4126. AWS-EC2-User Data and MetadataAWS, EC2, User Data, and Metadata
Launch instance with User Data.
1. Instance User Data
1.1 Running Commands with User Data
When you launch an instance in Amazon EC2, you have the option of passing user data to the instance that can be used to perform common automated configuration tasks and even run scripts after the instance starts. You can pass two types of user data to Amazon EC2: shell scripts and cloud-init directives. You can also pass this data into the launch wizard as plain text, as a file (this is useful for launching instances using the command line tools), or as base64-encoded text (for API calls).
1.2 User data and shell scripts
If you are familiar with shell scripting, this is the easiest and most complete way to send instructions to an instance at launch. Adding these tasks at boot time adds to the amount of time it takes to boot the instance. You should allow a few minutes of extra time for the tasks to complete before you test that the user script has finished successfully.
2. Lab - User Data
2.1 Launch Instance with User Data
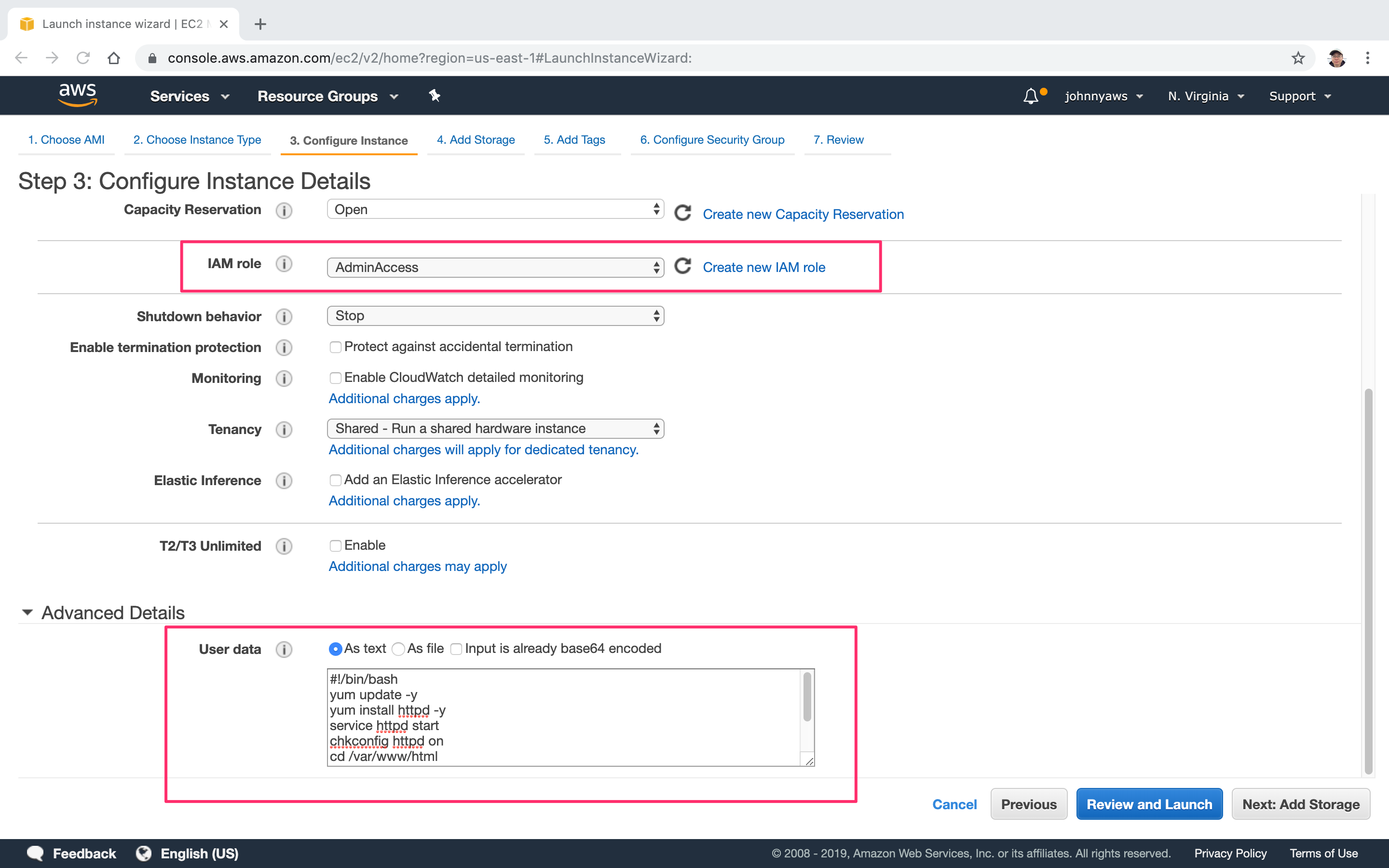
Launch new instance. In the step of “Configure Instance”, select the role created in previous blog for IAM roles. Copy the following script. This shell script will install httpd service(Apache Server) and start it, then create an html page. Later, create an S3 bucket and copy the html file into the bucket.
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install httpd -y
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
echo 'Hello Johnny, Welcome To My Webpage' > index.html
aws s3 mb s3://johnny-aws-guru-s3-bootstrap-01
aws s3 cp index.html s3://johnny-aws-guru-s3-bootstrap-01
Paste the script into the user data text box.
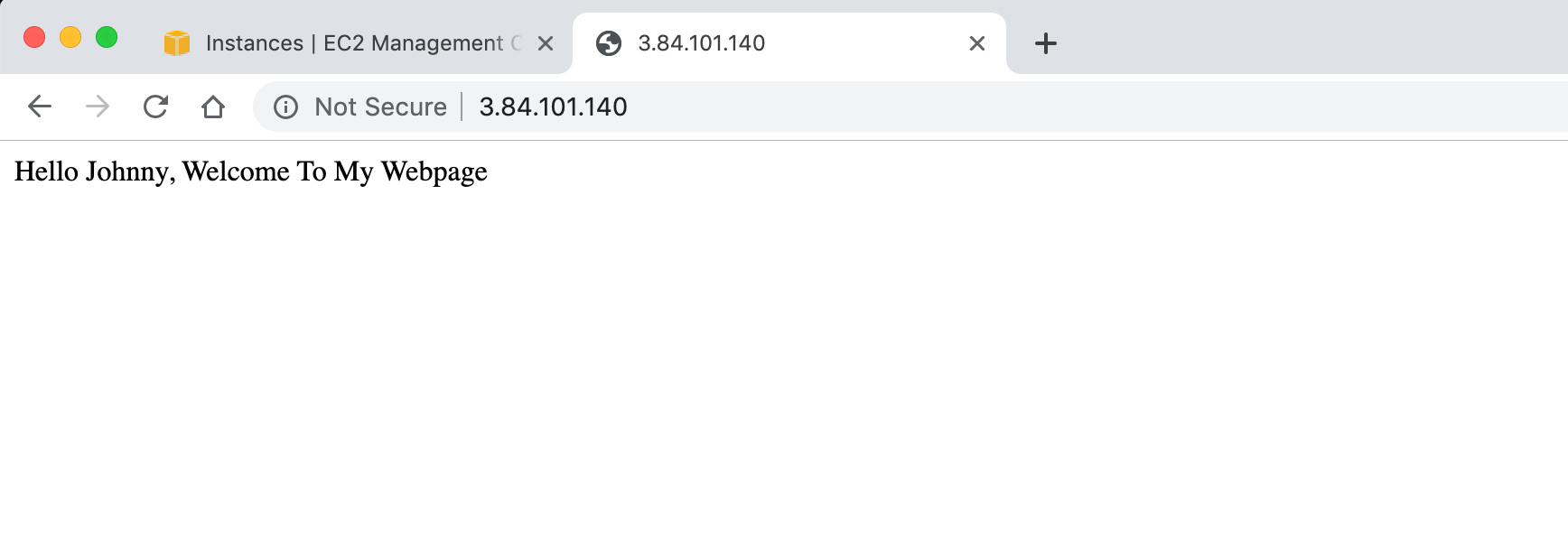
 After the instance is launched successfully, access its public ip address, we should see the web page.
After the instance is launched successfully, access its public ip address, we should see the web page.
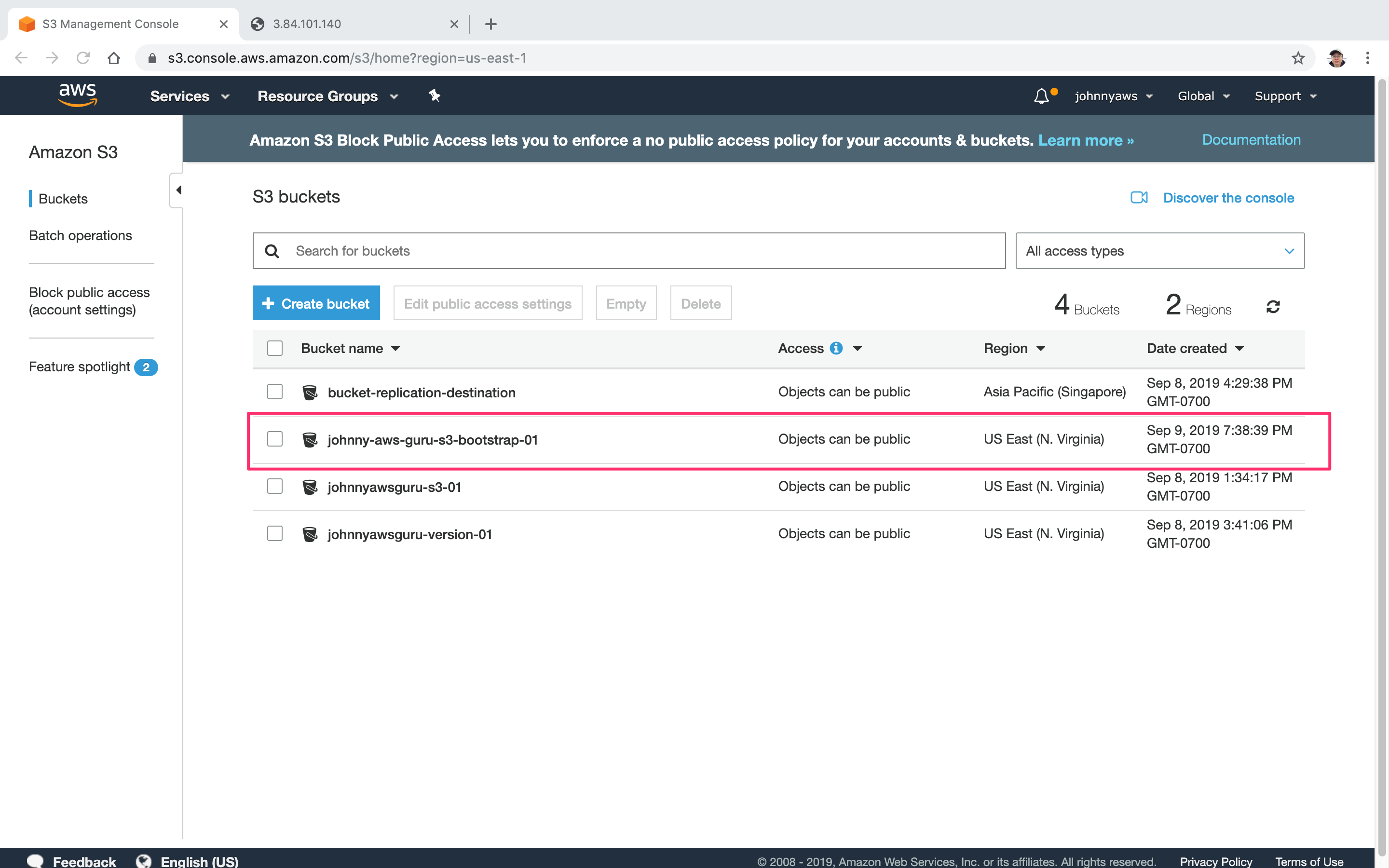
2.2 Checking the S3 Bucket
We will see the new S3 bucket.
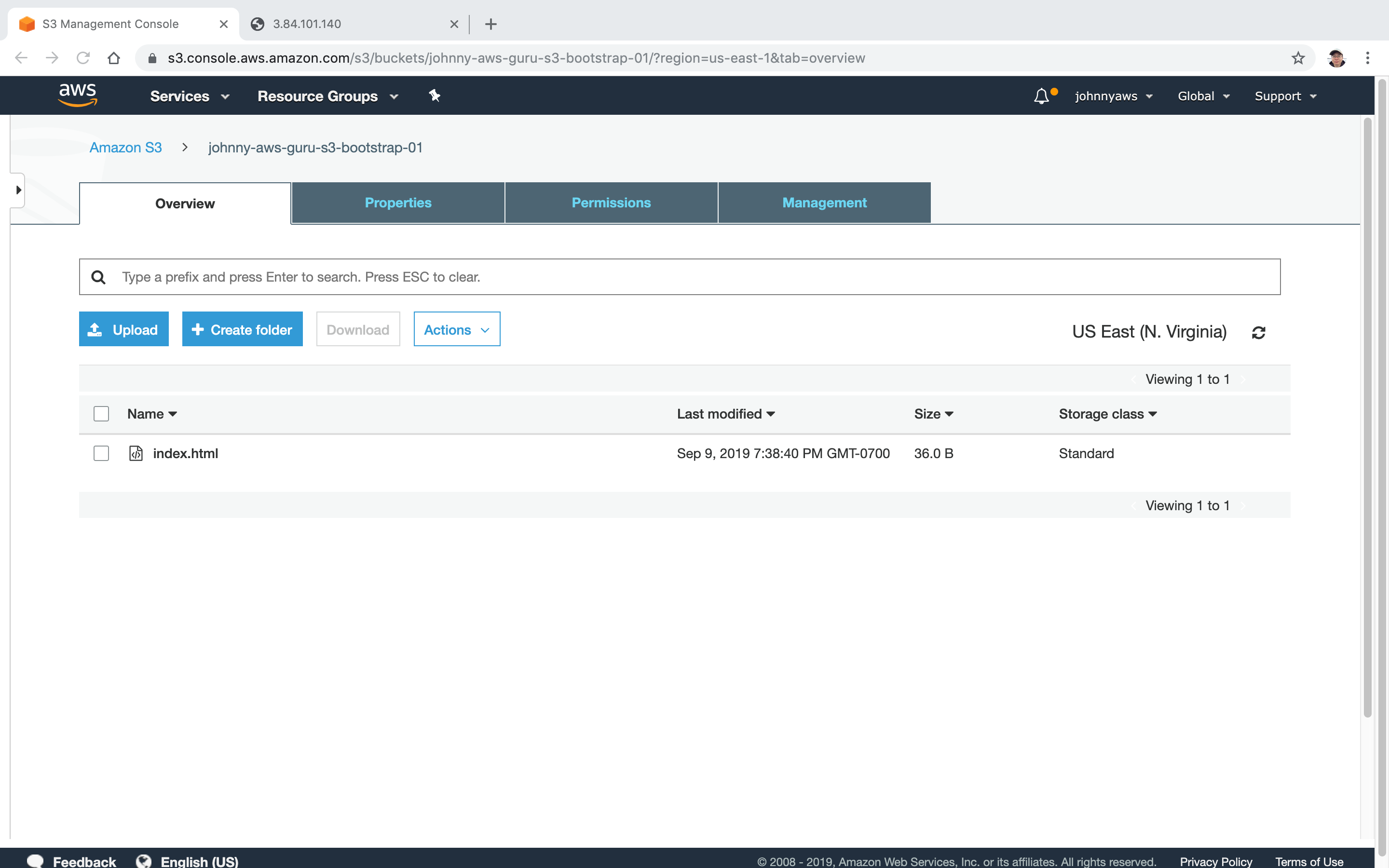
 The index.html file is copied to this bucket.
The index.html file is copied to this bucket.
3. Instance Metadata
3.1 Instance Metadata
Instance metadata is data about your instance that you can use to configure or manage the running instance. Instance metadata is divided into categories, for example, host name, events, and security groups.
3.2 Accessing Metadata and User Data
You can only access instance metadata and user data from within the instance itself. Use the following two commands to get user data and meta data. The IP address 169.254.169.254 is a link-local address and is valid only from the instance.
- curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data/
- curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/
Remote connect to EC2 instance through ssh, then run the following command to get the user data.
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data/
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install httpd -y
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
echo 'Hello Johnny, Welcome To My Webpage' > index.html
aws s3 mb s3://johnny-aws-guru-s3-bootstrap-01
aws s3 cp index.html s3://johnny-aws-guru-s3-bootstrap-01
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]#
Run the following command to get the public IP address of the current instance.
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4
3.84.101.140
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]#
We can also save user data and metadata into files.
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data/ > bootstrap.bash
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 281 100 281 0 0 56200 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 56200
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# ls
bootstrap.bash
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4 > public-ip.txt
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 12 100 12 0 0 2400 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 2400
[root@ip-172-31-94-19 ec2-user]# ls
bootstrap.bash public-ip.txt