2323. Java Core - SocketSocket, TCP, and UDP
Use socket to communicate through TCP and UDP between applications.
1. Socket
Sockets provide the communication mechanism between two computers. A client program creates a socket on its end of the communication and attempts to connect that socket to a server.
There are two common network protocols: TCP and UDP.
1.1 TCP
TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol, which allows for reliable communication between two applications. TCP is typically used over the Internet Protocol, which is referred to as TCP/IP.
1.2 UDP
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol, a connection-less protocol that allows for packets of data to be transmitted between applications.
2. TCP Example
We will create two programs with java sockets. One acts as client, another acts as server. The TCP client receives input from user, and sends it to TCP server. TCP server receives request(string) from client, converts it to upper case and sends back to the client. Finally, client displays the response(upper case string) to the screen.
2.1 Creating TCP Server
Create a file named TCPServer.java with following content.
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TCPServer {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
int port = 8722;
Socket socket = null;
BufferedReader reader = null; // Local reader from the client
PrintStream outputStream = null; // Output stream to the client
String clientRequest = "";
String responseToClient = "";
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("TCP Server is starting up, listening at port " + port + ".");
while (true) {
// Get request from client
socket = ss.accept();
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
clientRequest = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("[TCPServer] Get request [" + clientRequest + "] from Client.");
// Send response to client
outputStream = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
responseToClient = clientRequest.toUpperCase();
outputStream.println(responseToClient);
System.out.println("[TCPServer] Send out response [" + responseToClient + "] to Client.");
}
}
}
2.2 Creating TCP Client
Create a file named TCPClient.java with following content.
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TCPClient {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String serverName = "localhost";
int port = 8722; // Same port number with the server
Socket socket = null;
PrintStream toServer = null;
BufferedReader fromServer = null;
System.out.println("TCP Client launched, using server: " + serverName + ", Port: " + port);
// Read from user input
BufferedReader inFromUser = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String userInput = "";
do {
System.out.print("Enter any string now, (quit) to end: ");
System.out.flush();
userInput = inFromUser.readLine();
if (userInput.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) {
break;
}
// Open a new socket connection to the server with the specified port number
socket = new Socket(serverName, port);
// Send user input to server
toServer = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
toServer.println(userInput);
System.out.println("[TCPClient] Send out user input [" + userInput + "] to Server.");
// Get response from server
fromServer = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String responseFromServer = fromServer.readLine();
System.out.println("[TCPClient] Get response [" + responseFromServer + "] from Server.");
} while (!userInput.equals("quit")); // End the client if 'quit' is an input
// Close connection
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
}
}
2.3 Compiling
Open terminal, navigate to the folder where these two java files locate. Use javac to compile them.
$ javac TCPServer.java
$ javac TCPClient.java
2.4 Testing
Launch TCP server with following command.
$ java TCPServer
TCP Server is starting up, listening at port 8722.
Open another terminal, launch TCP client.
$ java TCPClient
TCP Client launched, using server: localhost, Port: 8722
Enter any string now, (quit) to end:
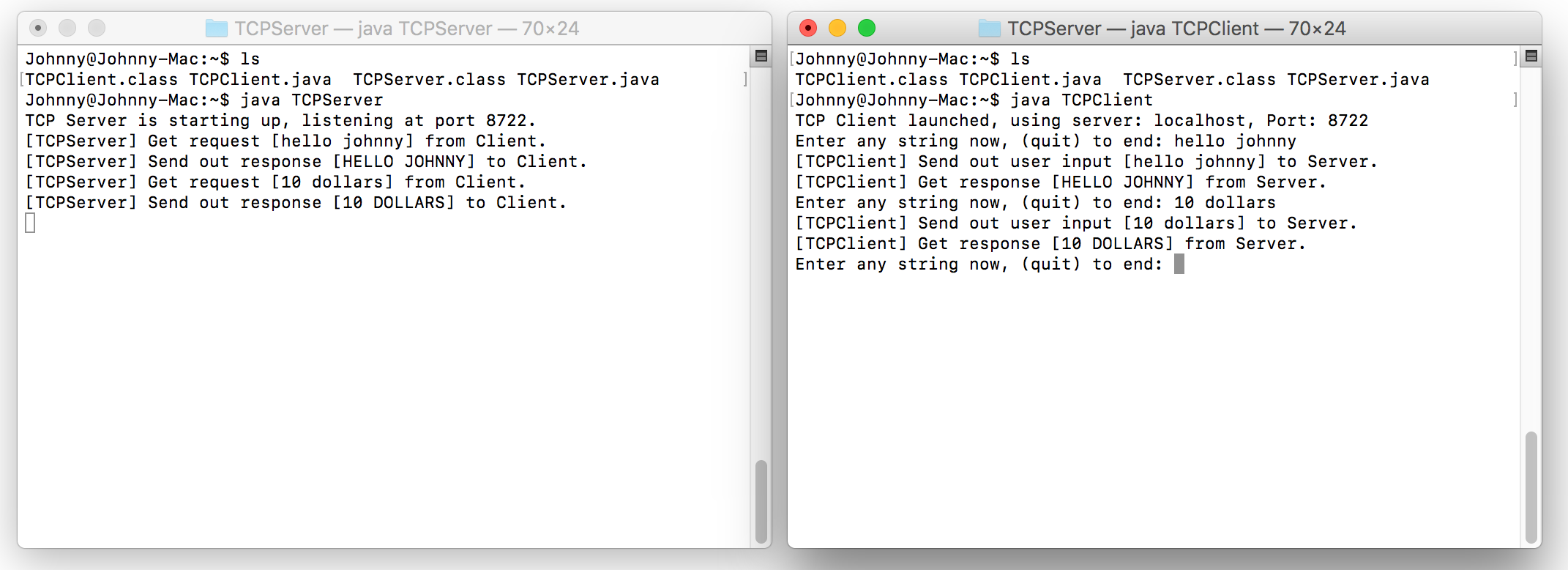
In the terminal for TCP Client(Right one of the following screenshot), input any string and Enter. You will see the response from TCP Server.
3. UDP Example
Create UDP Server and UDP Client with same function as TCP Server and TCP Client.
3.1 Creating UDP Server
Create a file named UDPServer.java with following content.
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
int port = 8722; // Same port number with the server
Socket socket = null;
DatagramSocket serverSocket = new DatagramSocket(port);
byte[] receiveData = new byte[1024];
byte[] sendData = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("UDP Server is starting up, waiting for request...");
while(true) {
receiveData = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket receivePacket = new DatagramPacket(receiveData, receiveData.length);
serverSocket.receive(receivePacket);
// get actual date with proper length
byte[] actualData = new byte[receivePacket.getLength()];
System.arraycopy(receivePacket.getData(), receivePacket.getOffset(),
actualData, 0, receivePacket.getLength());
String clientInput = new String(actualData);
System.out.println("[UPDServer] Received input [" + clientInput + "] from Client.");
// Find the ip address and port of sender
InetAddress IPAddress = receivePacket.getAddress();
port = receivePacket.getPort();
String responseToClient = clientInput.toUpperCase();
sendData = responseToClient.getBytes();
// Define upd package
DatagramPacket sendPacket = new DatagramPacket(sendData, sendData.length, IPAddress, port);
// Send
serverSocket.send(sendPacket);
System.out.println("[UPDServer] Send out response [" + responseToClient + "] to Client.");
}
}
}
3.2 Creating UDP Client
Create a file named UDPClient.java with following content.
public class UDPClient {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String serverName = "localhost";
int port = 8722; // Same port number with the server
byte[] sendData = new byte[1024];
byte[] receiveData = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("UPD Client launched, using server: " + serverName + ", Port: " + port);
BufferedReader inFromUser = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
DatagramSocket clientSocket = new DatagramSocket();
InetAddress IPAddress = InetAddress.getByName(serverName);
String userInput = "";
do {
userInput = "";
System.out.print("Enter any string now, (quit) to end: ");
System.out.flush();
userInput = inFromUser.readLine();
if (userInput.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) {
break;
}
sendData = userInput.getBytes();
// Define upd package and send to server
DatagramPacket sendPacket = new DatagramPacket(sendData, sendData.length, IPAddress, port);
clientSocket.send(sendPacket);
System.out.println("[UDPClient] Send out user input [" + userInput + "] to Server.");
//
DatagramPacket receivePacket = new DatagramPacket(receiveData, receiveData.length);
clientSocket.receive(receivePacket);
// get actual date with proper length
byte[] actualData = new byte[receivePacket.getLength()];
System.arraycopy(receivePacket.getData(), receivePacket.getOffset(),
actualData, 0, receivePacket.getLength());
String responseFromServer = new String(actualData);
System.out.println("[UDPClient] Get response [" + responseFromServer + "] from Server.");
} while (!userInput.equals("quit")); // End the client if 'quit' is an input
// Close connection
if (clientSocket != null) {
clientSocket.close();
}
}
}
3.3 Compiling
Open terminal, navigate to the folder where these two java files locate. Use javac to compile them.
$ javac UDPServer.java
$ javac UDPClient.java
3.4 Testing
Launch UDP server with following command.
$ java UDPServer
UDP Server is starting up, waiting for request...
Open another terminal, launch UDP client.
$ java UDPClient
UDP Client launched, using server: localhost, Port: 8722
Enter any string now, (quit) to end:
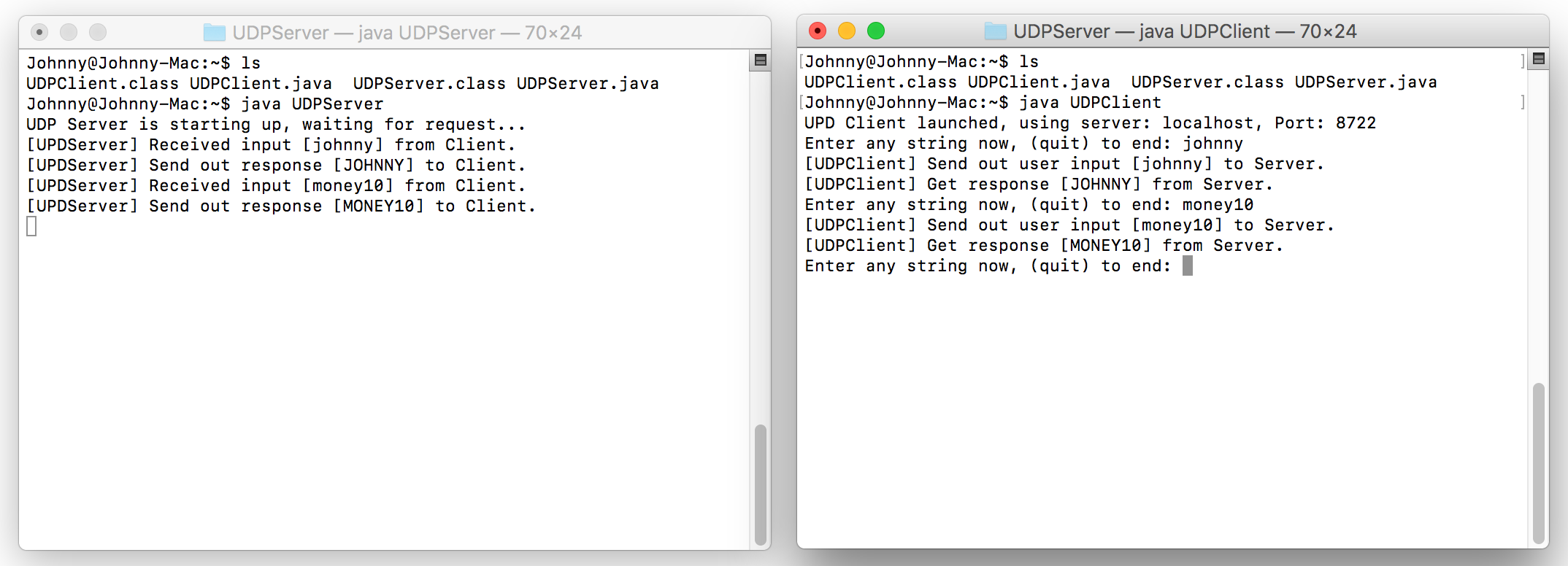
In the terminal for UDP Client(Right one of the following screenshot), input any string and Enter. You will see the response from UDP Server.