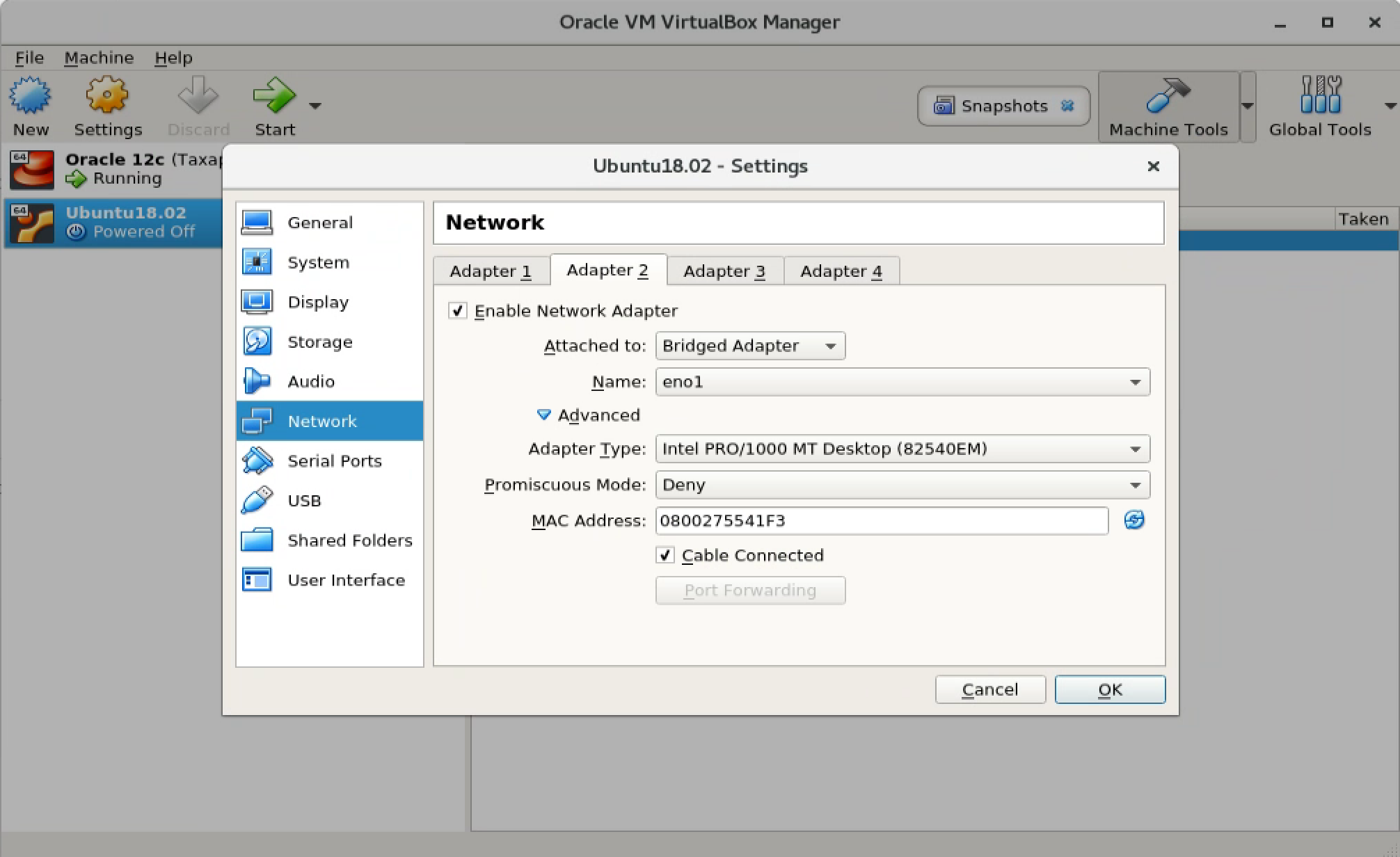
Stop Ubuntu VM, then click Settings, switch to Network. It already has the NAT Network Adapter in Adapter 1.
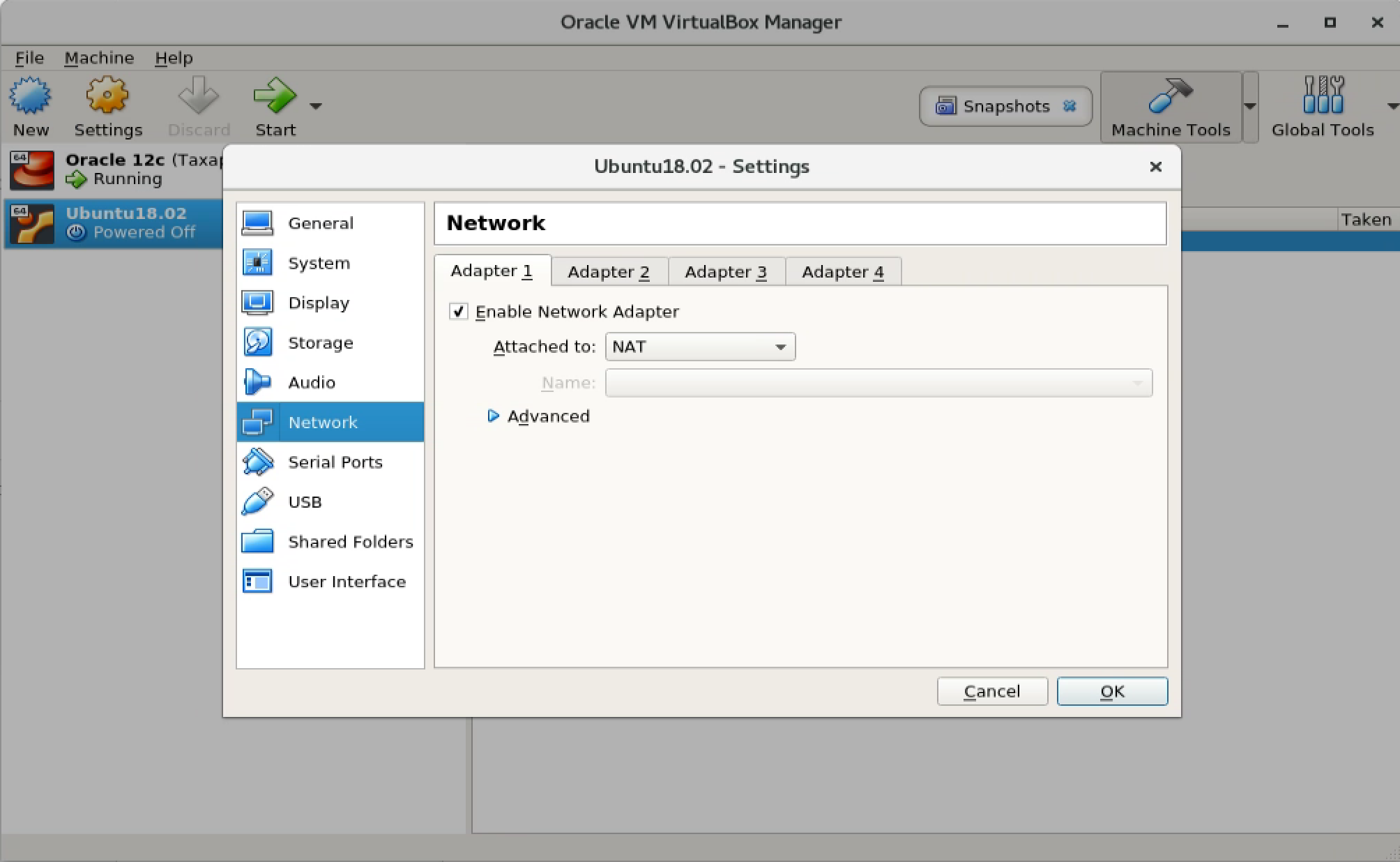 Switch to Adapter 2 tab, enable
Switch to Adapter 2 tab, enable Bridged Adapter.
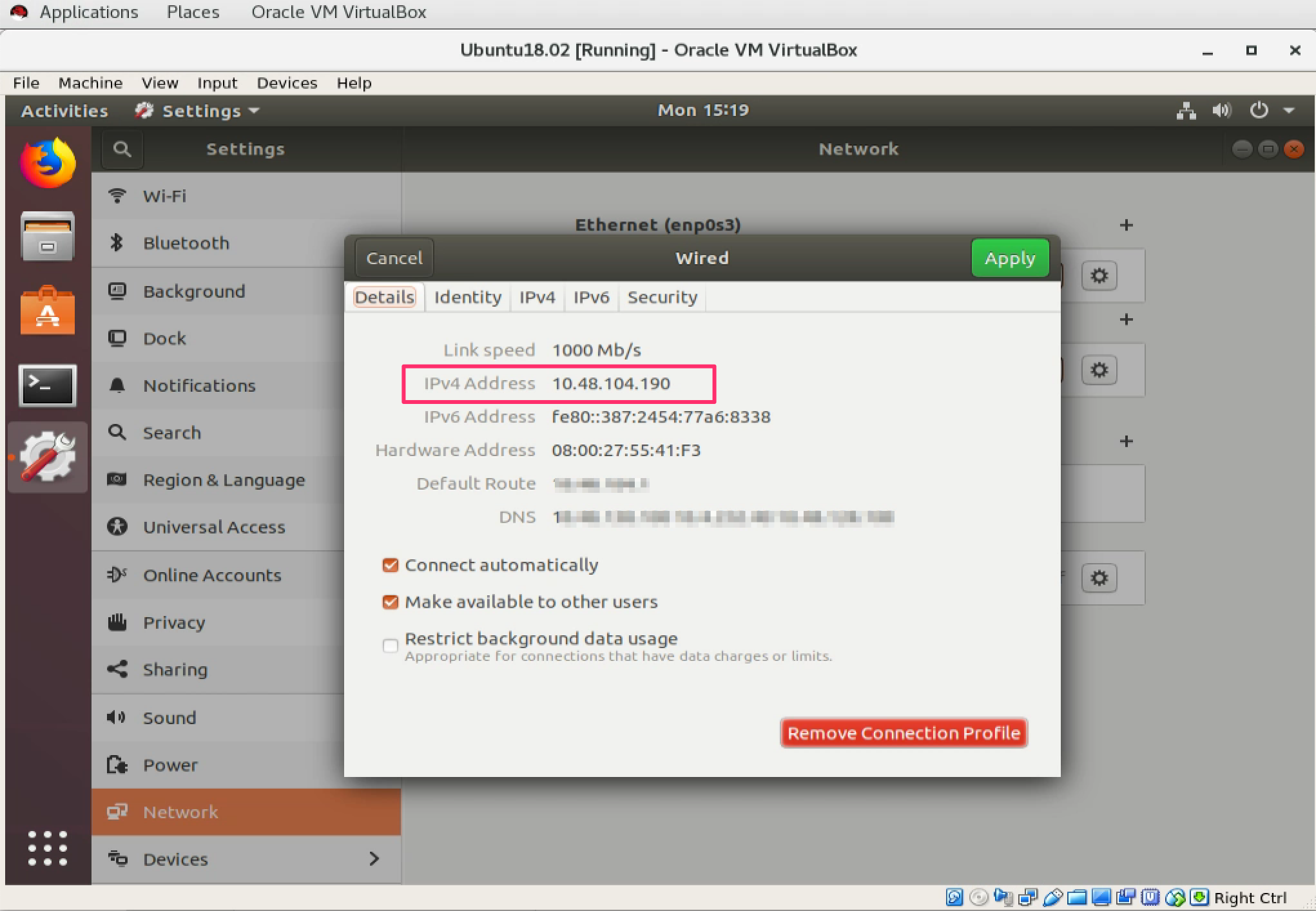
 Restart the Ubuntu VM. Go to Network to get the IP address
Restart the Ubuntu VM. Go to Network to get the IP address 10.48.104.190 for bridged adapter.
 Start the OpenGrok from docker. You may first need to delete the existing container created previously.
Start the OpenGrok from docker. You may first need to delete the existing container created previously.
Show all existing containers.
docker ps -a
Remove one particular container with id.
docker rm [container id]
The OpenGrok application can be accessed through http://10.48.104.190:31030/source/
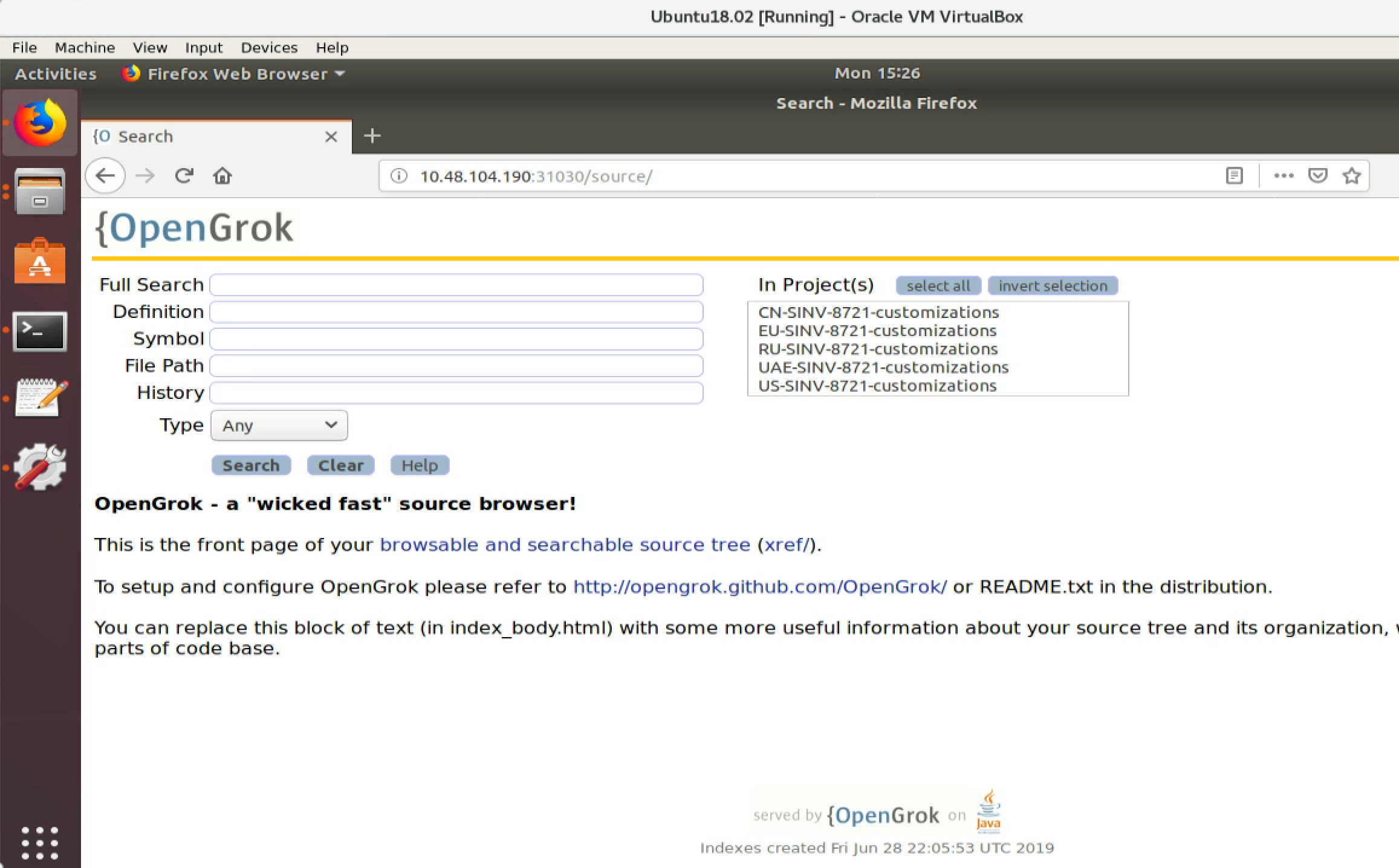 With the IP address, we can also access OpenGrok from host machine(RedHat).
With the IP address, we can also access OpenGrok from host machine(RedHat).
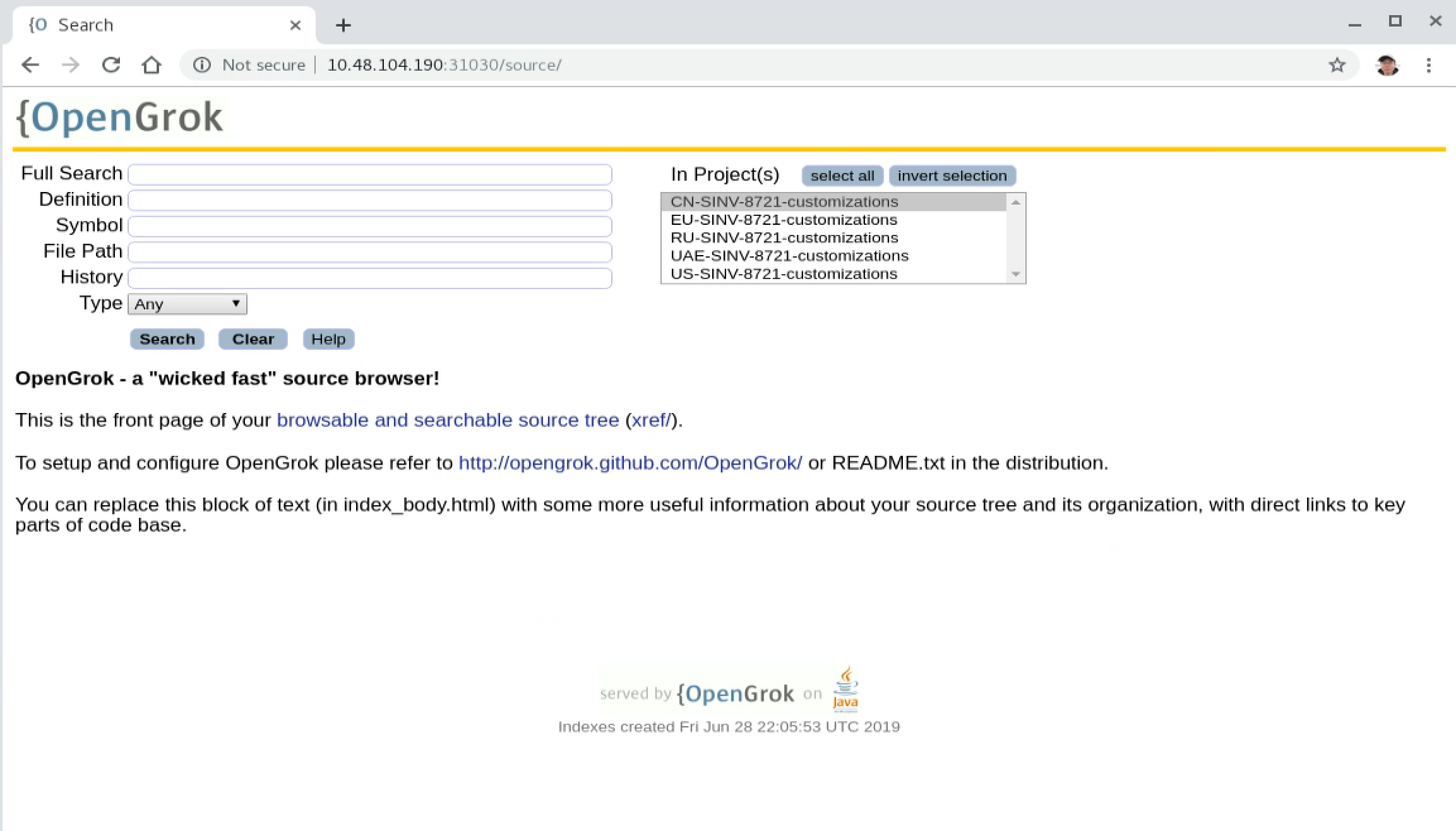
2.7 Access OpenGrok from Another Machine
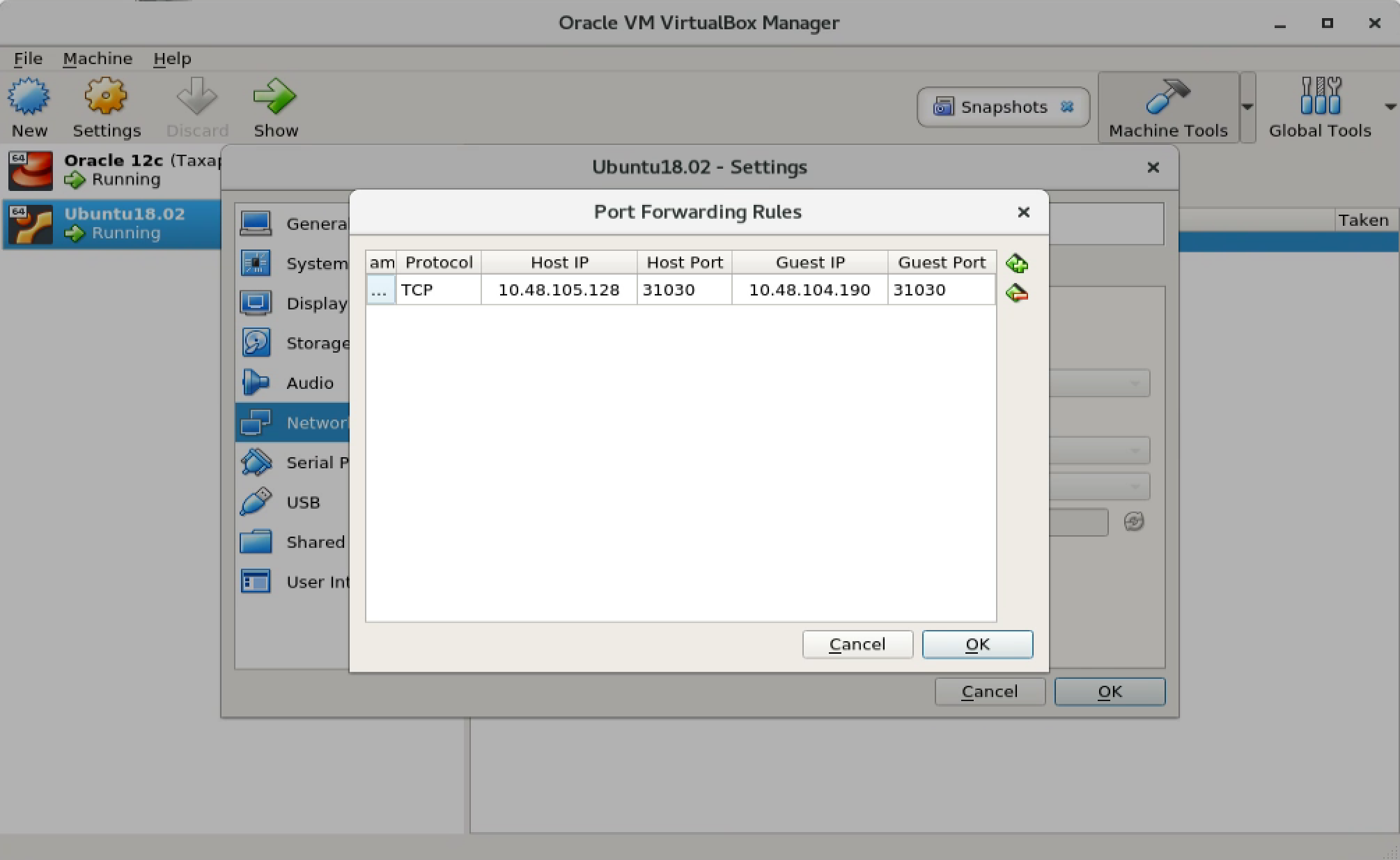
Stop Ubuntu VM, then click Settings, switch to Network. In NAT Network Adapter, click ‘Port Forwarding’ button. Setup Port Forwarding rule. 10.48.105.128 is the public IP address of the host machine. The following rule means, the request to http://10.48.105.128:31030 will be forwarded to http://10.48.104.190:31030.
Finally, the OpenGrok application can be accessed through http://10.48.105.128:31030/source/ from another machine.