4121. AWS-EC2-InstanceAWS and EC2
Creating EC2 Instances.
1. EC2
1.1 What is EC2?
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers.
1.2 Amazon EC2 Pricing
There are four ways to pay for Amazon EC2 instances:
On Demand- Allows you to pay a fixed rate by the hour (or by the second) with no commitment.Reserved- Provides you with a capacity reservation, and offer a significant discount on the hourly charge for an instance. Contract Terms are 1 or 3 Year Terms.Spot- Enables you to bid whatever price you want for instance capacity, providing for even greater savings if your applications have flexible start and end times.Dedicated Hosts- Physical EC2 server dedicated for your use. Dedicated Hosts can help you reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses.
1.3 On Demand Pricing
On Demand pricing is useful for:
- Users that want the low cost and flexibility of Amazon EC2 without any up-front payment or long-term commitment.
- Applications with short term, spiky, or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted.
- Applications being developed or tested on Amazon EC2 for the first time.
1.4 Reserved Pricing
Reserved Pricing Reserved pricing is useful for:
- Applications with steady state or predictable usage.
- Applications that require reserved capacity.
- Users able to make upfront payments to reduce their total computing costs even further
Reserved Pricing Types:
- Standard Reserved instances - These offer up to 75% off on demand instances. The more you pay up front and the longer the contract, the greater the discount.
- Convertible Reserved Instances - These offer up to 54% off on demand capability to change the attributes of the RI as long as the exchange results in the creation of Reserved Instances of equal or greater value.
- Scheduled Reserved Instances - These are available to launch within the time windows you reserve. This option allows you to match your capacity reservation to a predictable recurring schedule that only requires a fraction of a day, a week, or a month.
1.5 Spot Pricing
Spot pricing is useful for:
- Applications that have flexible start and end times.
- Applications that are only feasible at very low compute prices.
- Users with urgent computing needs for large amounts of additional capacity.
1.6 Dedicated Hosts Pricing
Dedicated Hosts pricing is useful for:
- Useful for regulatory requirements that may not support multi-tenant virtualization.
- Great for licensing which does not support multi-tenancy or cloud deployments.
- Can be purchased On-Demand (hourly).
- Can be purchased as a Reservation for up to 70% off the On-Demand price.
1.7 EC2 Instance Types
| Family | Speciality | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | Field Programmable Gate Array | Genomics research, financial analytics, real-time video processing, big data etc |
| I3 | High Speed Storage | NoSQL DBs, Data Warehousing etc |
| G3 | Graphics Intensive | Video Encoding/ 3D Application Streaming |
| H1 | High Disk Throughput | MapReduce-based workloads, distributed file systems such as HDFS and MapR-FS |
| T3 | Lowest Cost, General Purpose | Web Servers/Small DBs |
| D2 | Dense Storage | Fileservers/Data Warehousing/Hadoop |
| R5 | Memory Optimized | Memory Intensive Apps/DBs |
| M5 | General Purpose | Application Servers |
| C5 | Compute Optimized | CPU Intensive Apps/DBs |
| P3 | Graphics/General Purpose GPU | Machine Learning, Bit Coin Mining etc |
| X1 | Memory Optimized | SAP HANA/Apache Spark etc |
| Z1D | High compute capacity and a high memory footprint | Ideal for electronic design automation (EDA) and certain relational database workloads with high per-core licensing costs. |
| A1 | Arm-based workloads | Scale-out workloads such as web servers |
| U-6tb1 | Bare Metal | Bare metal capabilities that eliminate virtualization overhead |
2. Lab - EC2 Instance
2.1 Creating EC2 Instance
Go to Services->EC2, Launch Instance.
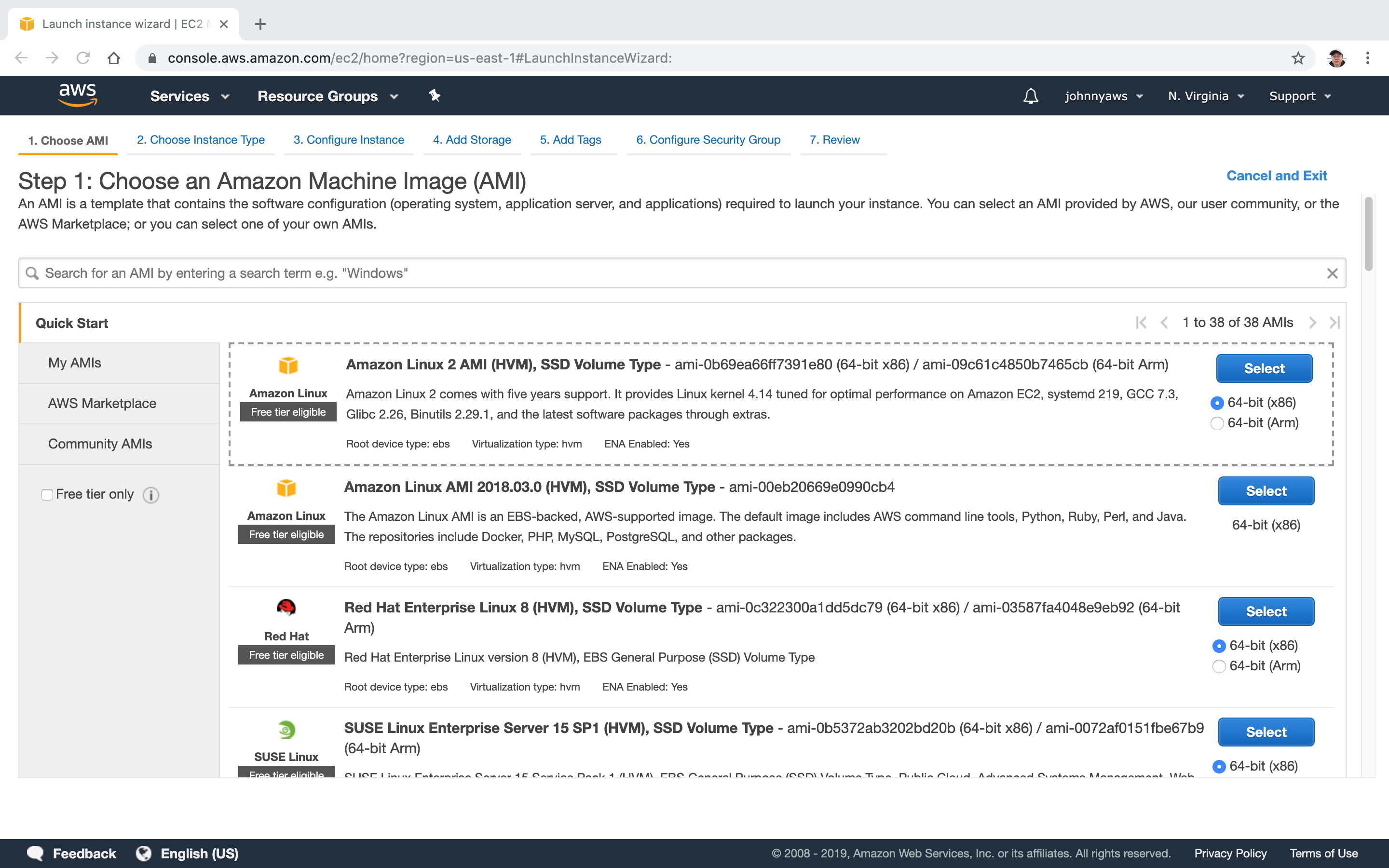
 Choose AMI(Amazon Machine Image).
Choose AMI(Amazon Machine Image).
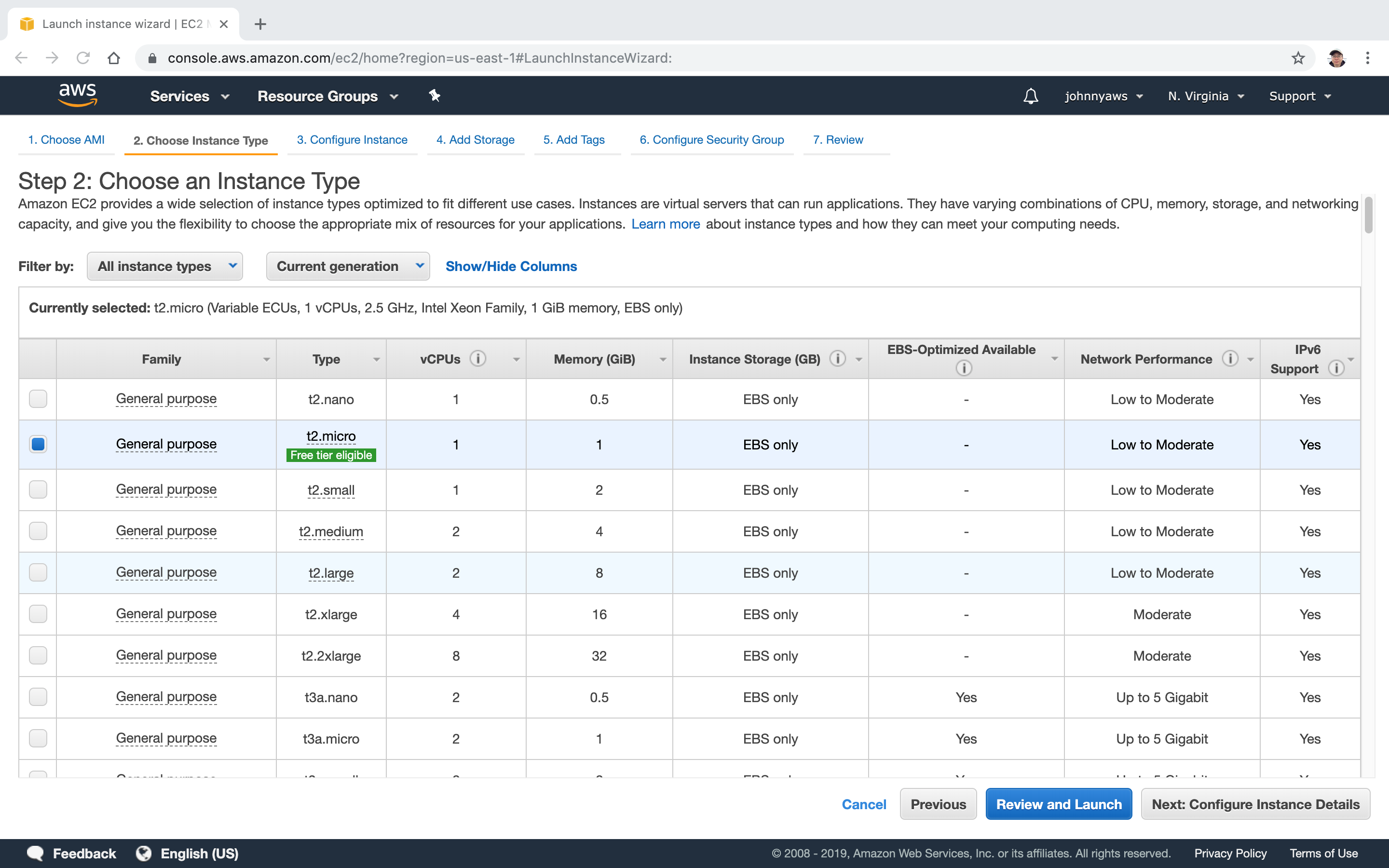
 Choose Instance Type which is Free Tier Eligible.
Choose Instance Type which is Free Tier Eligible.
 Configure Instance Details, check “Protect against accidental termination”.
Configure Instance Details, check “Protect against accidental termination”.
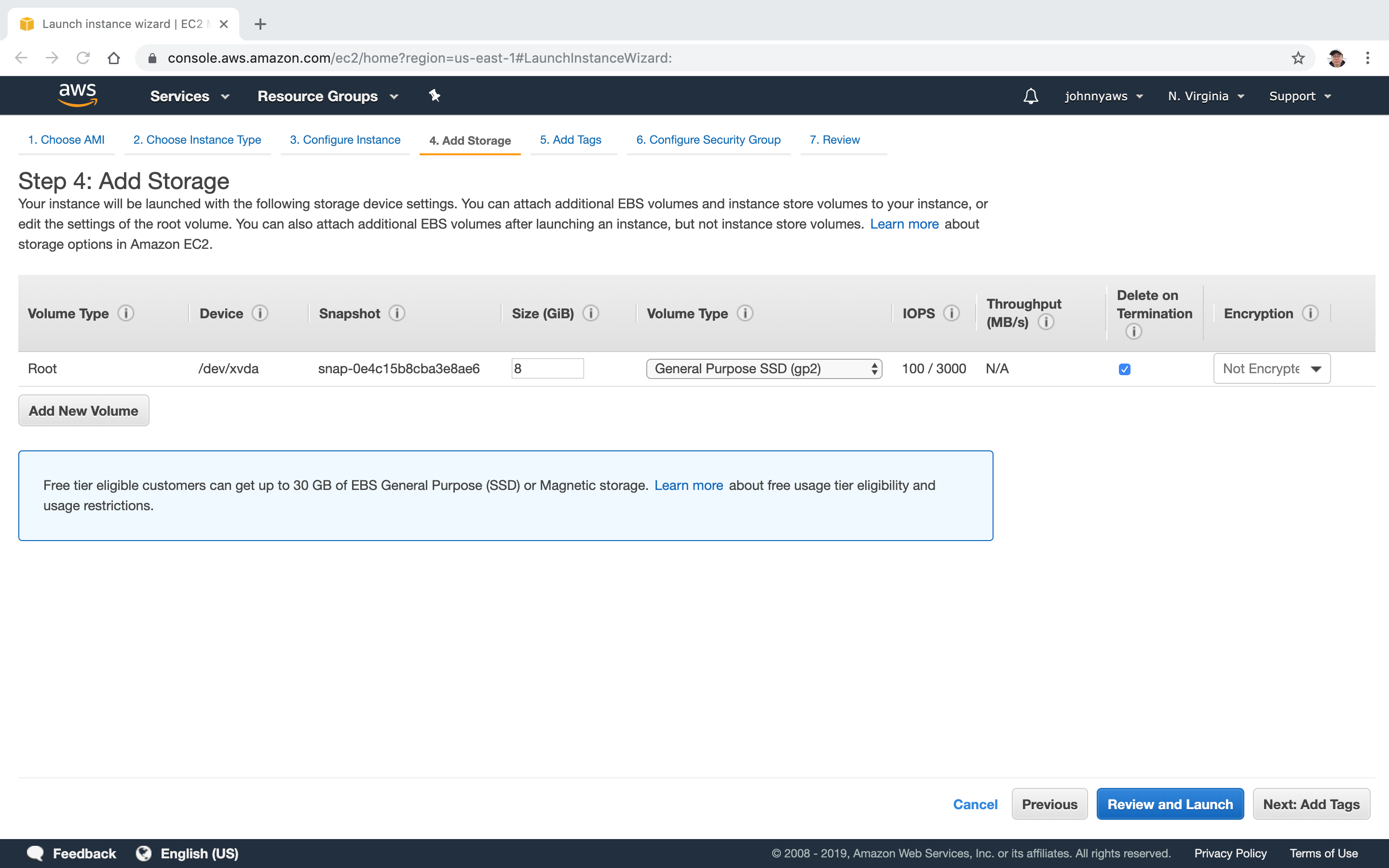
 Add Storage, leave the default settings.
Add Storage, leave the default settings.
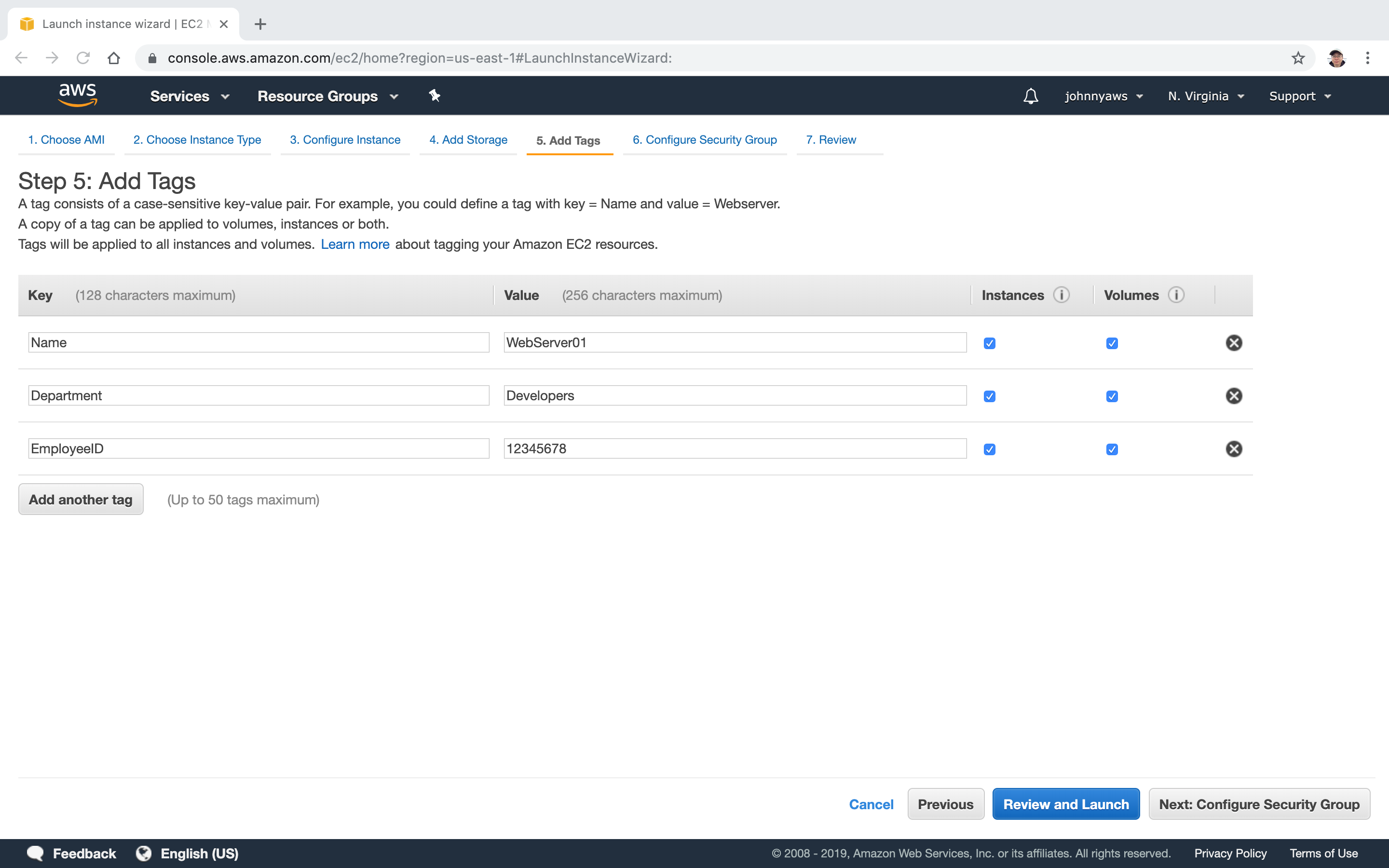
 Add Tags. For example, add name value pair to set instance’s name.
Add Tags. For example, add name value pair to set instance’s name.
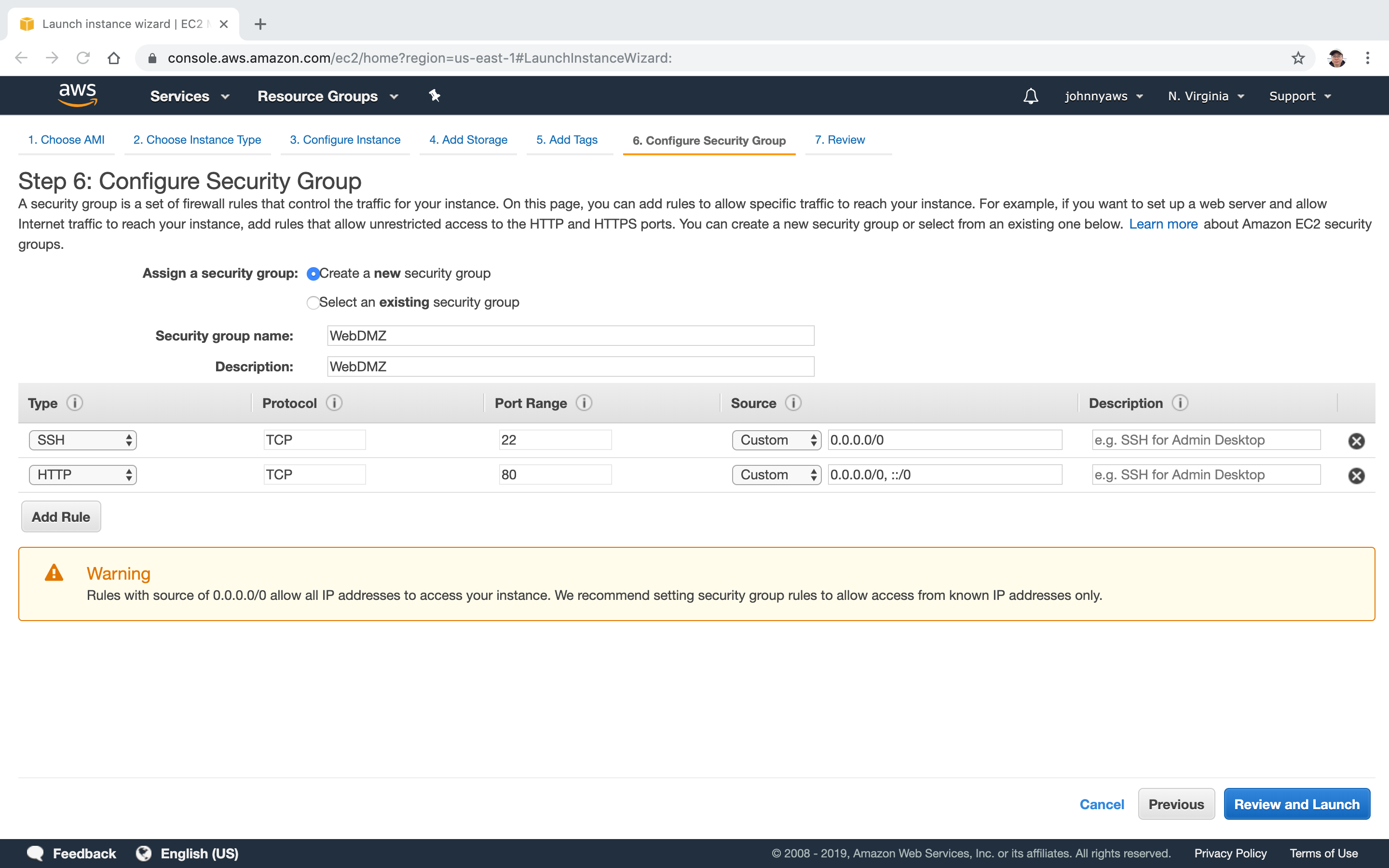
 Security Group. Expose port 80 if the instance acts as web server. Expose port 22 for remote connection with ssh.
Security Group. Expose port 80 if the instance acts as web server. Expose port 22 for remote connection with ssh.
 Launch.
Launch.
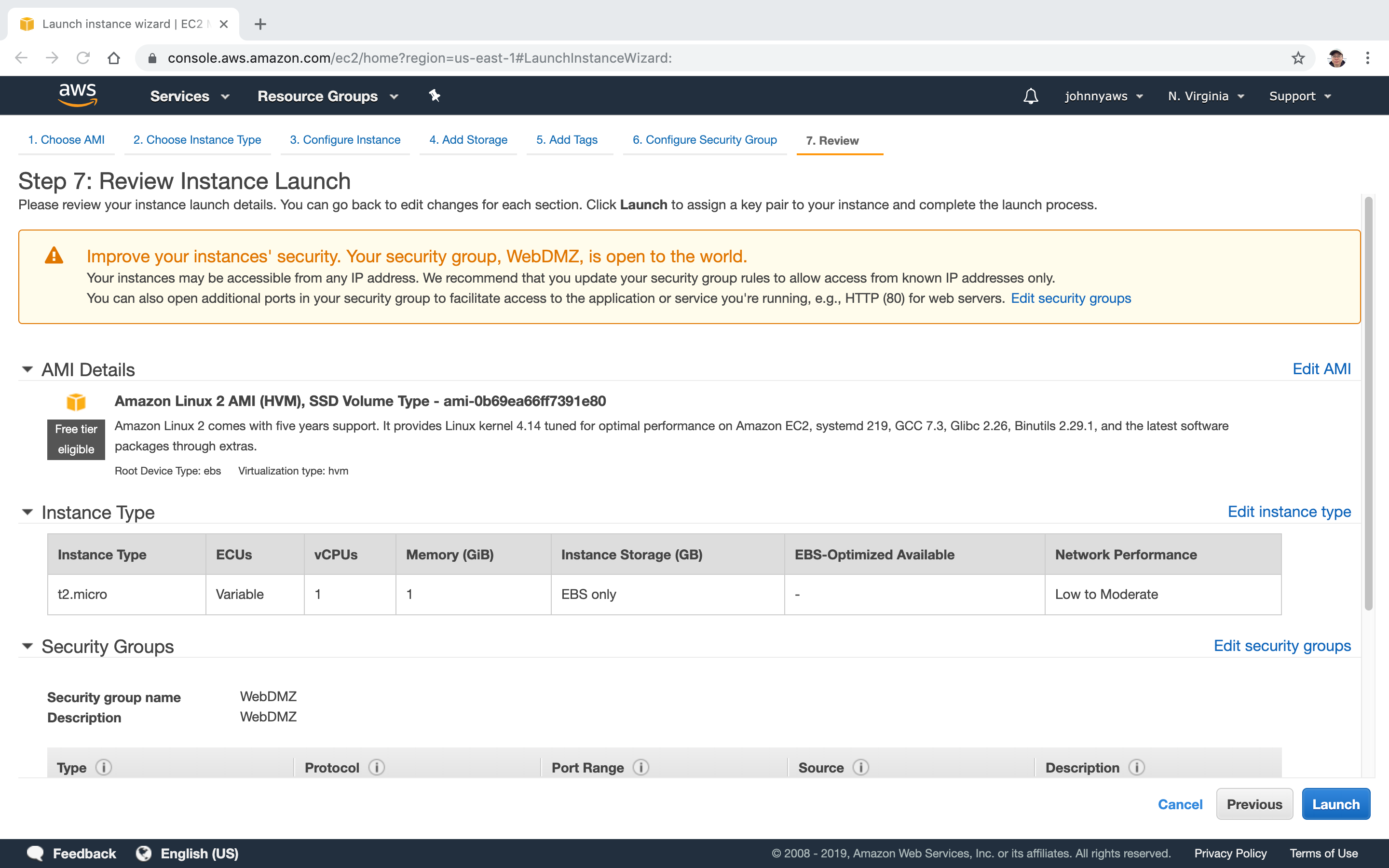 Create key pair, eg. ‘johnny-aws-ec2-keypair’.
Create key pair, eg. ‘johnny-aws-ec2-keypair’.
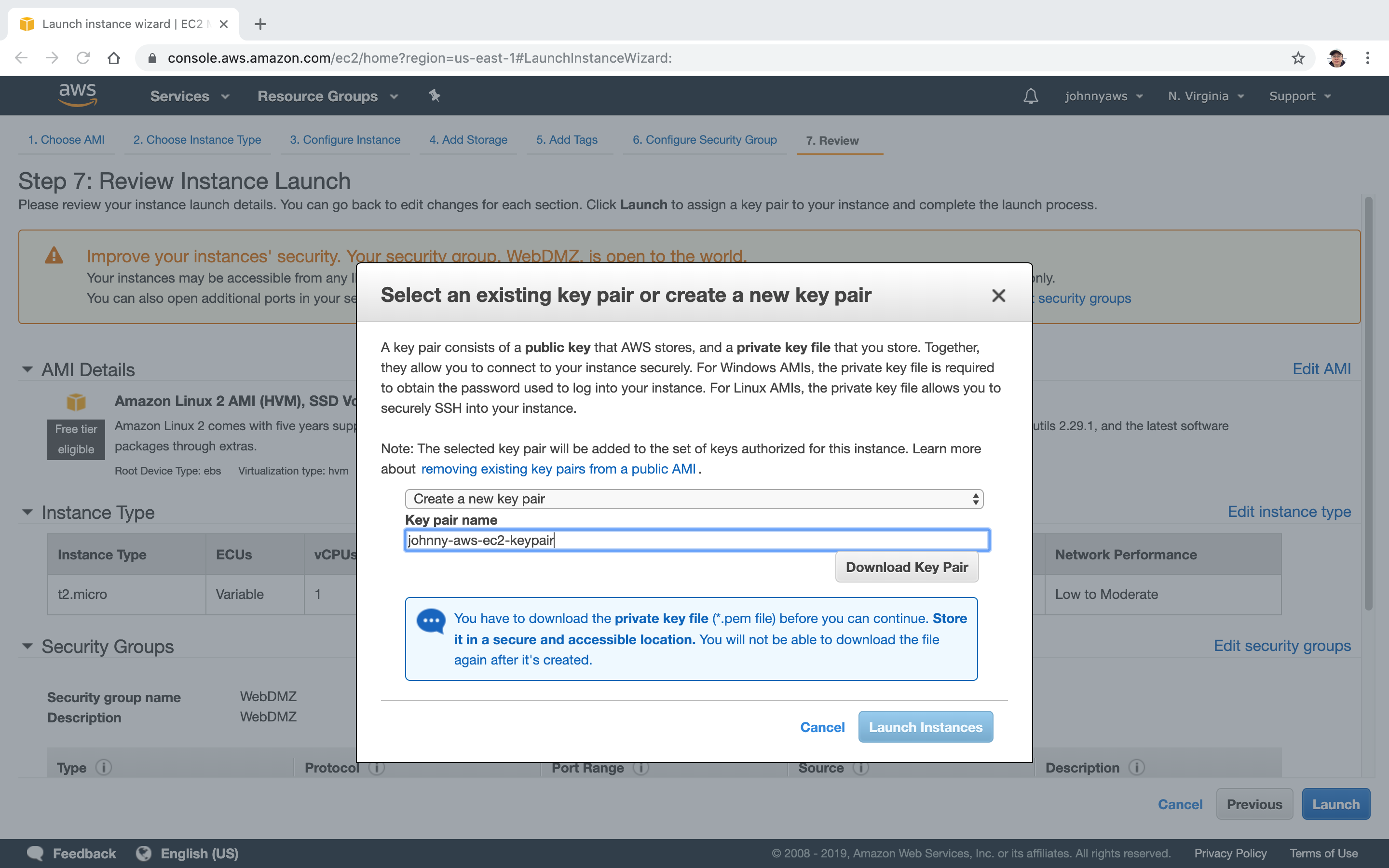 Download Key Pair and Launch Instances. Save the key pair in your local machine, we will use it for remote ssh to AWS server.
Download Key Pair and Launch Instances. Save the key pair in your local machine, we will use it for remote ssh to AWS server.
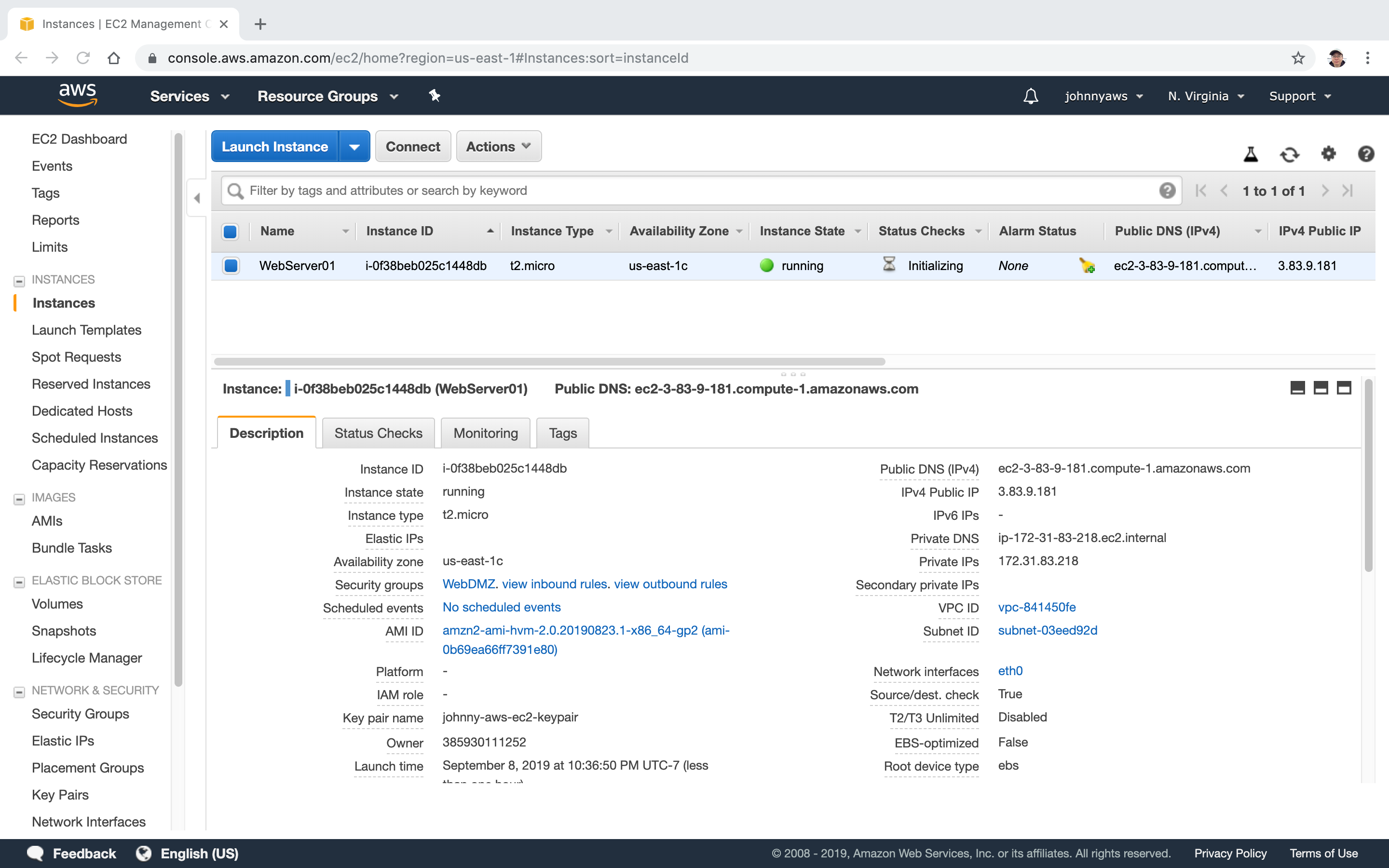
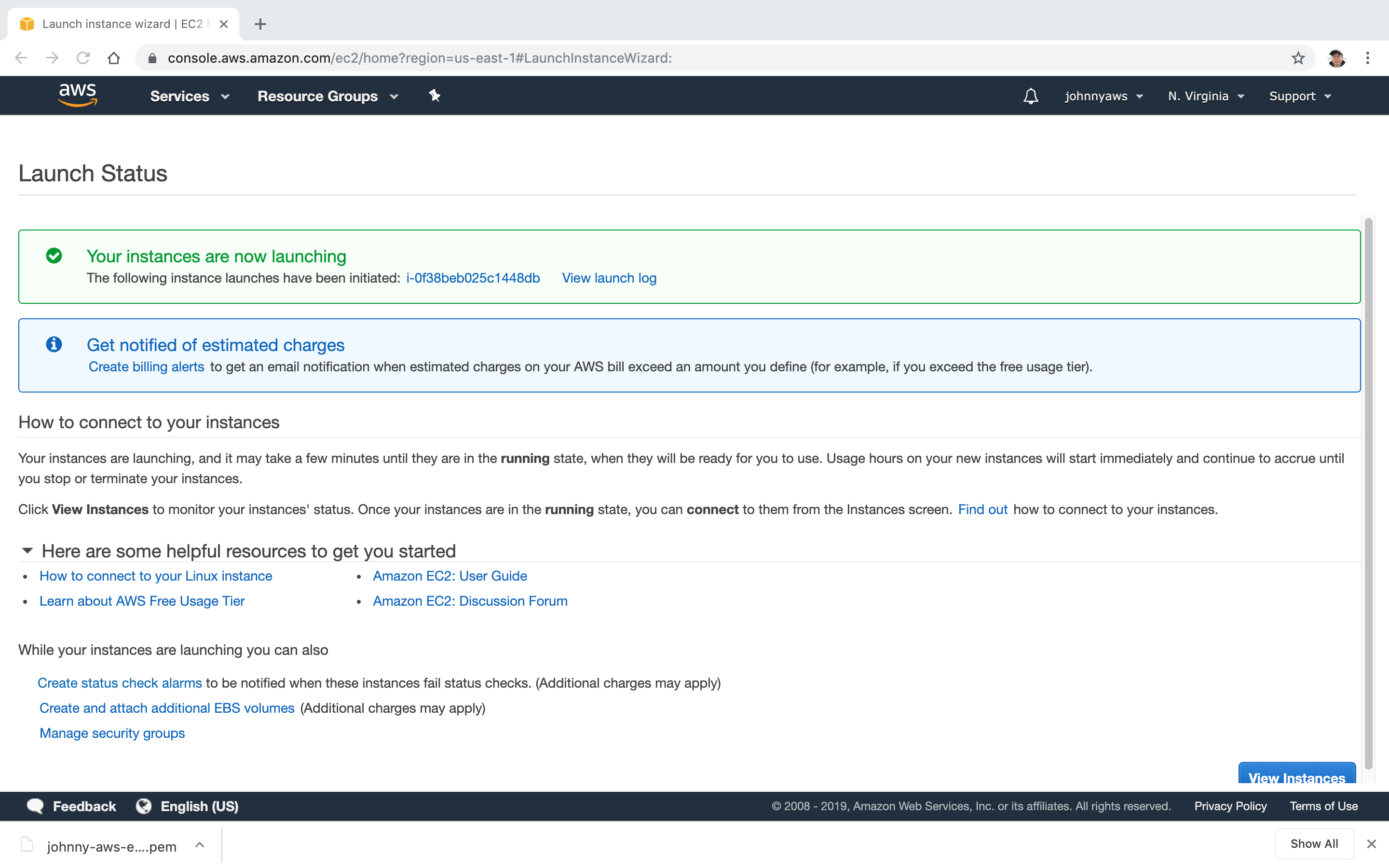 Instance is created and launched. Note down the public ip ‘3.83.9.181’.
Instance is created and launched. Note down the public ip ‘3.83.9.181’.
2.2 Connecting to EC2 Instance Remotely
In your local machine, launch terminal, go to the directory where the key pair locates.
Assign proper access permissions of the key pair file.
chmod 400 johnny-aws-ec2-keypair.pem
Use ssh command to connect ec2 instance remotely.
ssh ec2-user@[the public ip of ec2 instance] -i [key pair file]
See the demo below.
> ls
johnny-aws-ec2-keypair.pem
> chmod 400 johnny-aws-ec2-keypair.pem
> ssh ec2-user@3.83.9.181 -i johnny-aws-ec2-keypair.pem
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:U8mtdYsvO0ltiT2L/GY+p+4+n/td8Q7qzWkGovkIlPI.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '3.83.9.181' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
__| __|_ )
_| ( / Amazon Linux 2 AMI
___|\___|___|
https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-2/
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-83-218 ~]$
2.3 Installing Apache Server
Install httpd(Apache HTTP Server) in EC2 instance.
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-83-218 ~]$ sudo su
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 ec2-user]# yum update -y
Loaded plugins: extras_suggestions, langpacks, priorities, update-motd
amzn2-core | 2.4 kB 00:00:00
No packages marked for update
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 ec2-user]# yum install httpd -y
Create an html page under /var/www/html with the following content.
<html>
<h1>Hello Johnny from EC2!</h1>
</html>
Then start the Apache server.
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 ec2-user]# cd /var/www/html
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 html]# nano index.html
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 html]# ls
index.html
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 html]# service httpd start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start httpd.service
[root@ip-172-31-83-218 html]# chkconfig on
2.4 Testing the Static Site
Visit the public ip address of EC2 instance(eg. 3.83.9.181) or http://3.83.9.181/index.html in web browser. The web page is shown properly.
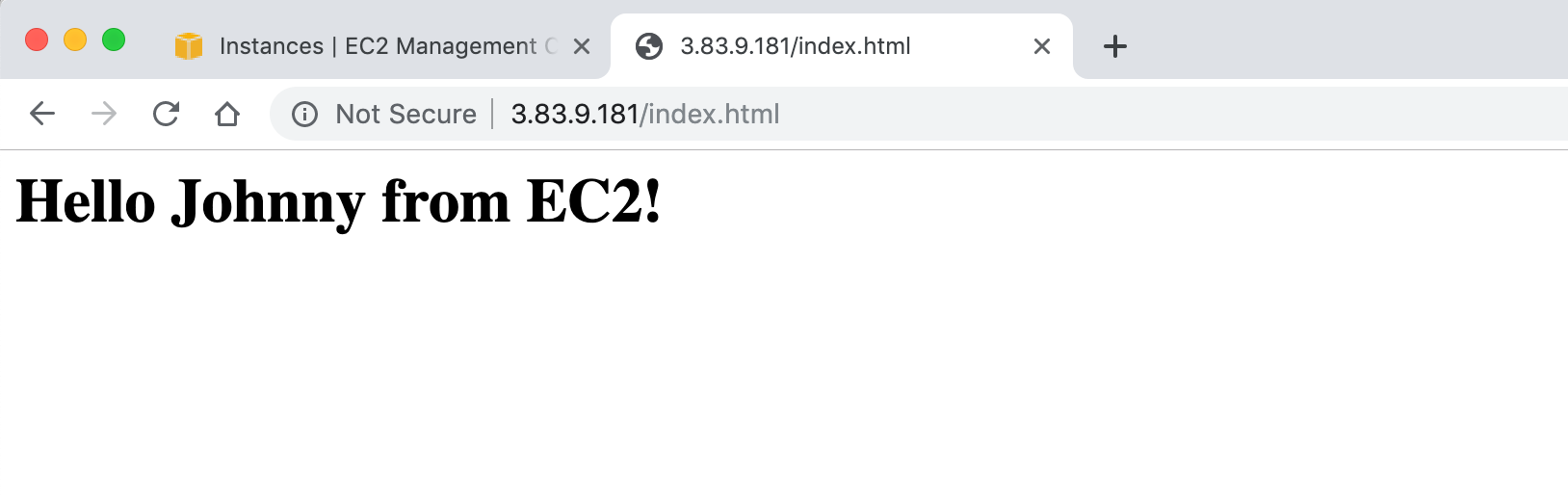
2.5 Summary
- Termination Protection is turned off by default, you must turn it on.
- On an EBS-backed instance, the default action is for the root EBS volume to be deleted when the instance is terminated.
- EBS Root Volumes of your DEFAULT AMI’s cannot be encrypted. You can also use a third party tool (such as bit locker etc) to encrypt the root volume, or this can be done when creating AMIs in the AWS console or using the API.
- Additional volumes can be encrypted.
3. Security Groups
A security group acts as a virtual firewall for your instance to control inbound and outbound traffic. When you launch an instance in a VPC, you can assign up to five security groups to the instance. Security groups act at the instance level, not the subnet level. Therefore, each instance in a subnet in your VPC can be assigned to a different set of security groups.
If you launch an instance using the Amazon EC2 API or a command line tool and you don’t specify a security group, the instance is automatically assigned to the default security group for the VPC. If you launch an instance using the Amazon EC2 console, you have an option to create a new security group for the instance.
For each security group, you add rules that control the inbound traffic to instances, and a separate set of rules that control the outbound traffic. This section describes the basic things that you need to know about security groups for your VPC and their rules.
3.1 Security Group Basics
The following are the basic characteristics of security groups for your VPC:
- You can specify allow rules, but not deny rules.
- All Inbound traffic is blocked by default.
- All Outbound traffic is allowed.
- Changes to Security Groups take effect immediately.
- You can have any number of EC2 instances within a security group.
- You can have multiple security groups attached to EC2 Instances.
- Security Groups are stateful.
- If you create an inbound rule allowing traffic in, that traffic is automatically allowed back out again.
- You cannot block specific IP addresses using Security Groups, instead use Network Access Control Lists.
3.2 Security Group on Instance
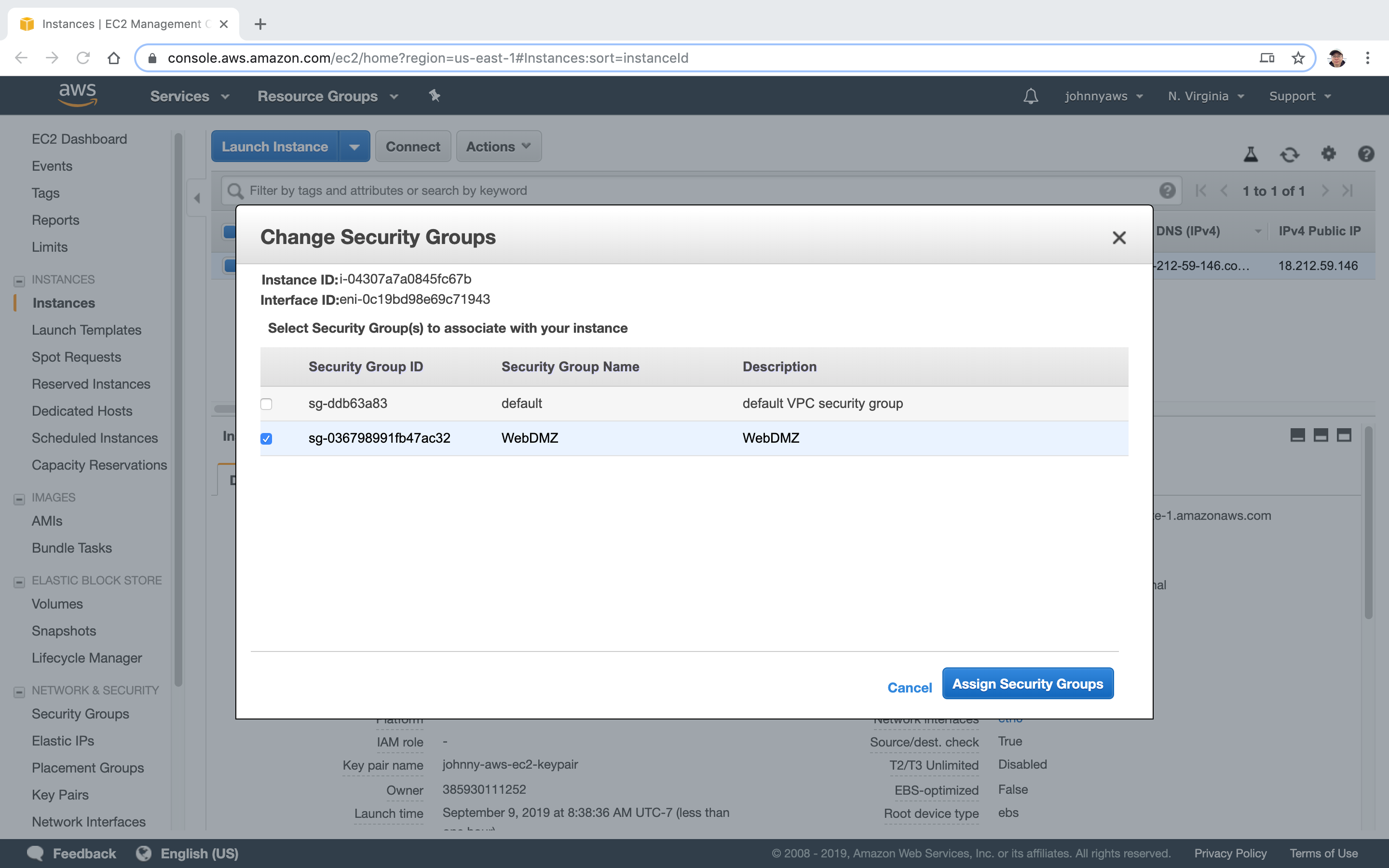
Select the EC2 instance, you will see the assigned security groups.
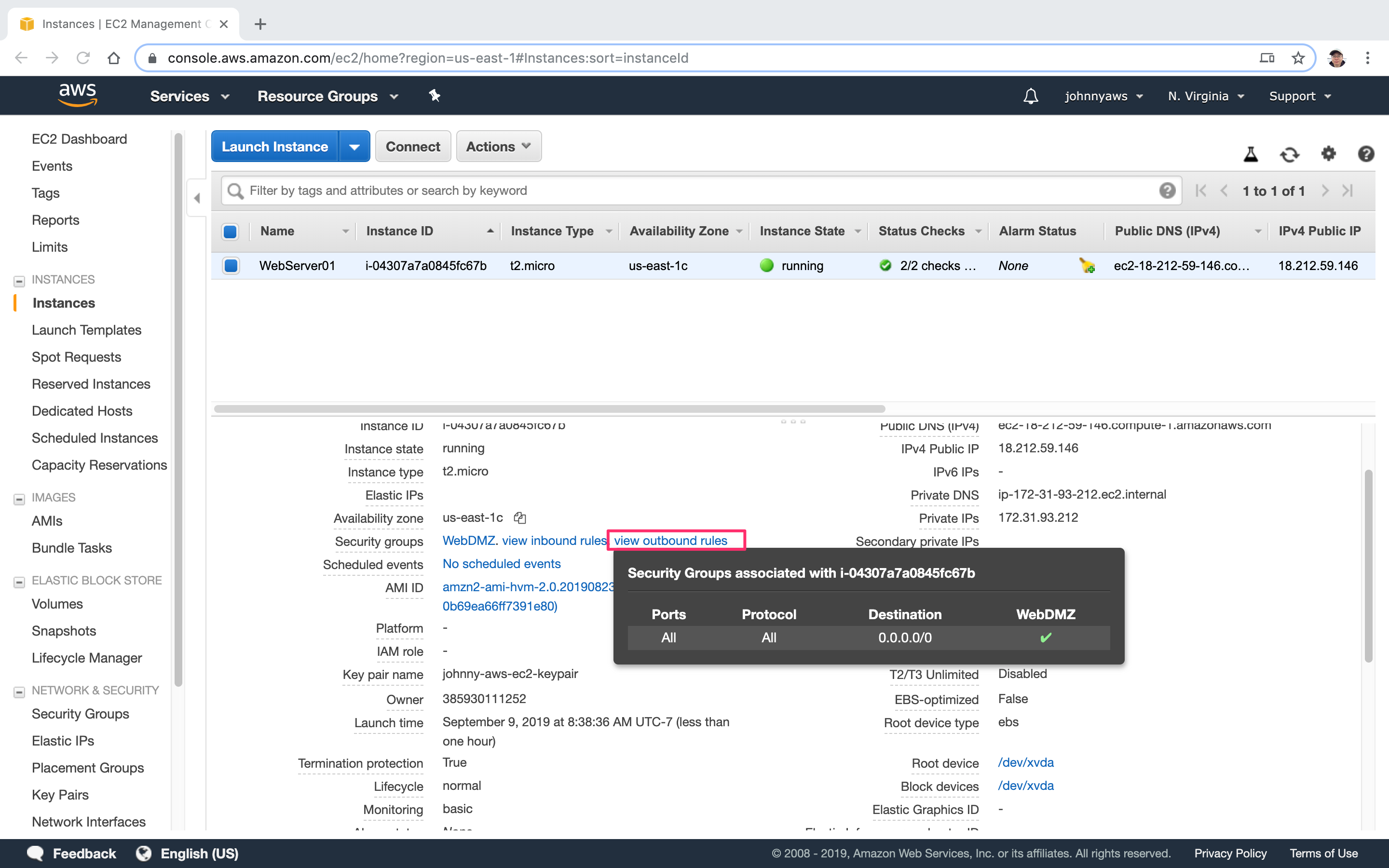 You can have multiple security groups attached to EC2 instance. (Instance->Actions->NetWorking->Change Security Groups)
You can have multiple security groups attached to EC2 instance. (Instance->Actions->NetWorking->Change Security Groups)