8532. Cross-platform Mobile Apps Development with XamarinXamarin, Visual Studio, Mono, and Xcode
Introduce how to setup mobile development environment with Xamarin on Mac.
1. Xamarin
Xamarin is based on Mono and .NET framework, written in C#. Xamarin enables developers to create cross-platform mobile apps for iOS and Android. The benefit by using Xamarin is obvious, the development and maintenance cost is reduced, since the common libraries can be centralized and reused by other components. For developers, they can focus on UI of iOS and Android once the lower business logic component is finalized.
2. Setup Xamarin Development Environment
There are three approaches to setup the Xamarin development environment. The choice depends on what mobile platform you want to deliver your app.
| OS | IDE and SDK | iOS | Android | Windows Phone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Only | Visual Studio, Android SDK | No | Yes | Yes |
| Windows + Mac | Visual Studio, Android SDK, Xcode | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mac Only | Xcode, Visual Studio, Android SDK | Yes | Yes | No |
2.1 Windows Only
On the Windows machine, install Visual Studio, Android SDK or Android Studio. For Android App development, you can install third party simulator. You can’t develop iOS App in this approach, since there is no iOS simulator.
2.2 Windows + Mac
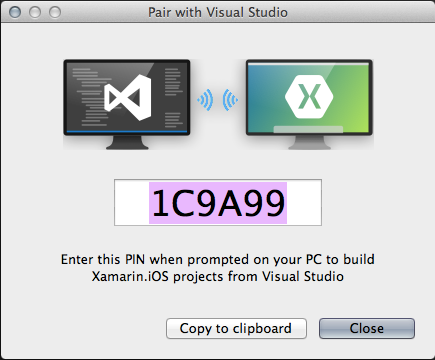
On the Windows machine, install Visual Studio, Android SDK or Android Studio. On the Mac machine, install Xcode and iOS simulator. For the iOS App development, you can code with Xamarin in VS on Windows, and send the app to simulator on Mac to see the result. The first step is to pair the Windows machine with the Mac machine.
For Android App development, both coding and simulation can be done through Visual Studio.
2.3 Mac Only
On the Mac machine, install Xcode, Visual Studio(Mac Version), Android SDK or Android Studio. For iOS and Android App development, coding and simulation can both be done in Visual Studio. You can’t develop Windows Phone App in this approach.
3. Installation
I choose the third approach to setup Xamarin development environment, since I like Mac and I don’t want to develop Windows Phone apps.
3.1 Installing Xcode
Go to App Store, search ‘xcode’, install.

3.2 Installing Visual Studio
Refer to Setting up .Net Development Environment on Mac to install Visual Studio on Mac.
3.3 Installing JDK and Android Studio
Refer to Setting up Android Development Environment on Mac to install JDK and Android Studio on Mac.
4. SDK Configuration in Visual Studio
4.1 iOS SDK
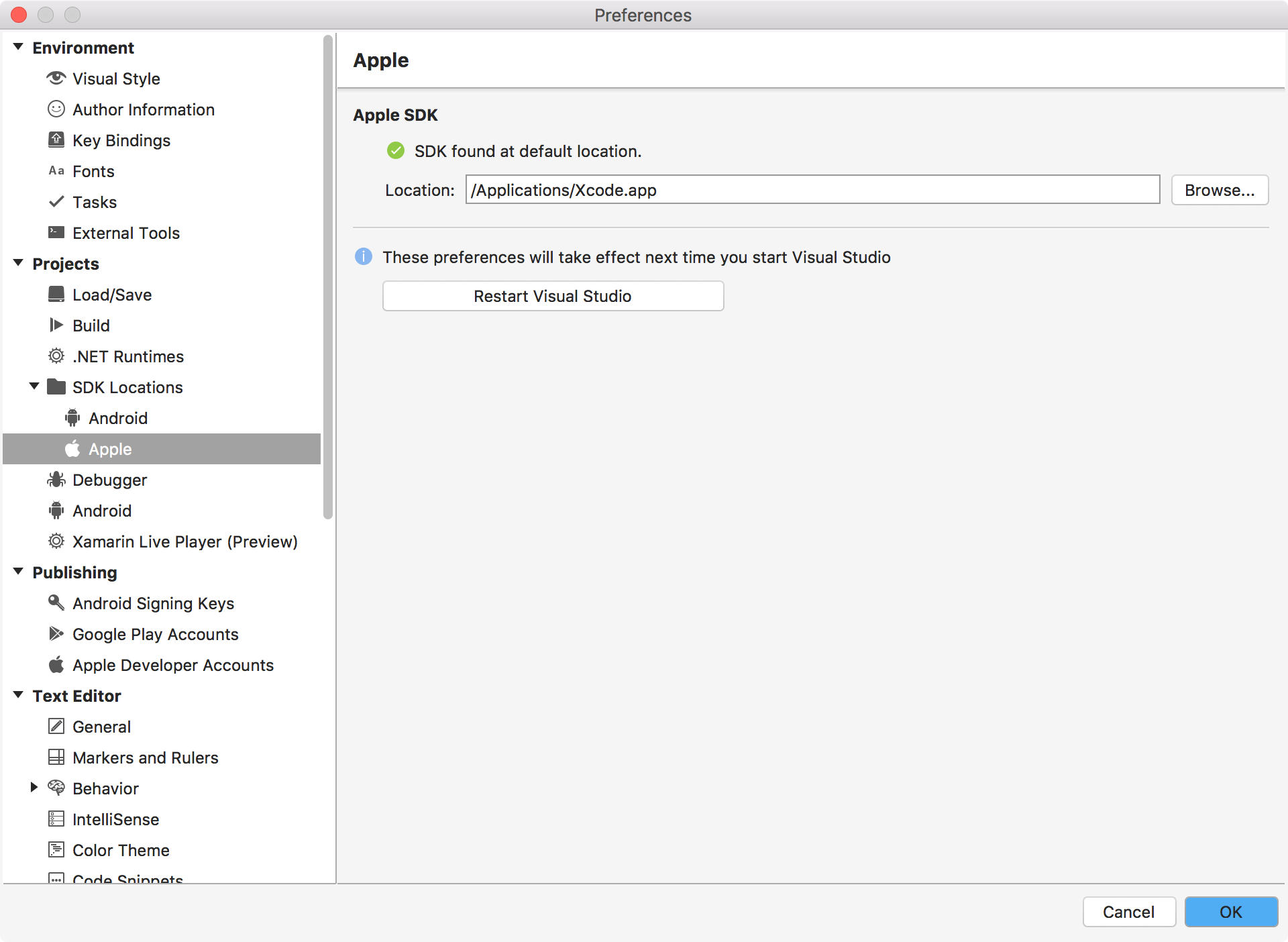
In Visual Studio, Tools->SDK Manager->Apple. The default path is the location of Xcode.
In the tool bar, the iOS simulator is available.
4.2 Android SDK
In Visual Studio, Tools->SDK Manager->Android. First, select the Android API versions.
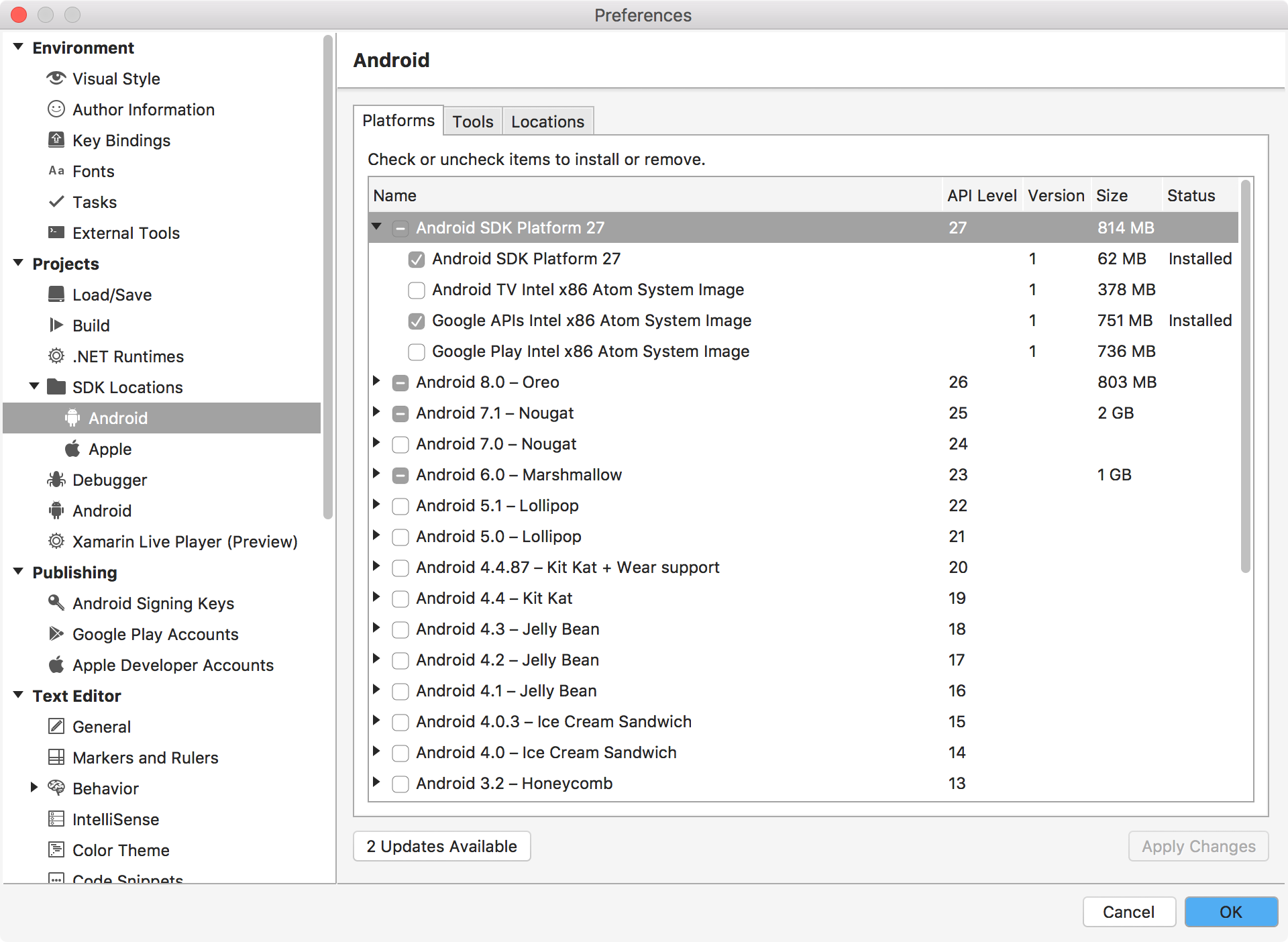
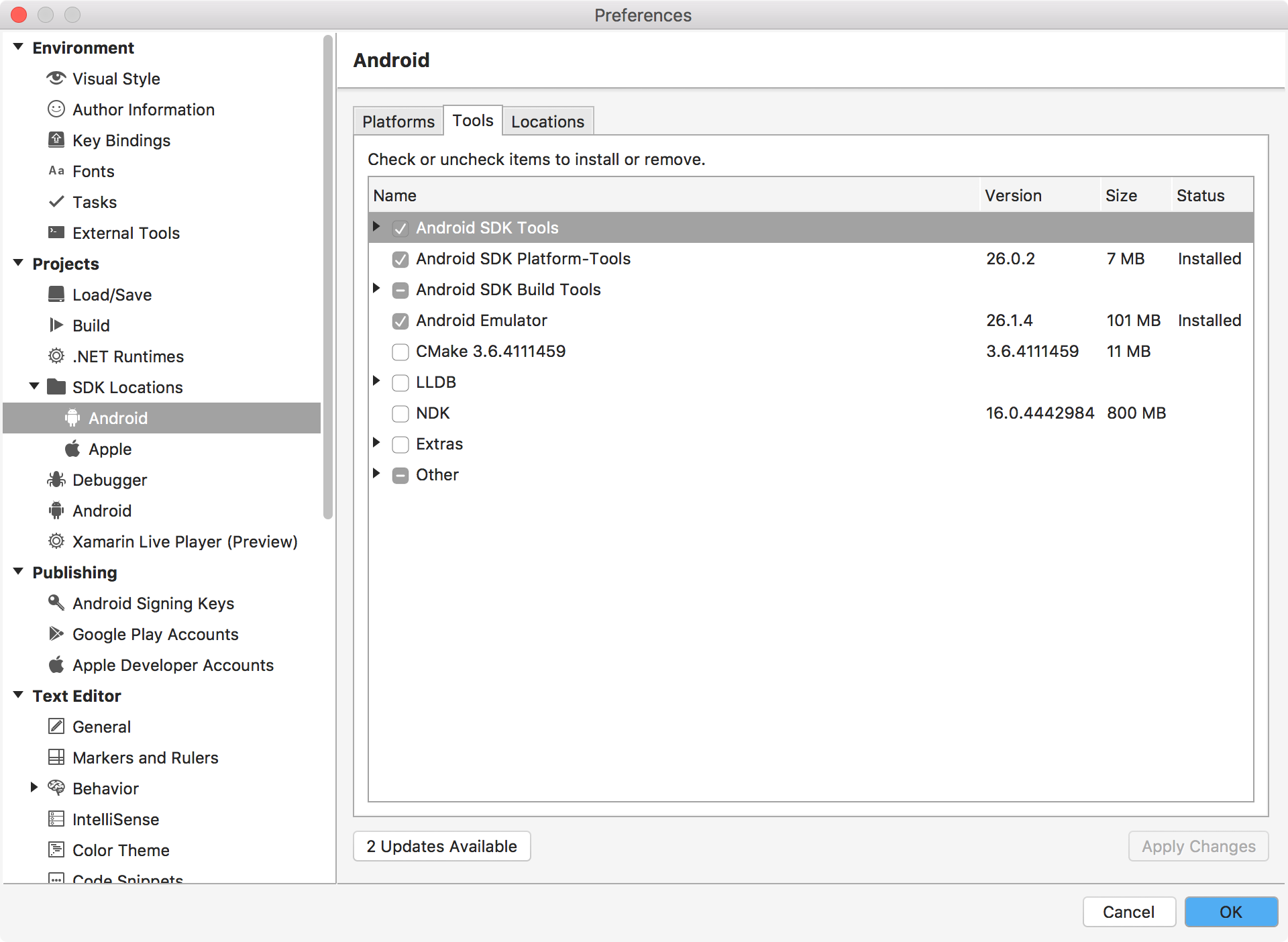
Second, choose the SDK Tools and Build Tools, Apply Changes.
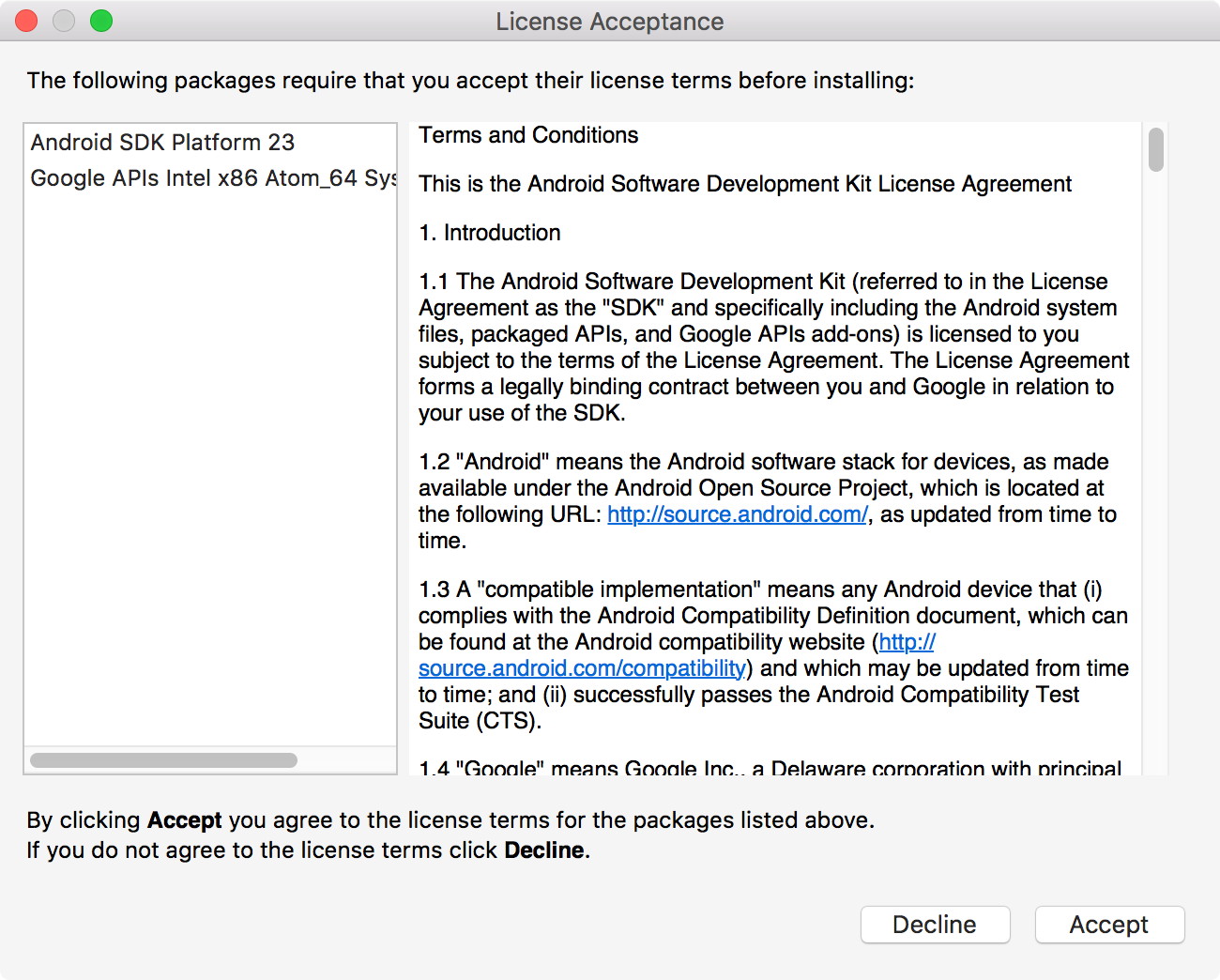
Accept the license, the selected items will be installed.
4.3 Android Emulator
In Visual Studio, Tools->Devices->Android. You can start or create Emulators.
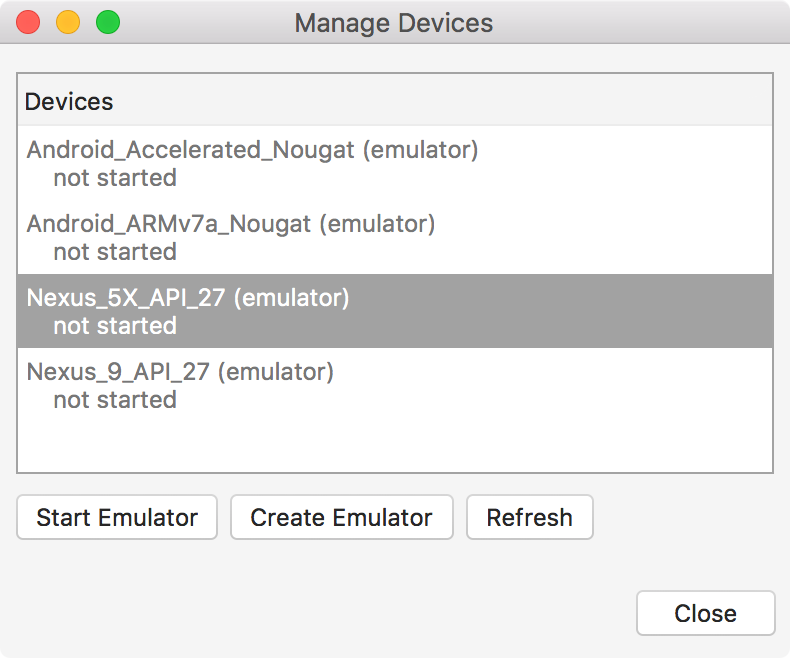
In Visual Studio, Tools->Devices->Create Emulator or Tools->Google Emulator Manager. You can create and start new AVD.
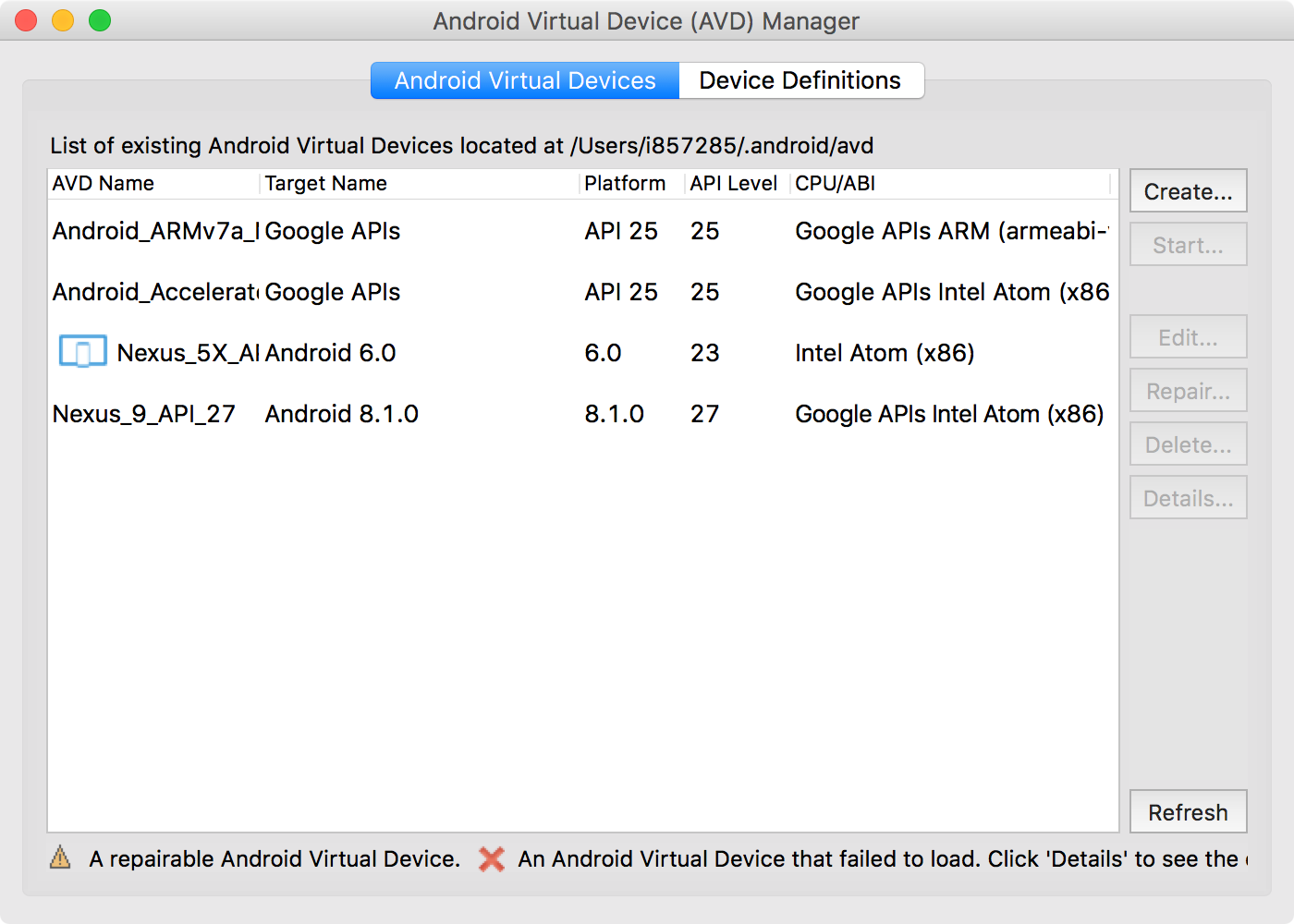
In the tool bar, the Android emulator is available.
5. Creating Xamarin Project
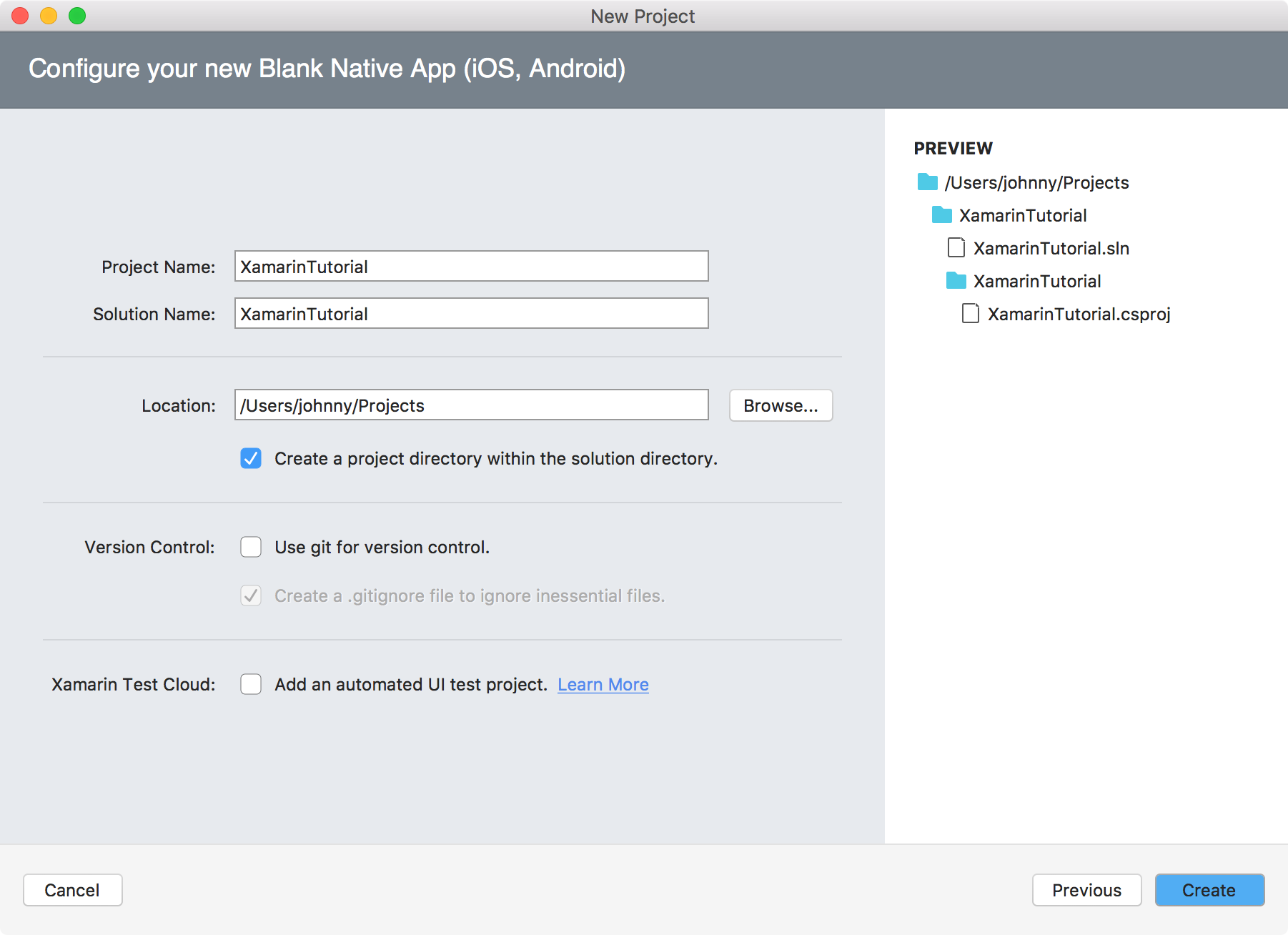
In Visual Studio, File->New Solution, select Multiplatform->App->Blank Native App(iOS, Android), Next.
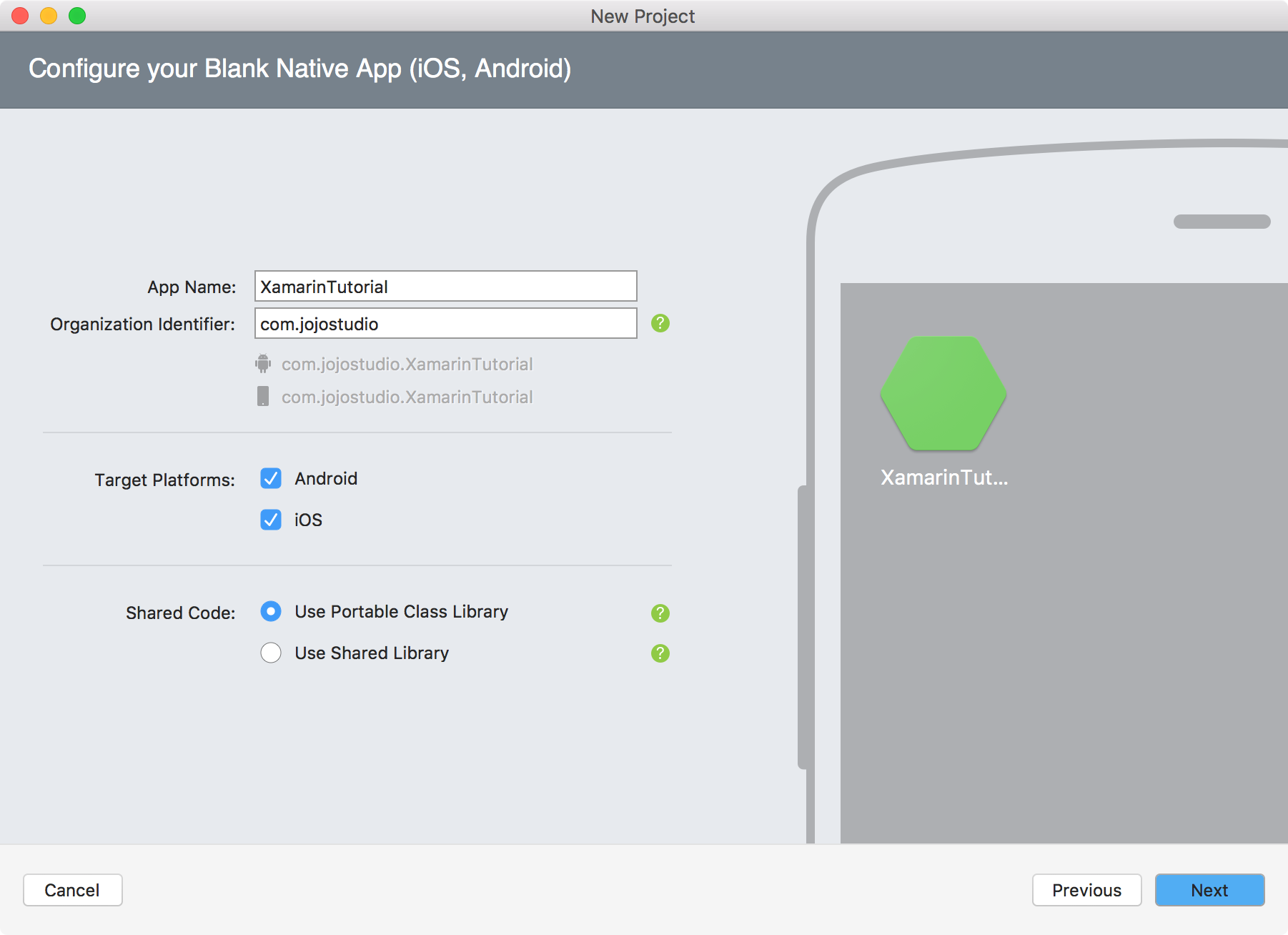
Specify the name and Organization Identifier, Next.
Specify the location where the source files will locate, Create.
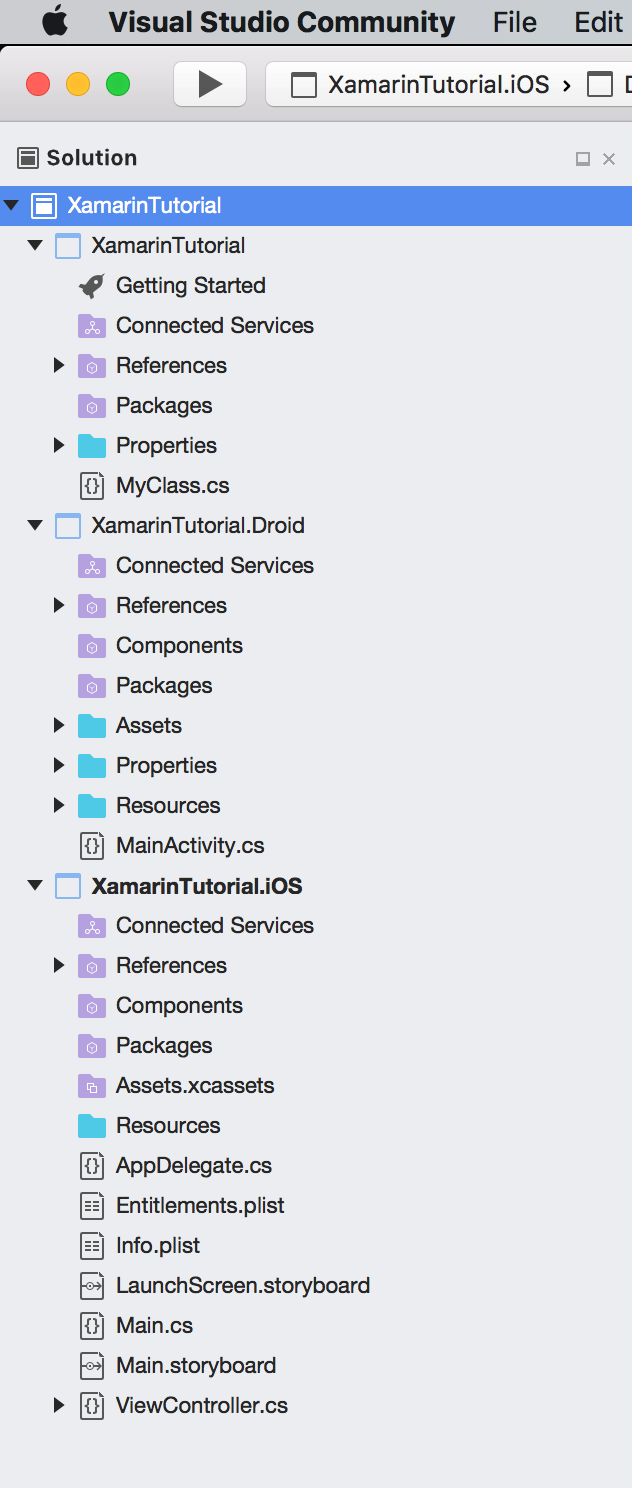
Three projects are created. ‘XamarinTutorial’ is a Portable .NET project, which contains common functions. ‘XamarinTutorial.Droid’ and ‘XamarinTutorial.iOS’ are responsible for UI, one for Android and another for iOS.
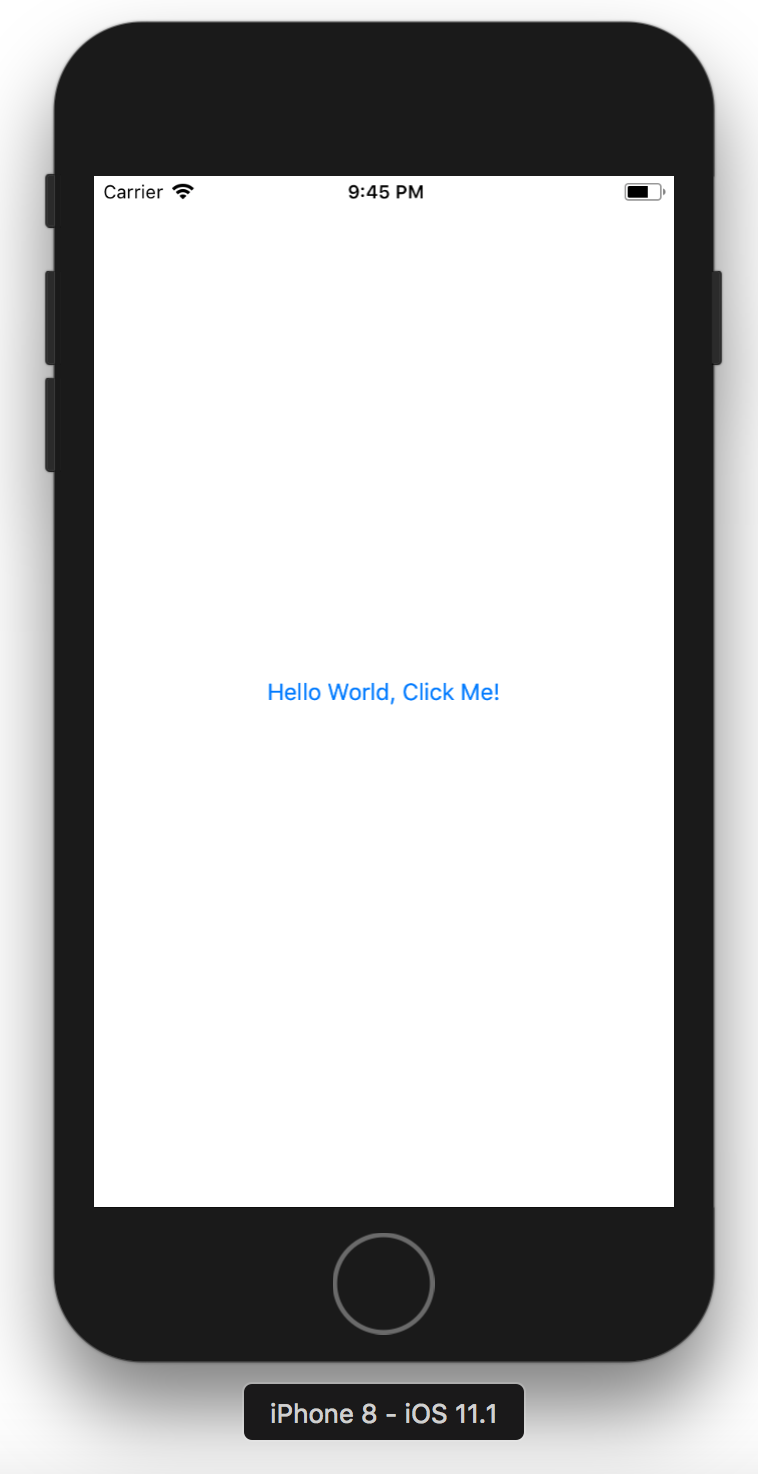
Right click on the ‘XamarinTutorial.iOS’ project, select ‘Set As Startup Project’ and Build. Then, run the app in simulator by clicking the Arrow button or Run->Start Without Debugging.
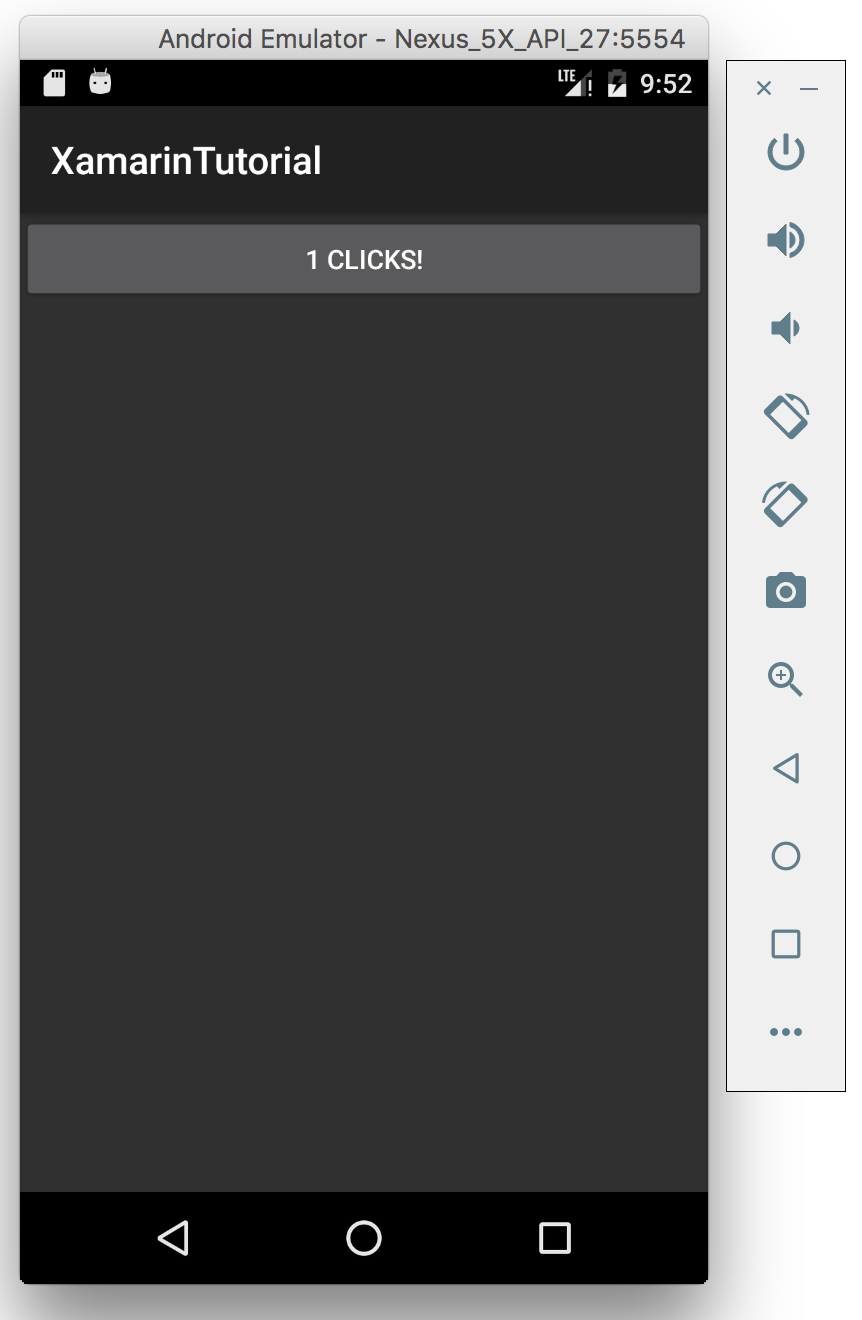
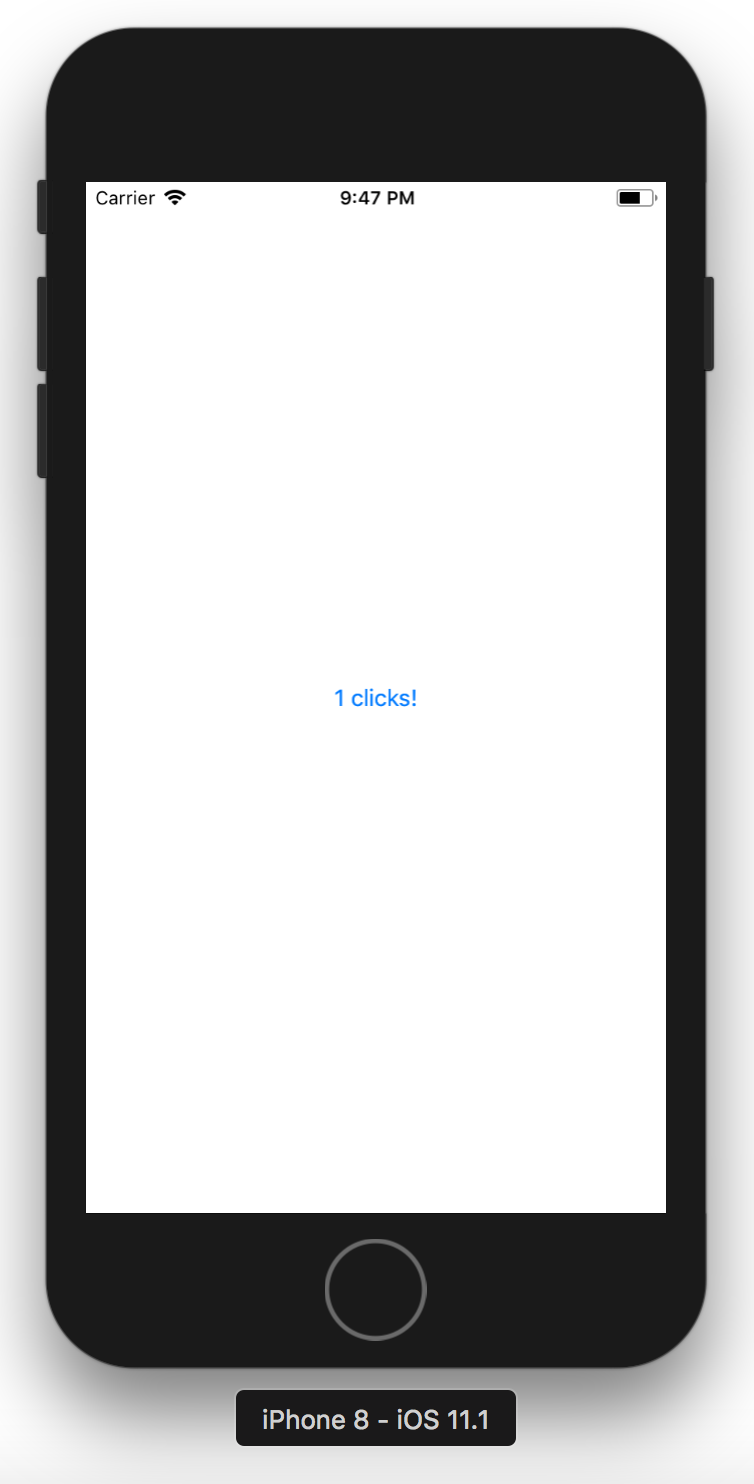
Tap on the button to see the effect.
Right click on the ‘XamarinTutorial.Droid’ project, select ‘Set As Startup Project’ and Build. Then, run the app in simulator by clicking the Arrow button or Run->Start Without Debugging.
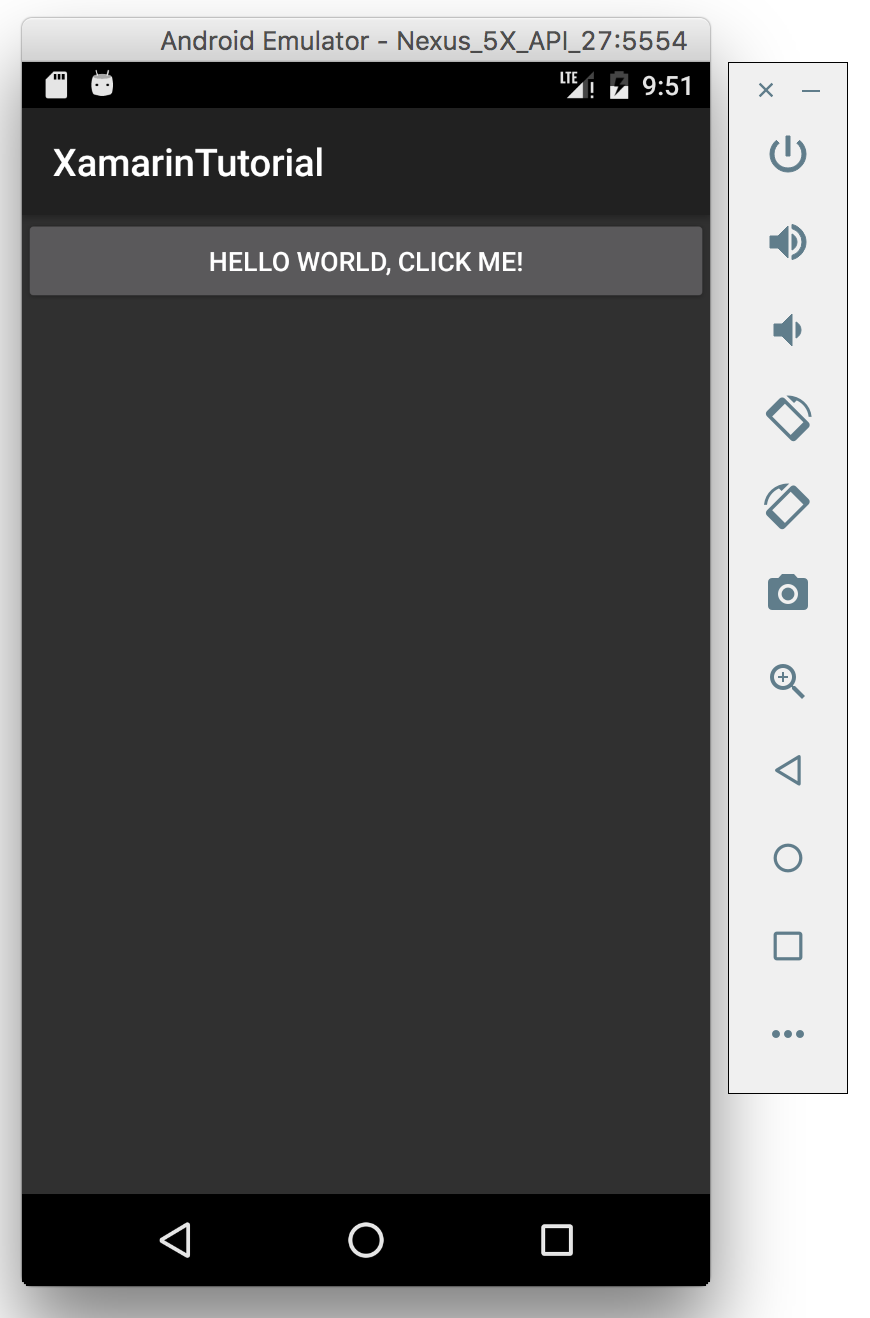
Tap on the button to see the effect.