2033. Using MongoDB in ShellMongoDB and CRUD
Tutorial for introducing how to create database, collection and documents in MongoDB.
1. Start MongoDB
Start MongoDB service.
$ sudo service mongod start // linux
$ brew services start mongodb // macOS
Launch MongoDB Shell with mongo command.
$ mongo
>
To exit the Shell, type quit() or use the <Ctrl+C> shortcut.
> quit()
2. Database
2.1 Show Existing Database
Check the current databases with show dbs command.
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
2.2 Create Database
Create a database named mymdb with use <DATABASE> command.
> use mymdb
switched to db mymdb
To check your currently selected database, use the command db.
> db
mymdb
If you use show dbs command to show the databases, mymdb is not present in list. To display the database, you need to insert at least one document into it.
> db.mymdb.insert({"name":"iPhone 8"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
mymdb 0.000GB
2.3 Drop Database
Delete database mymdb with db.dropDatabase() command.
> use mymdb
switched to db mymdb
> db.dropDatabase()
{ "dropped" : "mymdb", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
3. User
3.1 Adding a User to Database
Create user who will have both read and write privileges to the database.
> use mymdb
switched to db mymdb
> db.createUser({'user':'testuser', 'pwd':'abc123', roles:['readWrite']});
Successfully added user: { "user" : "testuser", "roles" : [ "readWrite" ] }
Create user who will have read-only access to the database.
db.createUser({'user':'testuser', 'pwd':'abc123', roles:['read']});
3.2 Connecting Database with the New User
Syntax:
mongo -u 'username' -p 'password' <servername>/databasename
Example:
$ mongo -u 'testuser' -p 'abc123' localhost:27017/mymdb
MongoDB shell version v3.4.10
connecting to: mongodb://localhost:27017/mymdb
4. Collection
4.1 Syntax of Creating Collection
Basic syntax of creating new collection in MongoDB.
db.createCollection(name, options)
Option list:
- capped: If true, enables a capped collection. Capped collection is a fixed size collection that automatically overwrites its oldest entries when it reaches its maximum size. If you specify true, you need to specify size parameter also.
- autoIndexId: If true, automatically create index on _id field.s Default value is false.
- size: Specifies a maximum size in bytes for a capped collection. If capped is true, then you need to specify this field also.
- max: Specifies the maximum number of documents allowed in the capped collection.
4.2 Creating Collection Without Options
Create database named store and collection named product.
> use store
switched to db store
> db.createCollection("product")
{ "ok" : 1 }
Check the created collection with show collection command.
> show collections
product
4.3 Creating Collection With Options
Create collection named productOptions with explicit options.
>db.createCollection("productOptions", { capped : true, autoIndexId : true, size : 2000000, max : 10000 } )
{ "ok" : 1 }
Check the collection list.
> show collections
product
productOptions
4.4 Creating Collection Implicitly
Collection named productImplicit is created automatically, when document is inserted into it.
> db.productImplicit.insert({"name":"iPhone 8"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> show collections
product
productImplicit
productOptions
>
4.5 Dropping Collection
Drop a collection from the database store with db.<Collection>.drop() command.
> use store
switched to db store
> db.productImplicit.drop()
true
> show collections
product
productOptions
>
5. Document
5.1 Creating Document
Syntax for creating document.
db.<Collection>.insert(document)
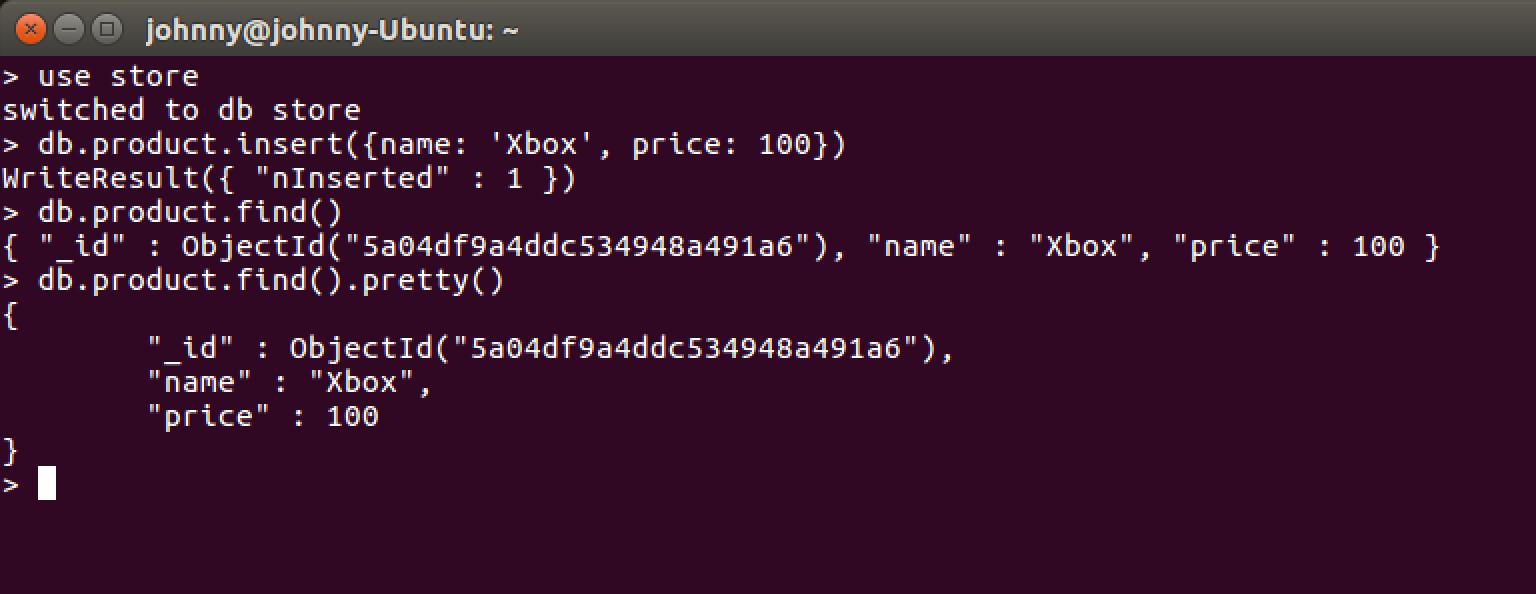
Create a document with two attributes in collection product.
> db.product.insert({name: 'Xbox', price: 100})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
Use db.<Collection>.find() command to show the documents.
> db.product.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"), "name" : "Xbox", "price" : 100 }
Use pretty() command to show the documents in a formatted way.
> db.product.find().pretty()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"),
"name" : "Xbox",
"price" : 100
}
>
You can also insert multiple documents by passing an array of documents in insert method.
> db.product.insert([{name: 'PS4',price: 400},{name: 'iPhone',price: 699}])
BulkWriteResult({
"writeErrors" : [ ],
"writeConcernErrors" : [ ],
"nInserted" : 2,
"nUpserted" : 0,
"nMatched" : 0,
"nModified" : 0,
"nRemoved" : 0,
"upserted" : [ ]
})
5.2 Updating Document
Syntax for updating document.
db.<Collection>.update(SELECTION_CRITERIA, UPDATED_DATA)
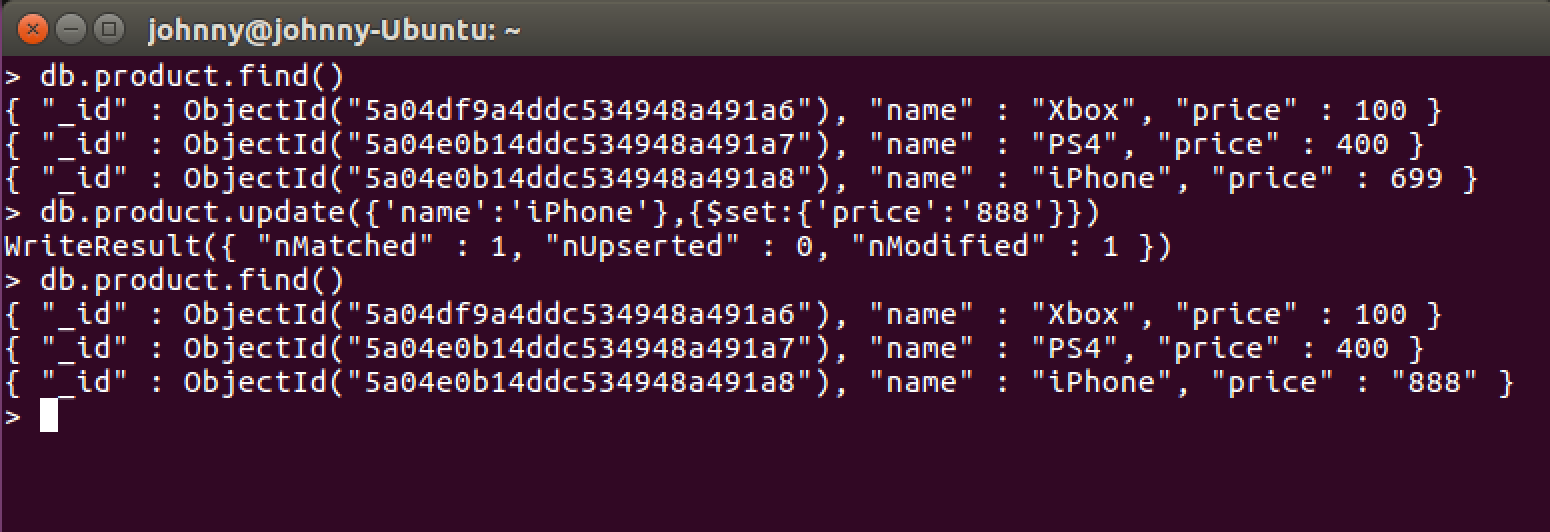
Check the existing documents.
> db.product.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"), "name" : "Xbox", "price" : 100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a7"), "name" : "PS4", "price" : 400 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a8"), "name" : "iPhone", "price" : 699 }
>
Update the price to ‘888’ for the product whose name is ‘iPhone’.
> db.product.update({'name':'iPhone'},{$set:{'price':'888'}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
Check the updated document.
> db.product.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"), "name" : "Xbox", "price" : 100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a7"), "name" : "PS4", "price" : 400 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a8"), "name" : "iPhone", "price" : "888" }
>
5.3 Deleting Document
Syntax for deleting document.
db.<Collection>.remove(DELLETION_CRITTERIA)
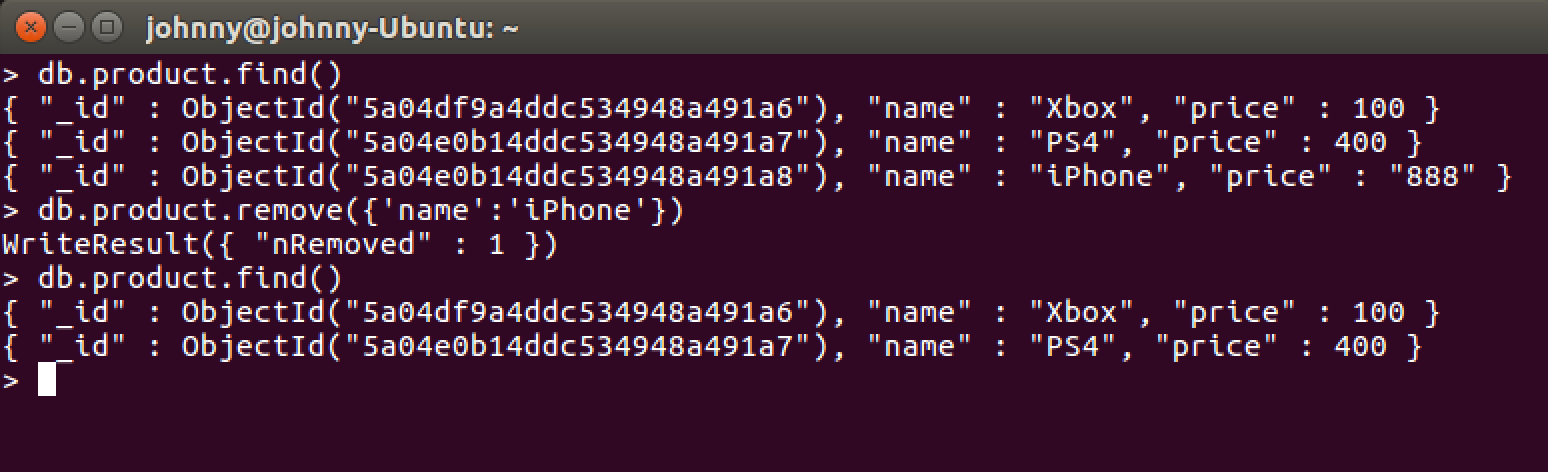
Check the existing documents.
> db.product.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"), "name" : "Xbox", "price" : 100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a7"), "name" : "PS4", "price" : 400 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a8"), "name" : "iPhone", "price" : "888" }
>
Delete the document whose name is ‘iPhone’.
> db.product.remove({'name':'iPhone'})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
Check the documents again.
> db.product.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04df9a4ddc534948a491a6"), "name" : "Xbox", "price" : 100 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a04e0b14ddc534948a491a7"), "name" : "PS4", "price" : 400 }
>
Specify ‘1’ in the delete method to delete only the first one if there are multiple records.
> db.<Collection>.remove(DELETION_CRITERIA,1)
Delete all documents if no deletion criteria is specified.
> db.<Collection>.remove()
6. Query In MongoDB
6.1 Finding Document
Display all the documents in collection.
> db.<Collection>.find()
Display all the documents in formatted way with pretty();
> db.<Collection>.find().pretty()
Return only one document from the collection.
> db.<Collection>.findOne()
6.2 Where Clause
Use following operations to query documents with some conditions.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equality | {<key>:<value>} | db.product.find({“name”:”iPhone”}) | where name = ‘iPhone’ |
| Less Than | {<key>:{$lt:<value>}} |
db.product.find({“price”:{$lt:400}}) | where price < 400 |
| Less Than Equals | {<key>:{$lte:<value>}} |
db.product.find({“price”:{$lte:400}}) | where price <= 400 |
| Greater Than | {<key>:{$gt:<value>}} |
db.product.find({“price”:{$gt:400}}) | where price > 400 |
| Greater Than Equals | {<key>:{$gte:<value>}} |
db.product.find({“price”:{$gte:400}}) | where price >= 400 |
| Not Equals | {<key>:{$ne:<value>}} |
db.product.find({“price”:{$ne:400}}) | where price != 400 |
6.3 AND in MongoDB
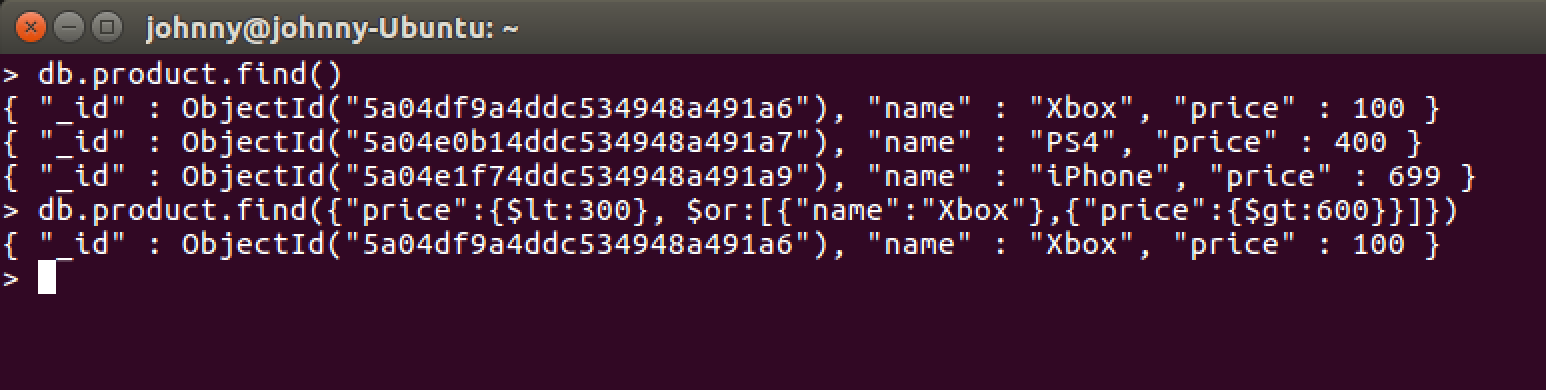
Find products whose price is greater than or equals to 400, and its price is less than 800.
> db.product.find({$and:[{"price":{$gte:400}},{"price":{$lt:800}}]})
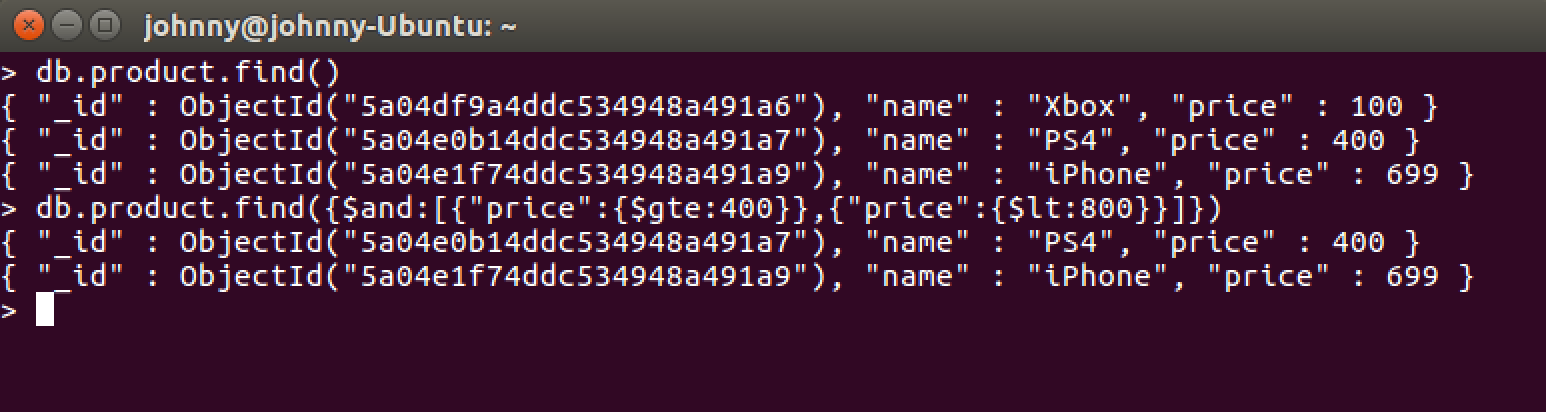
6.4 OR in MongoDB
Find products whose name is ‘Xbox’, or its price is greater than 600.
> db.product.find({$or:[{"name":"Xbox"},{"price":{$gt:600}}]})
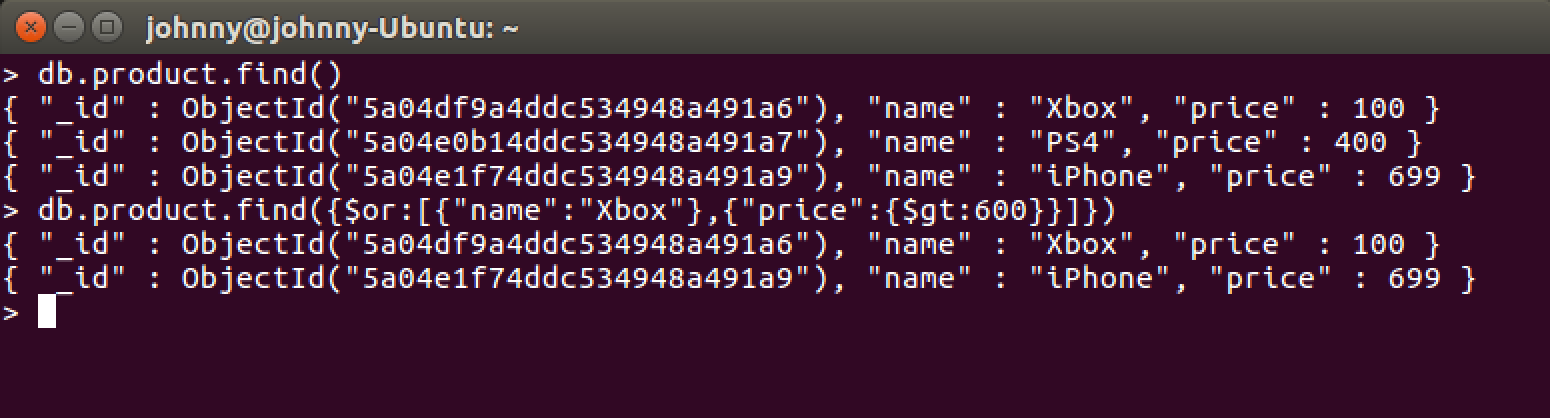
6.5 Using AND and OR Together
Find products whose name is ‘Xbox’, or its price is greater than 600, and its price is less than 300.
> db.product.find({"price":{$lt:300}, $or:[{"name":"Xbox"},{"price":{$gt:600}}]})