3501. Installing and Using Docker on UbuntuDocker and Docker Hub
Introduce how to install and use docker.
1. What is Docker?
Docker is a container management service. The keywords of Docker are develop, ship and run anywhere. The whole idea of Docker is for developers to easily develop applications, ship them into containers which can then be deployed anywhere.
Key concepts of Docker: Image, Container and Docker Hub.
1.1 Image
In Docker, everything is based on Images. An image is a combination of a file system, tools and configurations.
1.2 Container
Containers are instances of Docker images that can be run using the Docker run command. The basic purpose of Docker is to run containers.
1.3 Docker Hub
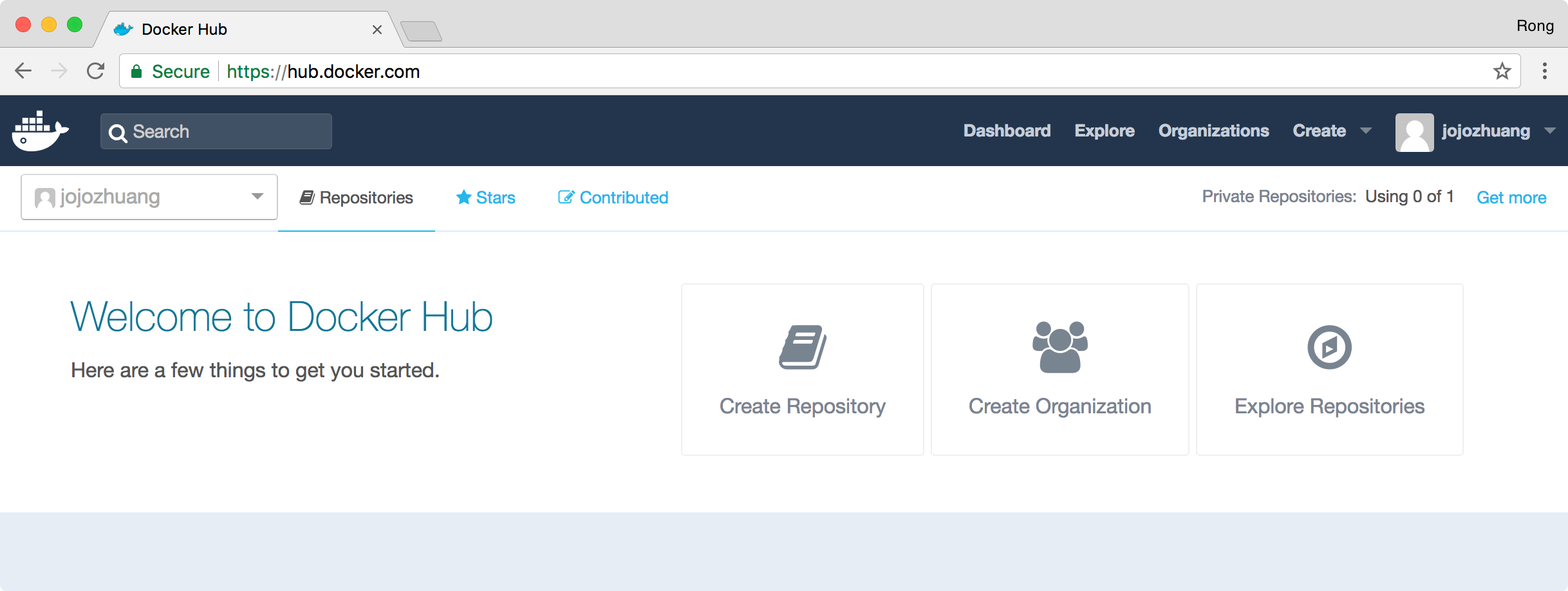
Docker Hub is a registry service on the cloud that allows you to download Docker images that are built by other communities. You can also upload your own Docker built images to Docker hub.
Go to https://hub.docker.com/ to create a Docker ID, then login. You will see there is no repository/image initially. We will create our own image later.
2. Installing Docker on Ubuntu
1) Add the GPG key for the official Docker repository to the system:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install curl
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
2) Add the Docker repository to APT sources:
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
3) Update the package database with the Docker packages from the newly added repo:
$ sudo apt-get update
4) Make sure you are about to install from the Docker repo instead of the default Ubuntu 16.04 repo:
$ apt-cache policy docker-ce
5) Install Docker:
$ sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce
6) Check Docker is Running:
$ sudo systemctl status docker
3. Executing the Docker Command Without Sudo (Optional)
By default, running the docker command requires root privileges — that is, you have to prefix the command with sudo. It can also be run by a user in the docker group, which is automatically created during the installation of Docker. If you attempt to run the docker command without prefixing it with sudo or without being in the docker group, you’ll get an output like this:
$ sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER} // add the current user to the docker group
$ sudo usermod -aG docker username // add a particular user to the docker group
$ su - ${USER} // apply the new group membership
$ id -nG // check user is now added to the docker group
johnny adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker vboxsf
4. Using Docker Commands
Syntax of Docker Command
$ docker [option] [command] [arguments]
4.1 Generic Docker Commands
$ docker version // check version
$ docker info // check system-wide information about Docker
$ docker search ubuntu // search image which is named 'ubuntu' from Docker Hub
$ docker pull ubuntu // download image from Docker Hub to local
4.2 Commands for Images:
$ docker images // list images
$ docker rmi image_name // delete image by name
$ docker rmi image_id // delete image by id
4.3 Commands for Containers
$ docker ps // list all active docker containers
$ docker ps -a // list all docker containers
$ docker run ubuntu // run a container with the selected image
$ docker run -it ubuntu // run a container with the selected image, and access the interactive shell
$ docker stop container-id // stop a running or active container
$ docker stop $(docker ps -a -q) // stop all of Docker containers
$ docker rm $(docker ps -a -q) // remove all of Docker containers
5. Creating Docker Image
We use the office ubuntu image for this demo. We will install node.js on it, then use it to create new image.
5.1 Preparing Image
Pull the ubuntu image from Docker Hub.
$ docker pull ubuntu
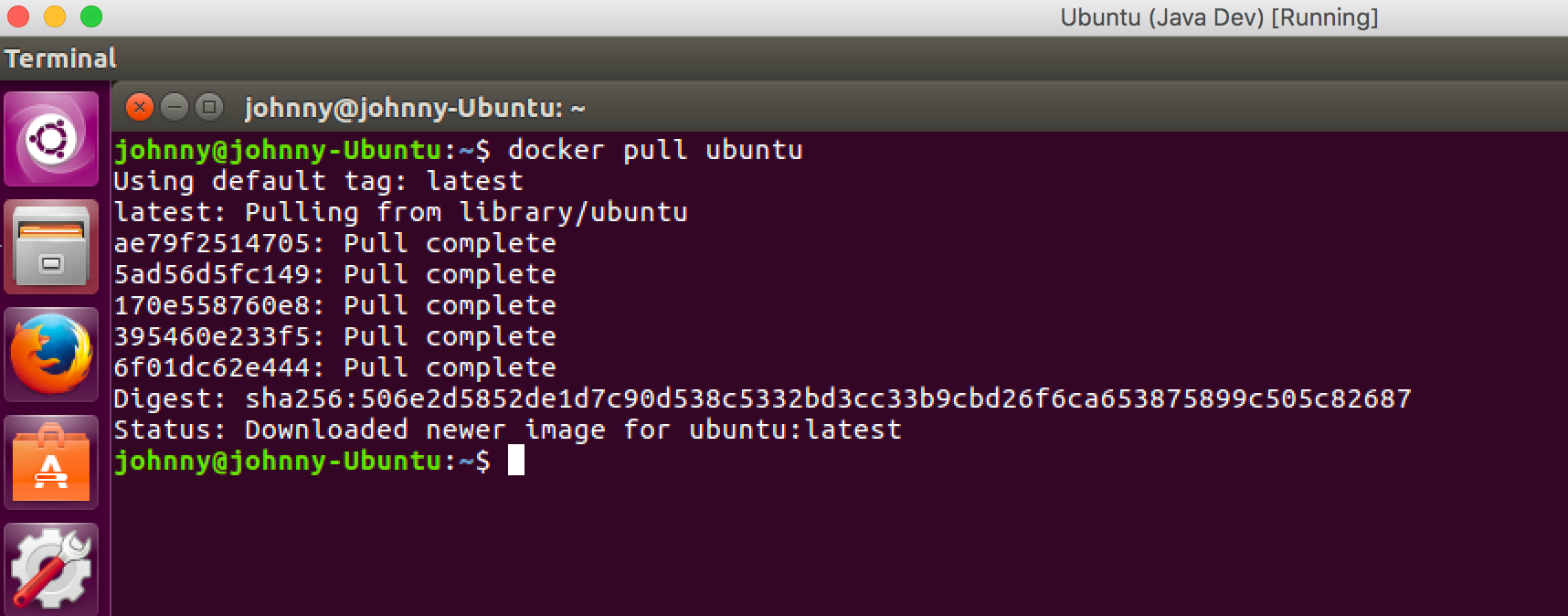
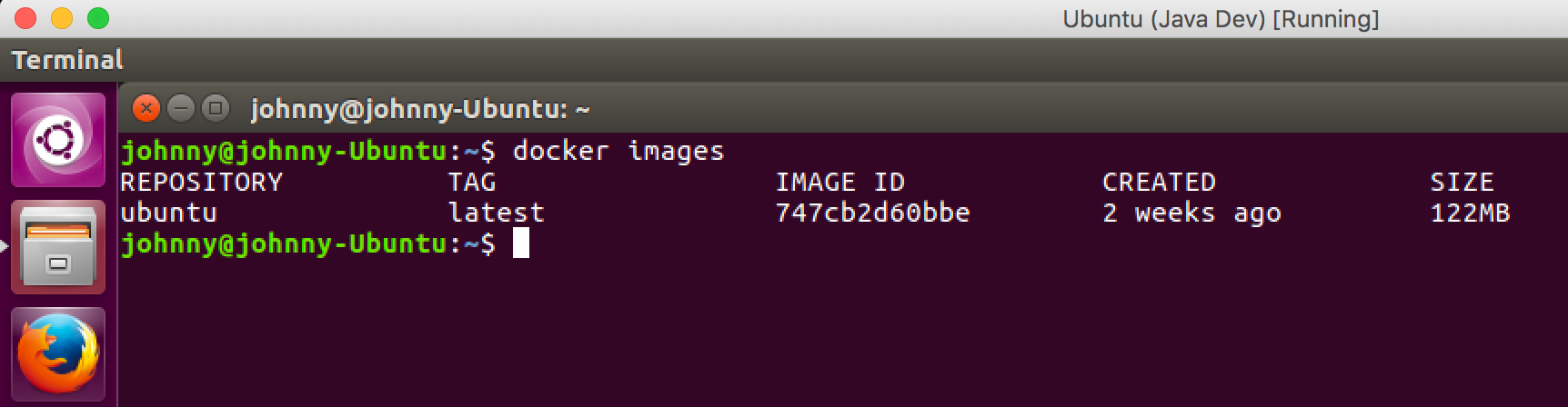
Check the existing images in the docker.
$ docker images
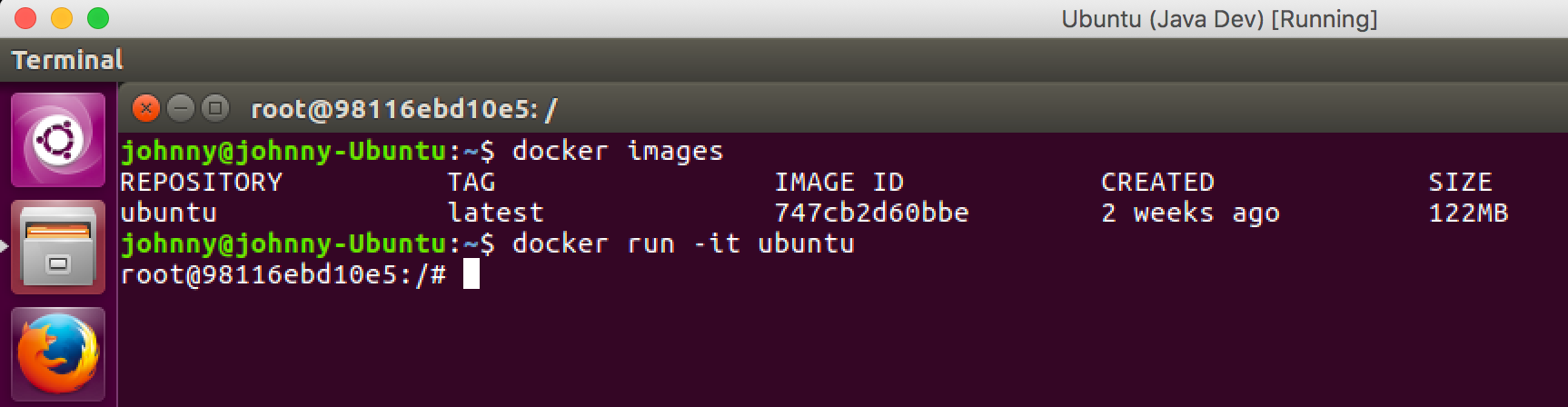
Start a Ubuntu container and go inside to its shell.
$ docker run -it ubuntu
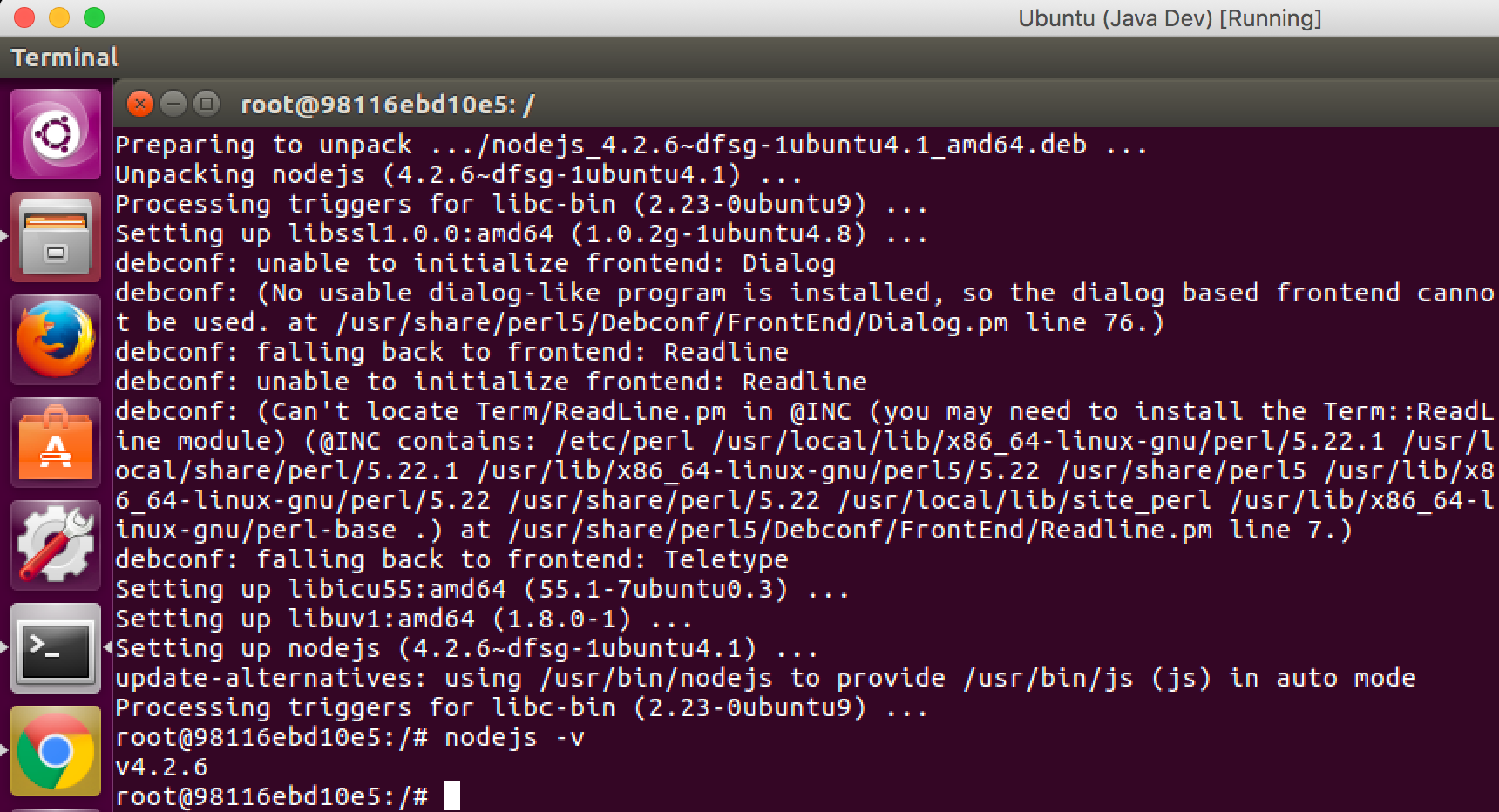
Install Node.js in Ubuntu container.
$ root@98116ebd10e5:/# apt-get update
$ root@98116ebd10e5:/# apt-get install -y nodejs
Check the node version to make sure the installation is properly completed.
$ root@98116ebd10e5:/# nodejs -v
5.2 Creating New Image
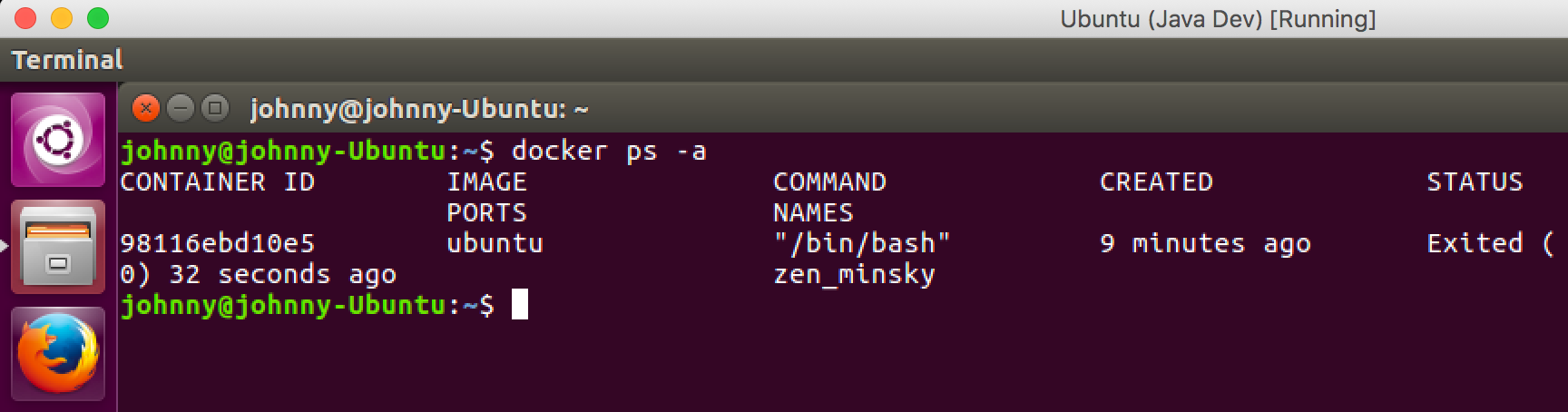
First, type ‘exit’ to quit the container. Then check the container id with following command.
$ docker ps -a
This command shows all of the existing containers. As you see, there is only one ubuntu container is running, which we just install node.js on it. Note down the container id.
Now, we are ready to create our own image.
Syntax of creating new image.
$ docker commit -m "What did you do to the image" -a "Author Name" container-id repository/new_image_name
Type the following command.
$ docker commit -m "added node.js" -a "Johnny" 98116ebd10e5 jojozhuang/ubuntu-nodejs
- ‘98116ebd10e5’ is the container id of the ubuntu container.
- ‘jojozhuang’ is my Docker ID which is used to log into Docker Hub.
- ‘ubuntu-nodejs’ is the new image name.
Show the image list to check whether our new image is created.
$ docker images
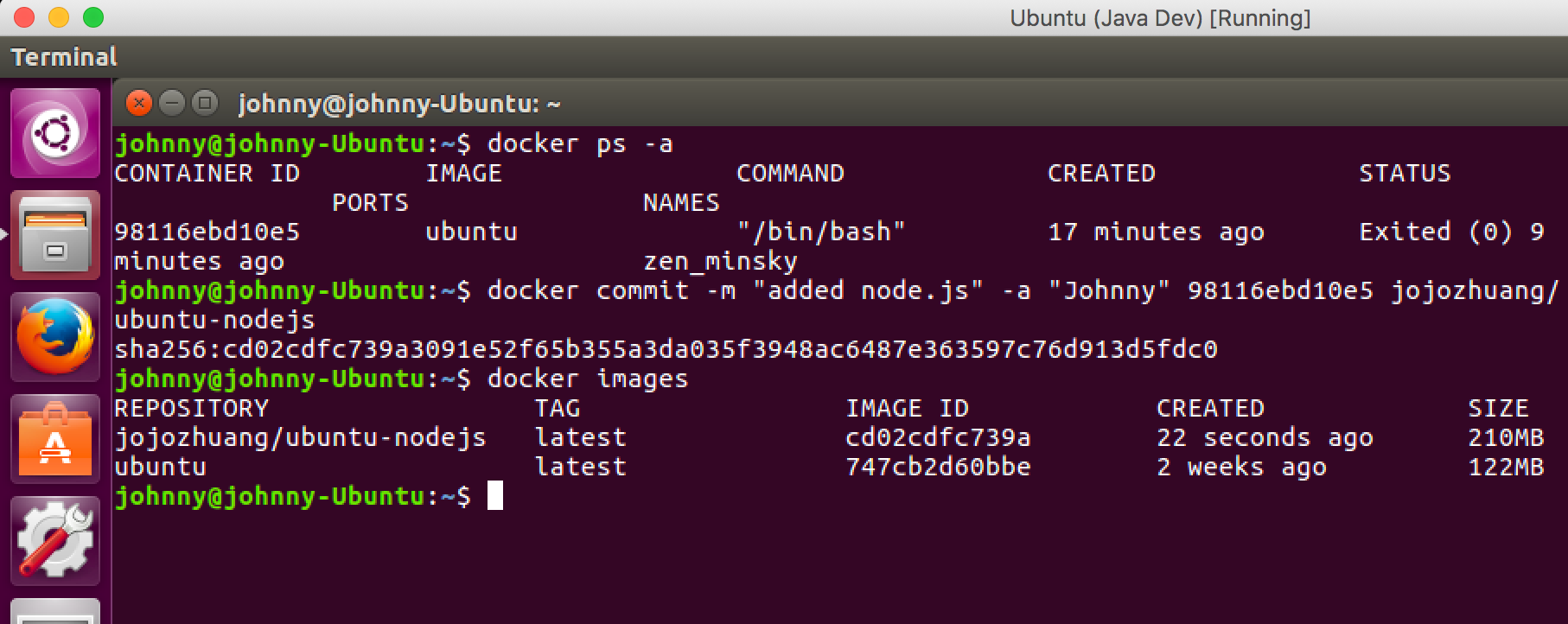
As you see, a new image named ‘jojozhuang/ubuntu-nodejs’ has been created. Notice that its size is bigger than the original ubuntu image. This is because we install node.js into it.
5.3 Using Dockerfile to Create New Images
Refer to the following blogs:
6. Pushing Docker Images to Docker Hub
6.1 Logging into Docker Hub
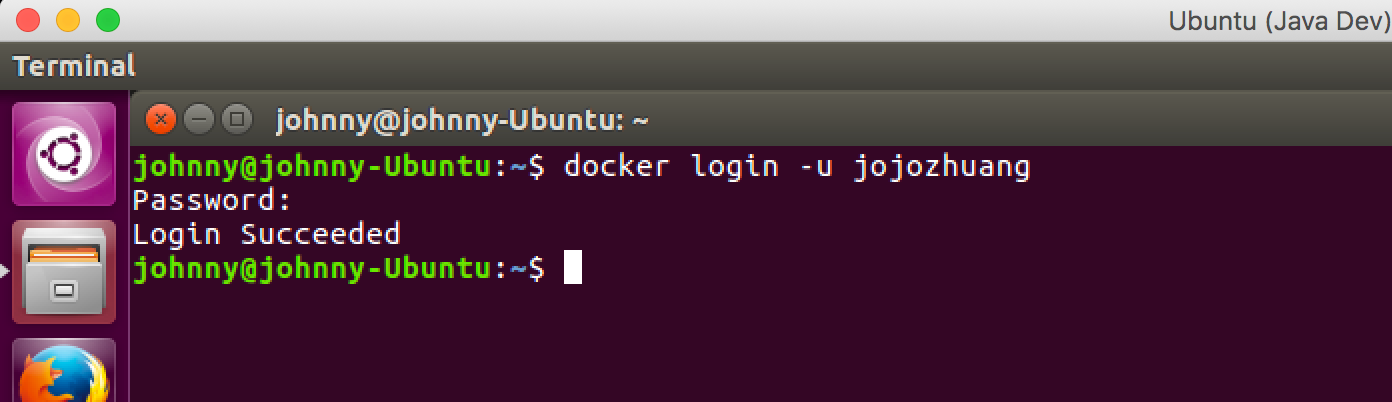
Syntax of login command.
$ docker login -u username
Type command as follows, then input password.
$ docker login -u jojozhuang
6.2 Pushing the Image
Syntax of push command.
$ docker push docker-registry-username/docker-image-name
Type command as follows, providing the full name of the new image.
$ docker push jojozhuang/ubuntu-nodejs
Then, docker starts to upload the image to its hub.
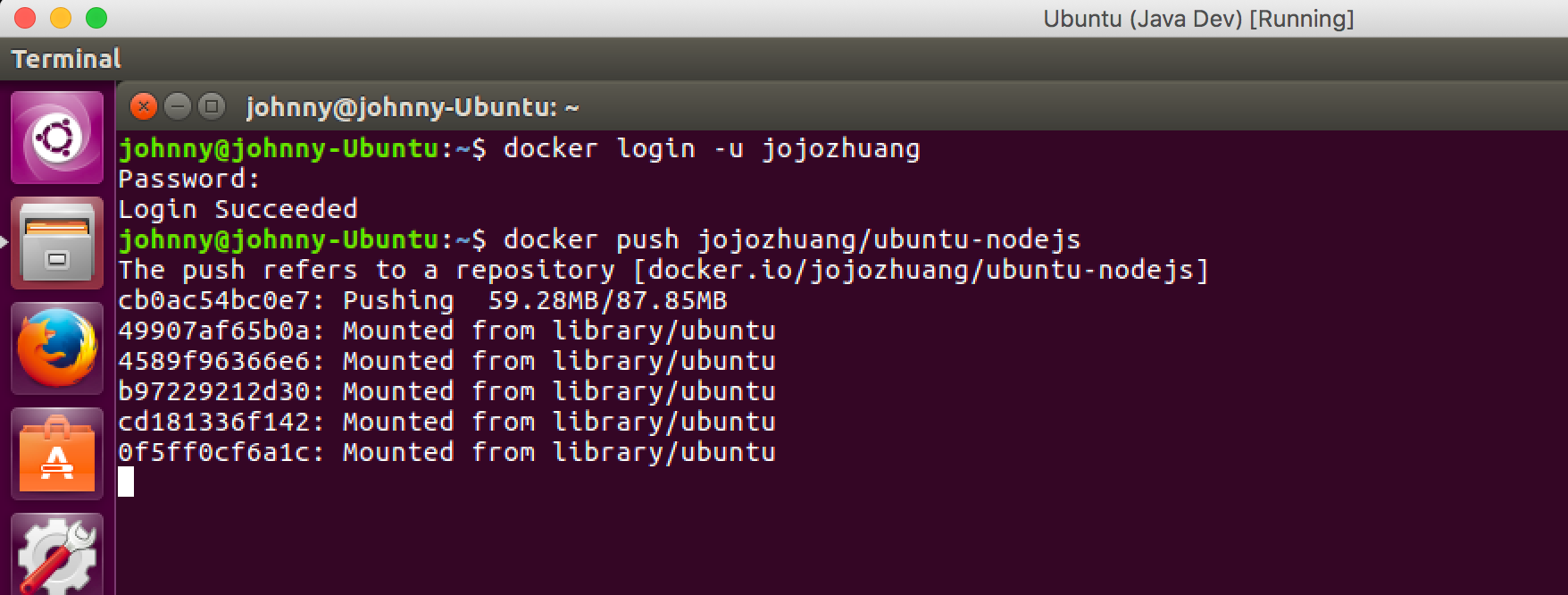
After the push is completed, you will see the ‘Pushed’ status.
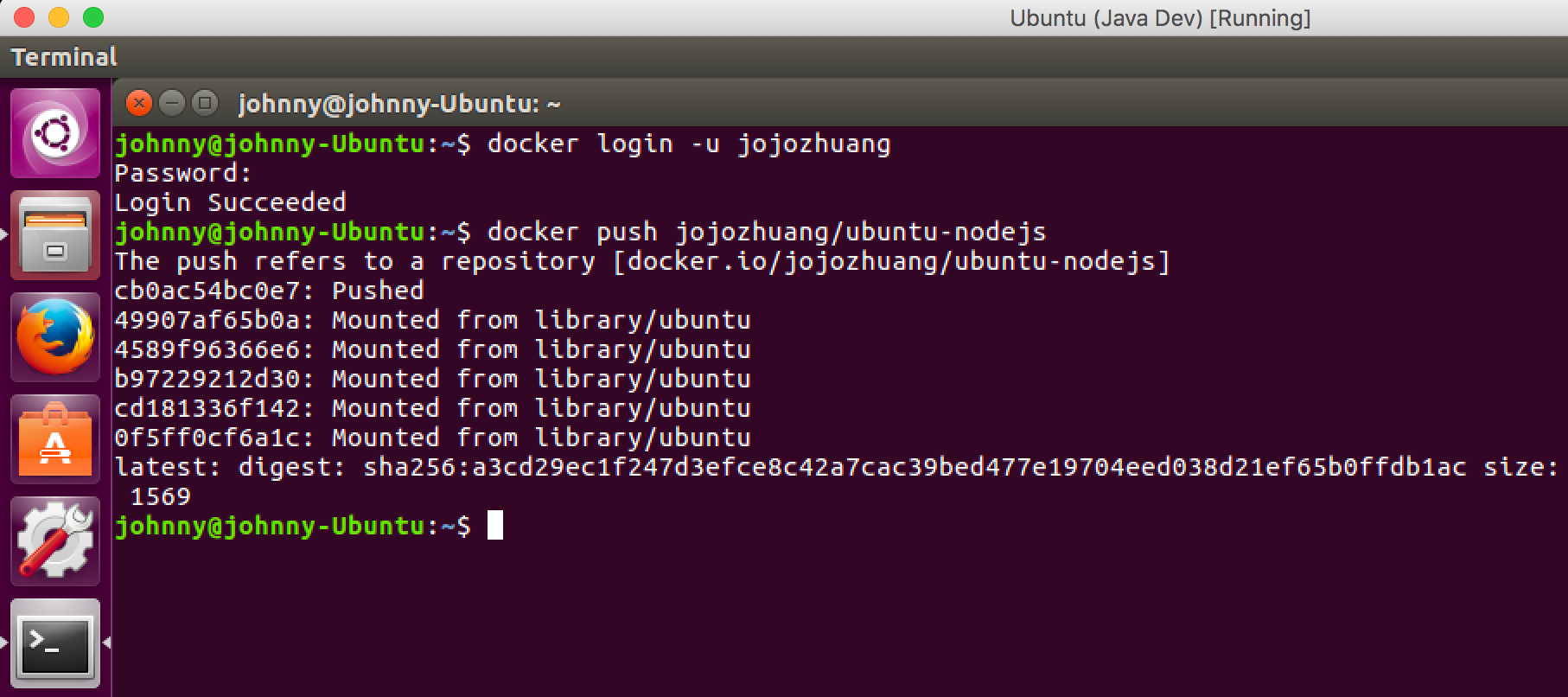
6.3 Checking The New Image in Docker Hub
Log into the Docker Hub, we see there is a new image.
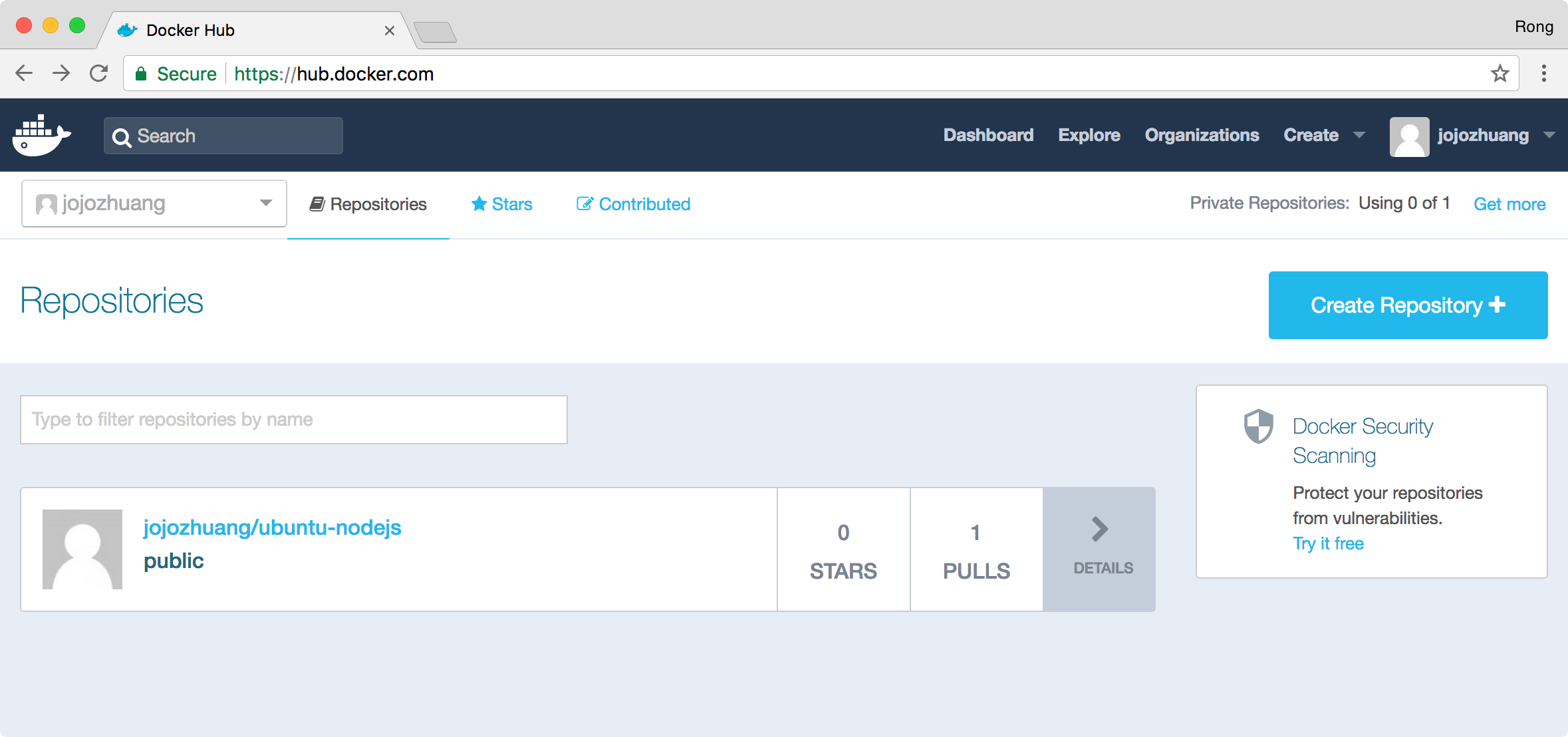
Now, you can share this image to others and you can pull this image from Docker Hub as well.
7. Pulling The New Image from Hub to Mac
Launch Docker Terminal on Mac, run the following command to pull the new image.
$ docker pull jojozhuang/ubuntu-nodejs
Run the following command to start the container and go to its shell.
$ docker run -it jojozhuang/ubuntu-nodejs
Check the nodejs version.
$ nodejs -v
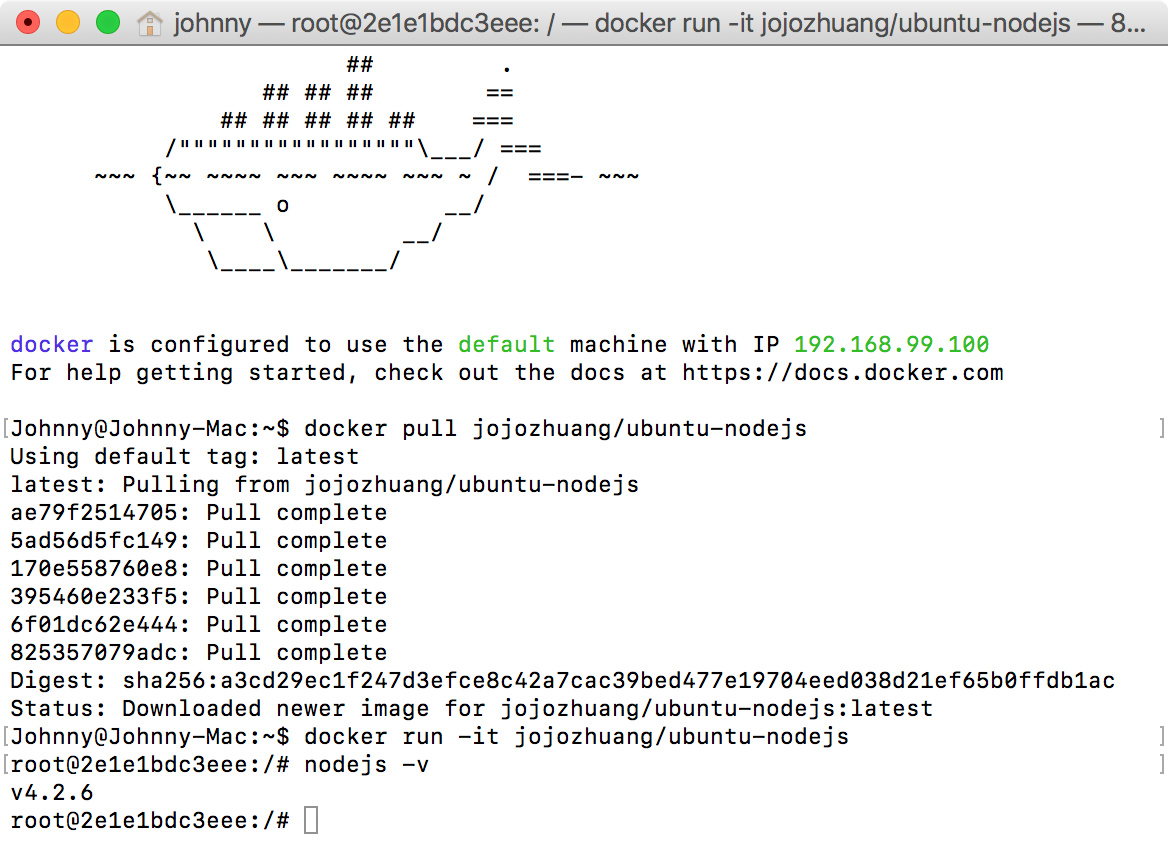
Yes, it’s our image!